38 growth plate in wrist diagram
A growth plate injury is an injury to the growth plates, which are located on each end of long bones. Children and teens with growth plate injuries often need immediate treatment to prevent problems with bone growth. Depending on the type of injury, your child may need surgery and a cast or splint. known as the epiphyseal line or growth plate, repre-sents an area of cartilage tissue that is consistently being replaced by new, bony tissue as the bone grows. Cartilage cells at the edge of the growth plate form new bone. This process is respon-sible for the lengthening of bones during child-hood and adolescence. The growth plate calcifi es
Growth plates are areas of soft tissue at the ends of your child's long bones. They are found in many places, including the thigh, forearm, and hand. As the name suggests, growth plates help your ...
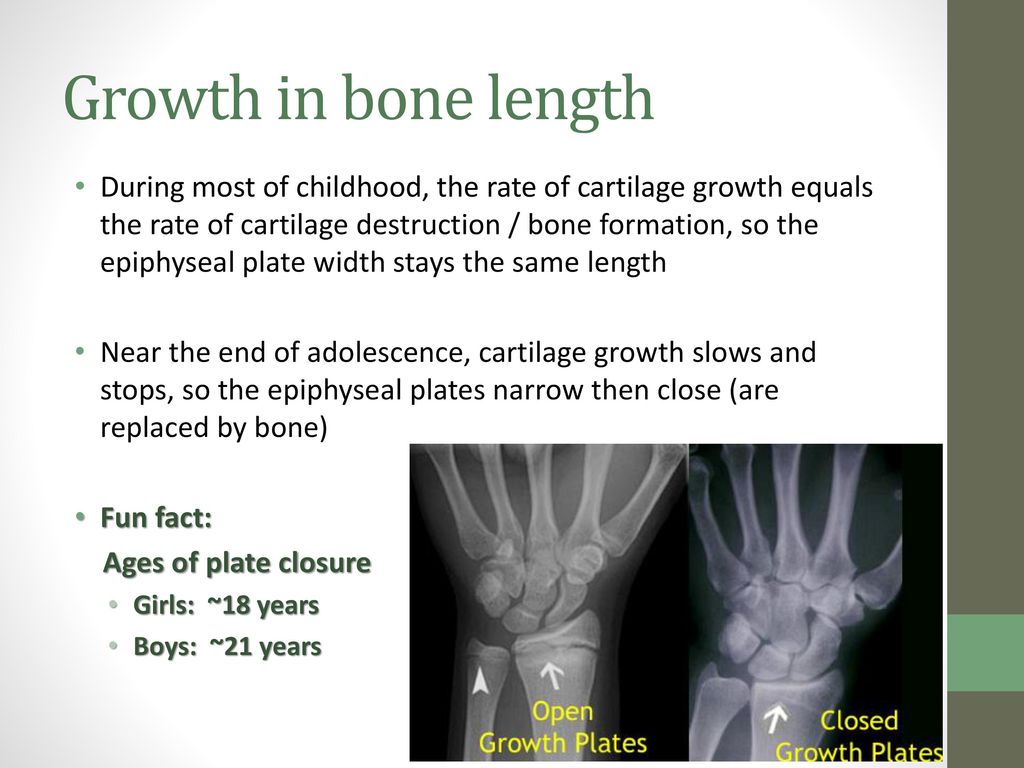
Growth plate in wrist diagram
Injuries to the growth plates can happen with any type of injury to bones in children and are very common. The fingers, wrist and lower leg bones are where these injuries most often occur, but we see them in all long bones. Growth plate injuries can occur with a single event like a fall, accident or sports-contact injury. Growth Plate Fracture What is a growth plate fracture of the distal radius? The radius and the ulna are the two long bones of the forearm, extending from the elbow to the wrist. The physis is the growth plate at the ends of these bones. Growth happens in the physis up through adolescence. A growth plate fracture of the distal radius is The growth plates around the knee are more sensitive to injury. A growth plate fracture at the knee can cause the leg to be shorter, longer or crooked if the growth plate has permanent damage. Growth plate injuries around the wrist and shoulder usually heal without problems.
Growth plate in wrist diagram. Injuries to the pediatric distal forearm and wrist have myriad manifestations. Growth plate injuries can occur in the skeletally immature child. An unfused growth plate is less robust than ligamentous complexes and therefore is more easily injured. The Salter-Harris fracture classification system is used to grade physeal injuries based on their imaging appearance. This grading has prognostic ... Growth Plate Anatomy. - last two or three cells in column of cartilage cells are in fourth zone, the zone of provisional calcification. - juncture between epiphyseal plate & metaphysis is secured by welding of metaphyseal bone to calcified cartilage matrix. - Localization of type X collagen in canine growth plate and adult canine articular ... Growth plate injuries tend to occur in the arms, legs, or fingers, and for the same reasons as sprains and other injuries: from falls, bumps, and other traumas during physical activity. Something as simple as a fall from the monkey bars or an awkward landing on a trampoline could lead to a growth plate injury. Wrist anatomy is the study of the bones, ligaments and other structures in the wrist. The wrist joint is a complex joint which connects the forearm to the hand, allowing a wide range of movement. ... A distal radial epiphysis injury is an injury to the growth plate at the wrist end of the radius bone in the forearm. It mostly…
The growth plates in the hand and wrist are at risk of injury and fracture because the cartilage located in these areas is weaker than surrounding ligaments. While an injury to the growth plate in the wrist or hand usually heals without complication, it is important to seek treatment in a timely manner to help prevent potential long-term growth ... The example is of a wrist, partly because about 50% of growth plate injures are at the wrist and partly because that is the most likely growth plate injury my patients will have. In this x-ray, the wrist bones are at the top and the forearm bones at the bottom; the radius is the bone on the right, it is the one on the thumb side of the hand ... Description. Most growth plate fractures occur in the long bones of the fingers. They are also common in the outer bone of the forearm (radius) and lower bones of the leg (tibia and fibula). Growth plate fractures vary greatly with regard to risk for growth problems. Factors that affect the risk of problems over time include: The patient's age. Pediatric Distal Forearm and Wrist Injury: An Imaging Review1 Injuries to the pediatric distal forearm and wrist have myriad mani-festations. Growth plate injuries can occur in the skeletally imma-ture child. An unfused growth plate is less robust than ligamentous complexes and therefore is more easily injured. The Salter-Harris
The physis appears as a radiolucent line in skeletally-immature patients located between the metaphysis and epiphysis. It contains zones of mesenchymal cells in various maturation stages (see physeal anatomy illustration). As the metaphysis and epiphysis mature and fuse, the physis thins, disappears, and endochondral ossification ceases. Download scientific diagram | Salter-Harris fracture classifications. ... Injuries to the pediatric distal forearm and wrist have myriad manifestations. Growth plate injuries can occur in the ... Commonly, hand-wrist radiographs are analyzed using the comparison method according to the atlas of Greulich and Pyle (1959), which was based on a longitudinal growth study. The atlas consists of plates of typical hand-wrist radiographs at 6 monthly intervals of chronological age. Grade 4A actually looks more fused than Grade 3A. "Grade 5 growth plate. (A) There is less than 5 mm fusion left of the fusion of the growth plate in plain radiograph. (B) Similar correlating appearance on T1-weighted MRI of the same patient (arrows)."<-And 5A looks even less fused. 5B however does look more fused than 4B. "Grade 6 growth plate.
Flashcard Words Spongy bone: contains red bone marrow, makes blood Medullary Cavity: contains yellow bone marrow, stores nutrients Periosteum: tough, living membrane on the outside of the bony layer Articular Cartilage: connective tissue that protects the bone ends Vertebra: backbone Sternum: bre...
Growth plates are one way bones grow. There are usually two growth plates in each long bone. They add length and width to the bone. As kids grow, the growth plates harden into solid bone. A growth plate that has completely hardened into solid bone is a closed growth plate. After a growth plate closes, the bones are no longer growing.
Scott H. Kozin MD, in Principles and Practice of Wrist Surgery, 2010. Growth Plate Arrest. Growth plate closure occurs in approximately 4% to 5% of all Salter-Harris distal radius fractures. 21,22 Therefore, all growth plate fractures mandate a follow-up x-ray 3 to 6 months after healing to ensure continued growth.
The pubertal growth spurt is a vital period in the orthodontic treatment and should be kept in mind when planning orthodontic treatment in growing children. One of the main objectives of taking hand and wrist radiograph is to determine the amount of growth and get used of it in patients with skeletal discrepancy during adolescence.
The growth plate, also known as the epiphyseal plate or physis, is the area of growing tissue near the end of the long bones in children and adolescents. Each long bone has at least two growth plates: one at each end. The growth plate determines the future length and shape of the mature bone. When growth is complete--sometime during adolescence ...
Download scientific diagram | Salter-Harris type III fracture in a 15-year- old male patient. Frontal radiograph of the wrist shows an intra-articular fracture (arrow) that extends through the ...
The growth plates in the hands and wrist are particularly susceptible to injury through falling on hands and wrists. Growth plates are weaker than the surrounding bone simply because they are not yet fully ossified. What Are Growth Plate Injuries? Growth plate injuries are usually fractures that affect the area in question.
Answer (1 of 2): Pardu's diagram is good. Here is a simpler table:
FPnotebook.com is a rapid access, point-of-care medical reference for primary care and emergency clinicians. Started in 1995, this collection now contains 7002 interlinked topic pages divided into a tree of 31 specialty books and 737 chapters.
The example is of a wrist, partly because about 50% of growth plate injures are at the wrist and partly because that is the most likely growth plate injury my patients will have. In this xray, the wrist bones are at the top and the forearm bones at the bottom; the radius is the bone on the right, it is the one on the thumb side of the hand ...
The peak age for injury to the growth plate is in the pre-adolescent growth spurt. The Salter-Harris type II fracture is the most common type. Distal radial physeal fractures are uncommon in children younger than five years. The most common mechanism of injury is a fall on an outstretched hand (Figure 1).
The growth plates around the knee are more sensitive to injury. A growth plate fracture at the knee can cause the leg to be shorter, longer or crooked if the growth plate has permanent damage. Growth plate injuries around the wrist and shoulder usually heal without problems.
Growth Plate Fracture What is a growth plate fracture of the distal radius? The radius and the ulna are the two long bones of the forearm, extending from the elbow to the wrist. The physis is the growth plate at the ends of these bones. Growth happens in the physis up through adolescence. A growth plate fracture of the distal radius is
Injuries to the growth plates can happen with any type of injury to bones in children and are very common. The fingers, wrist and lower leg bones are where these injuries most often occur, but we see them in all long bones. Growth plate injuries can occur with a single event like a fall, accident or sports-contact injury.



0 Response to "38 growth plate in wrist diagram"
Post a Comment