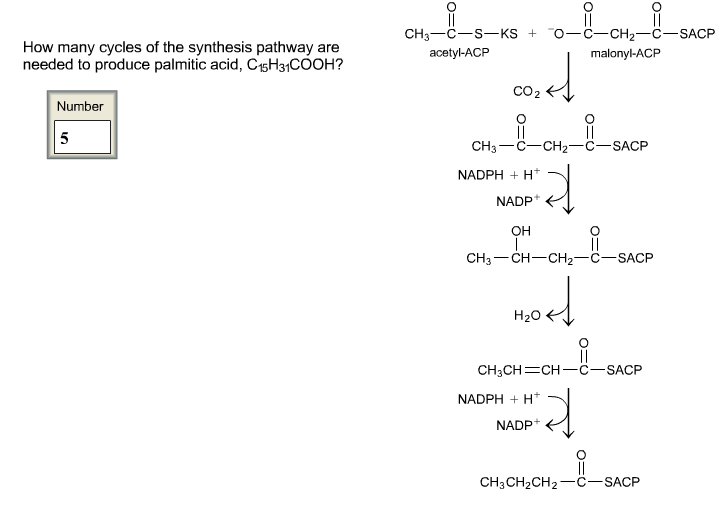
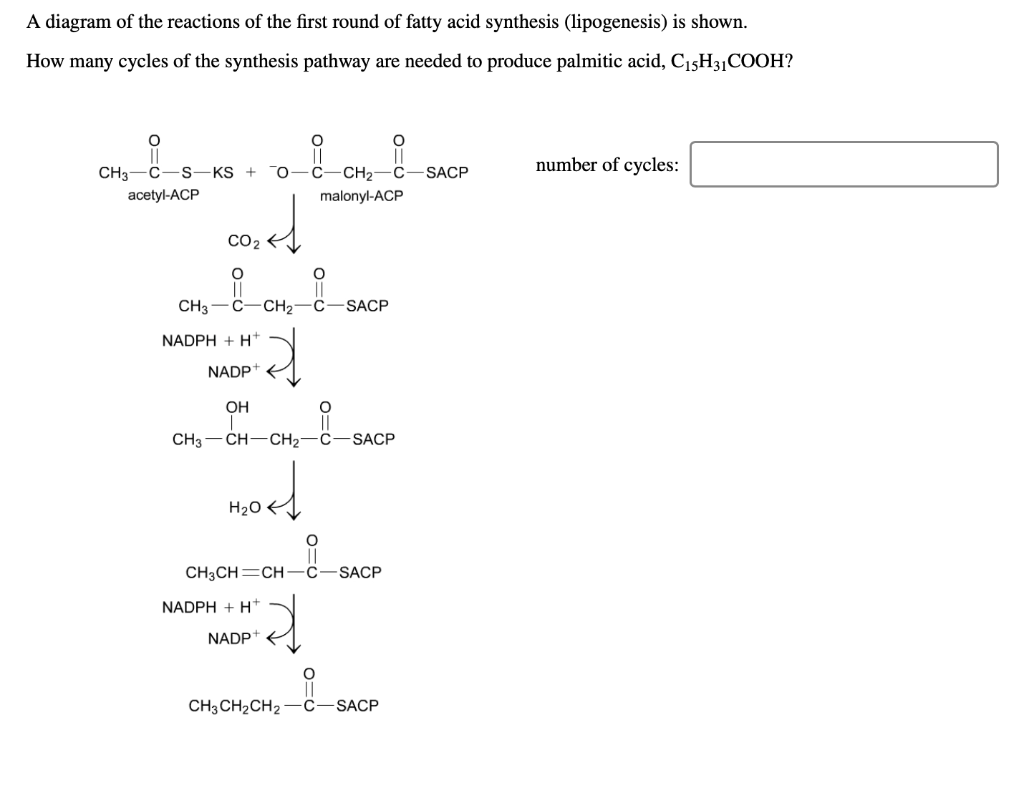
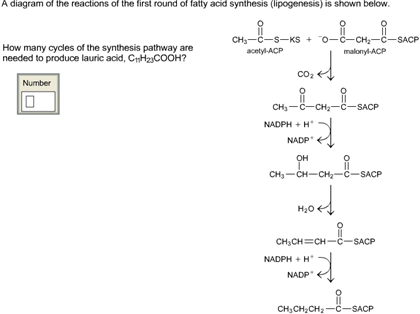
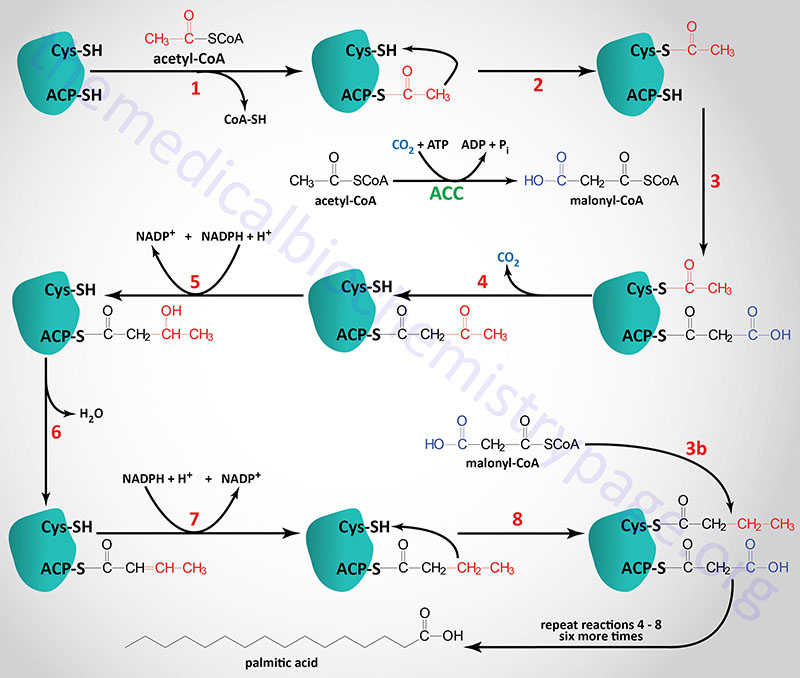
36 a diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis) is shown below.
The Pathway of Beta-Oxidation. In the mitochondria, the fatty acid undergoes a series of oxidation and hydration reactions, which results in the removal of a two-carbon group (in the form of acetyl CoA) from the fatty acid chain as well as the formation of one NADH and one FADH 2, which enter the electron transport chain to form five ATP.; The acetyl CoA formed will enter the citric acid cycle ... Synthesis of Cyclohexene The Dehydration of Cyclohexanol. The general approach towards carrying out an organic reaction: (1) Write out the balanced reaction, using structural formulas. (2) Construct a table of relevant information for reactants and products - e.g., MPs, BPs, MWs, densities, hazardous properties.
16. Reactions of the citric acid cycle Page: 610 Difficulty: 2 Ans: E The reaction of the citric acid cycle that is most similar to the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex-catalyzed conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA is the conversion of: A) citrate to isocitrate. B) fumarate to malate. C) malate to oxaloacetate. D) succinyl-CoA to succinate.

A diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis) is shown below.
Beta Oxidation Steps. Beta oxidation takes place in four steps: dehydrogenation, hydration, oxidation and thyolisis. Each step is catalyzed by a distinct enzyme. Briefly, each cycle of this process begins with an acyl-CoA chain and ends with one acetyl-CoA, one FADH2, one NADH and water, and the acyl-CoA chain becomes two carbons shorter. ) An acid ) A hydrox) A hydrog t happens ) The HCl m) The wate) The conc) The pH o) None of t h property mperature) High spec) High hea) High hea) A and B ) A, B, and atoms wou rus above pound tha ide ion en ion when hydr olecules s r had less f entration o f the water he above of water m for living o ific heat t of vaporiz t of fusion C ld ... Fatty acid synthesis starts with acetyl‐CoA, and the chain grows from the "tail end" so that carbon 1 and the alpha‐carbon of the complete fatty acid are added last. The first reaction is the transfer of the acetyl group to a pantothenate group of acyl carrier protein (ACP), a region of the large mammalian FAS protein.
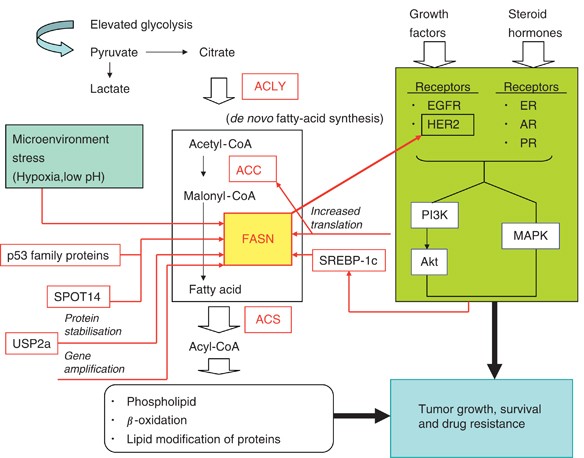
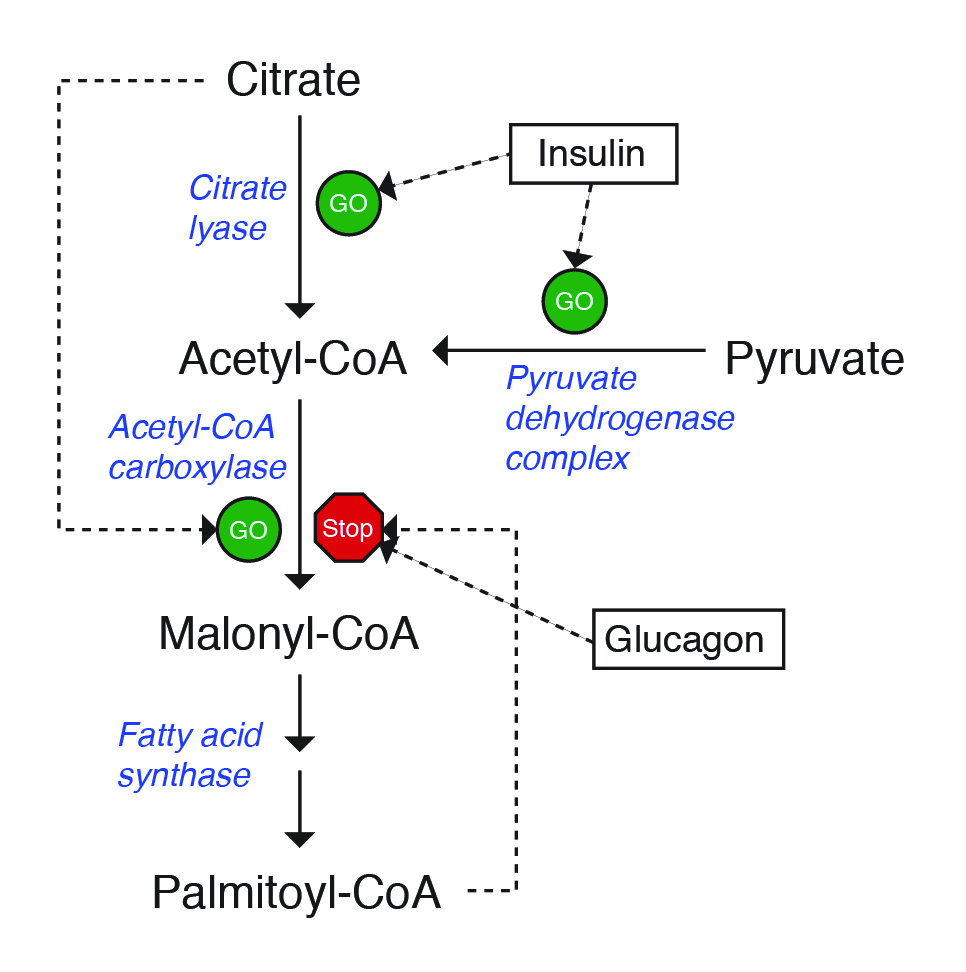
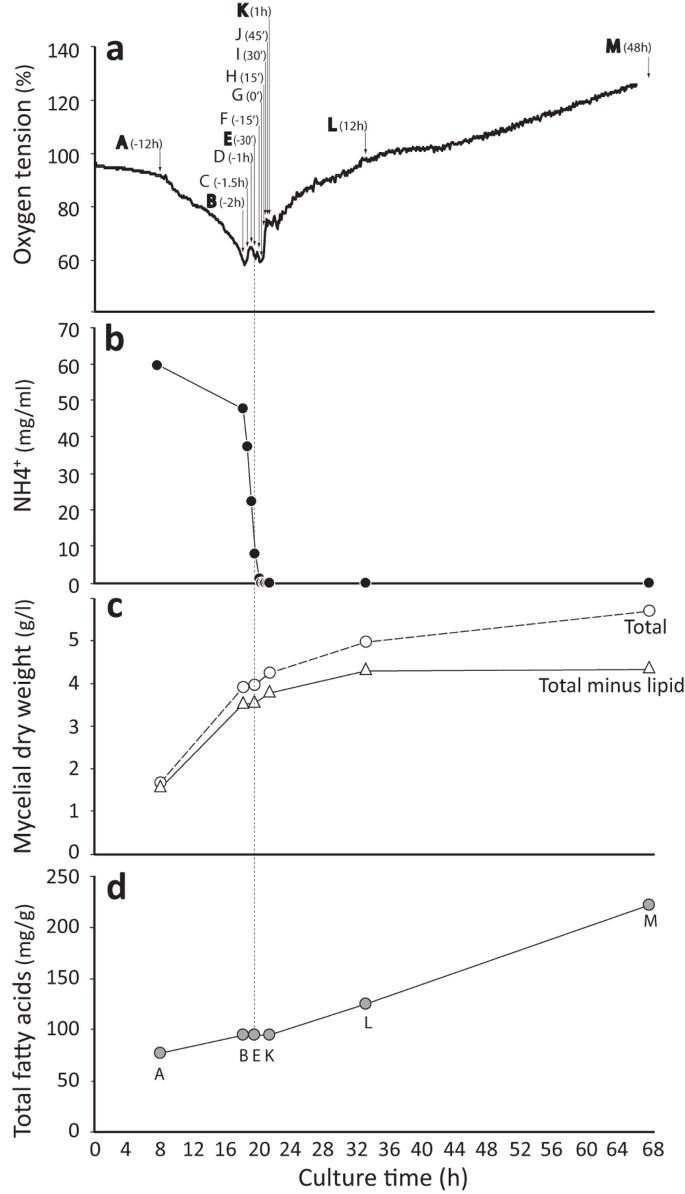
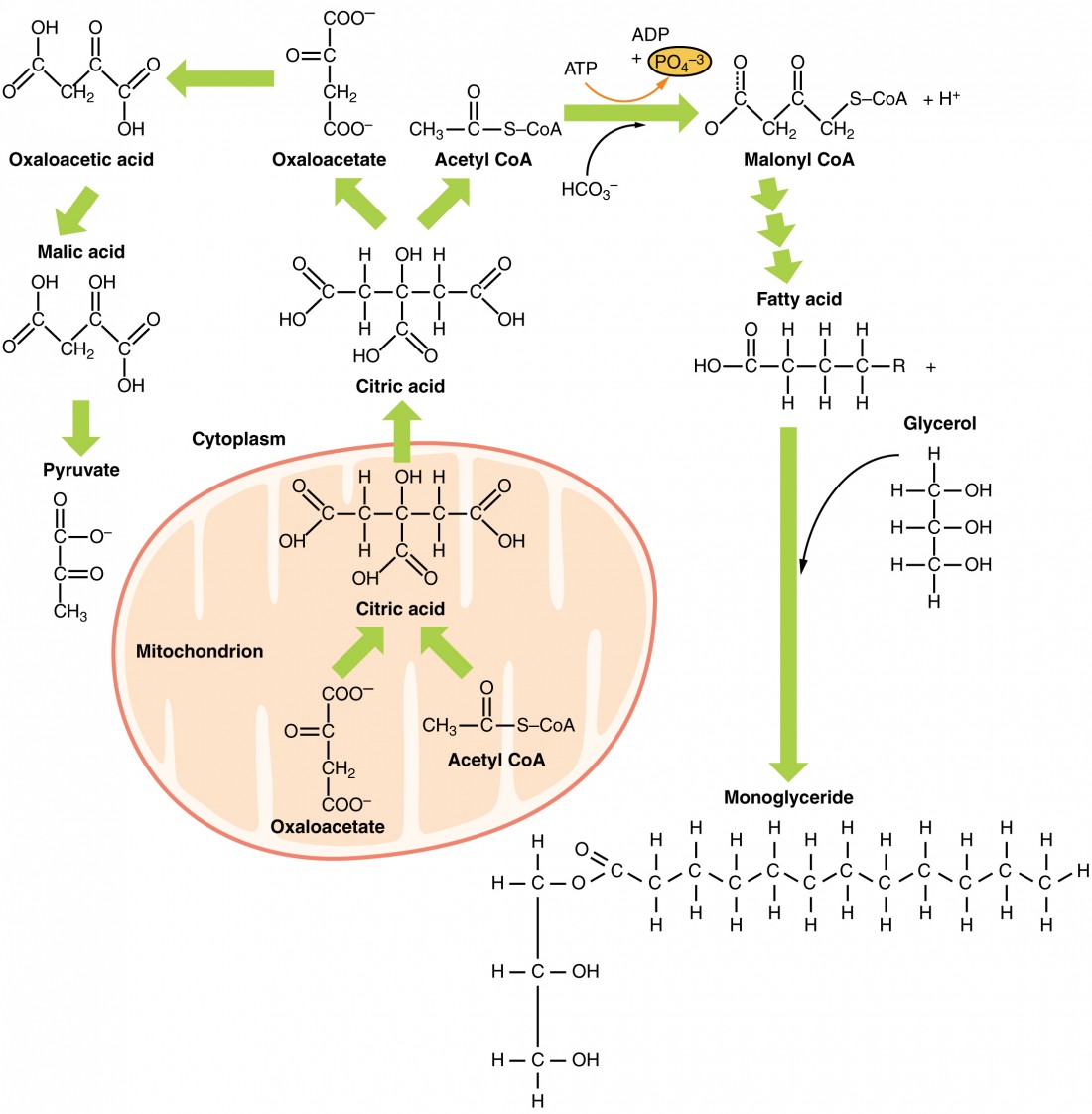
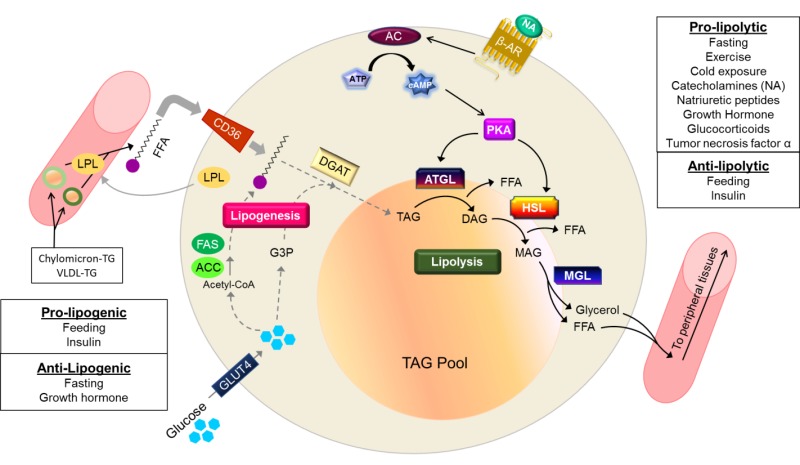
A diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis) is shown below.. Schematic diagram of fatty acid transport and beta-oxidation in the mitochondria. Click on image to enlarge. ATP synthesis . Acetyl-CoA generated by the beta-oxidation pathway enters the mitochondrial TCA cycle, where is further oxidized to generate NADH and FADH 2.The NADH and FADH 2 produced by both beta oxidation and the TCA cycle are used by the mitochondrial electron transport chain to ... Palmitic acid is the first fatty acid produced during lipogenesis (fatty acid synthesis) and from which longer fatty acids can be produced. Palmitate negatively feeds back on acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) which is responsible for converting acetyl-ACP to malonyl-ACP on the growing acyl chain, thus preventing further palmitate generation Fatty acid Synthesis Mechanism A. Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase. The first committed step of fatty acid biosynthesis is catalyzed by Acetyl-CoA carboxylase. The enzyme contains biotin and adds a CO2 (resulting in a carboxyl group) to the methyl end of acetyl CoA. Note that this reaction is an energy-requiring process (1 ATP per Malonyl-CoA formed). C3 cycle refers to the dark reaction of photosynthesis. It is indirectly dependent on light and the essential energy carriers are products of light-dependent reactions. In the first stage of the Calvin cycle, the light-independent reactions are initiated and carbon dioxide is fixed. In the second stage of the C3 cycle, ATP and NADPH reduce 3PGA ...
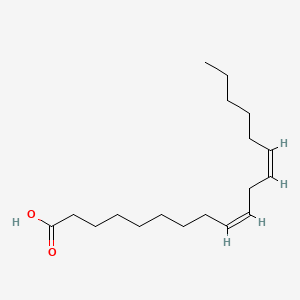
This is often related to a diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis) is shown below.. Linked to a diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis) is shown below., Acid reflux disorder is said while using the dilemma of acidic soreness, coronary heart burn up and heartache. Show transcribed image text A diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis) is shown below. How many cycles of the synthesis pathway are needed to produce palmitic acid, C_15H_31COOH? A diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis) is shown A diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis) is shown below. How many cycles of the synthesis pathway are needed to produce myristic acid, C13H27COOH? Question : A diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis) is shown below. In the Calvin cycle, carbon atoms from are fixed (incorporated into organic molecules) and used to build three-carbon sugars. This process is fueled by, and dependent on, ATP and NADPH from the light reactions. Unlike the light reactions, which take place in the thylakoid membrane, the reactions of the Calvin cycle take place in the stroma (the ...
Step 1. In the first step of the citric acid cycle, acetyl joins with a four-carbon molecule, oxaloacetate, releasing the group and forming a six-carbon molecule called citrate. Step 2. In the second step, citrate is converted into its isomer, isocitrate. The human digestive system, as shown in Figure 2, is a coiled, muscular tube (6-9 meters long when fully extended) stretching from the mouth to the anus. Several specialized compartments occur along this length: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. In the second step of the fatty acid oxidation cycle (Fig. 16-8a), water is added to the double bond of the trans-Δ 2-enoyl-CoA to form the L stereoisomer of β-hydroxyacyl-CoA (also designated β-hydroxyacyl-CoA).This reaction, catalyzed by enoyl-CoA hydratase, is formally analogous to the fumarase reaction in the citric acid cycle, in which H 2 O adds across an α-β double bond (p. 458). Lipogenesis, or fatty acid synthesis, occurs in several cycles. A diagram of the reactions of the first cycle of fatty acid synthesis is shown below. Which of the following statements are true? Select all the true statements. Acetyl-SCoA provides the carbon used for fatty acid synthesis.
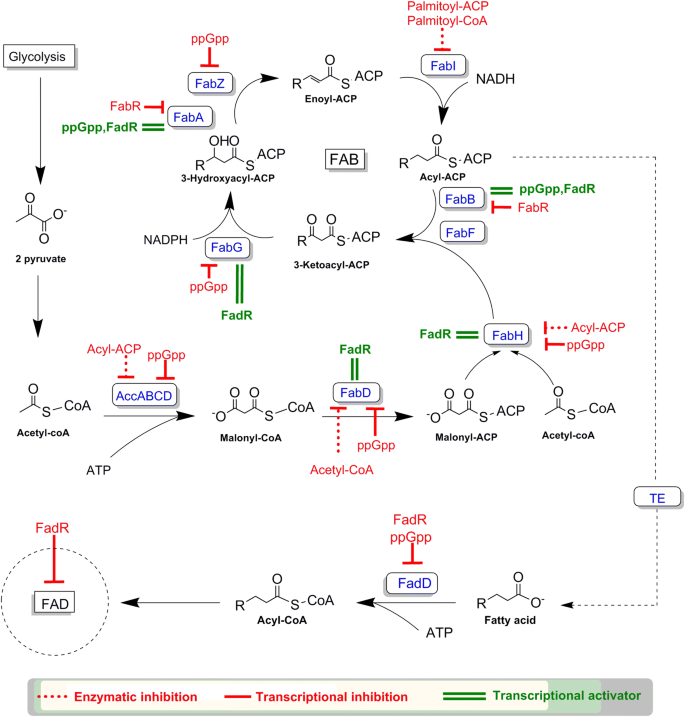
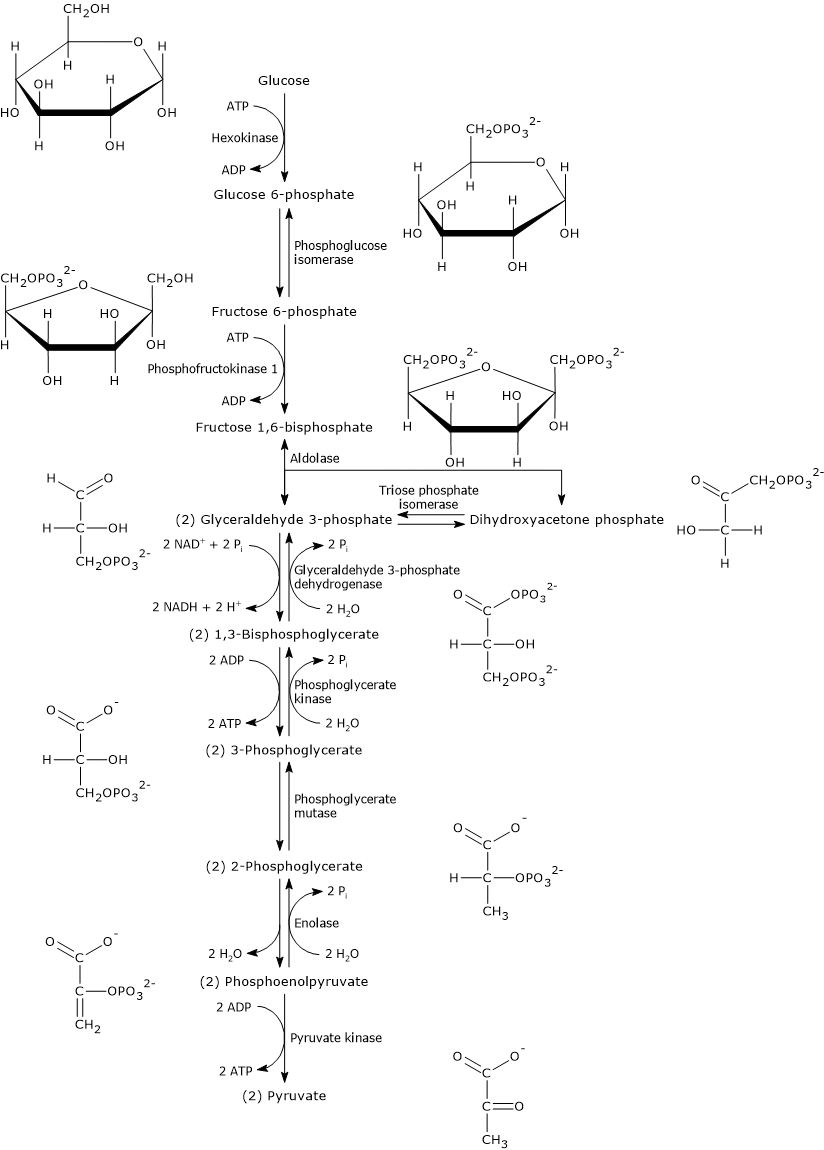
Summary of Glycolysis, TCA Cycle & Oxidative Phosphorylation. Carbohydrates in the form of glucose is the main source of energy for the body. Energy is needed for two types of metabolic processes; anabolism and catabolism. Anabolism is the process of making larger molecules using smaller molecules e.g. using fatty acids to make fats, or amino ...
4. Step 6 is the first step in which NAD+ is reduced to form NADH.Two NADH molecules are formed for every one glucose molecule. 5. Two molecules of ATP are generated for every one molecule of glucose in step 7 (powered by hydrolysis of the high energy phosphate bond on 1,3-
A diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis) is shown below. How many cycles of the synthesis pathway are needed to produce myristic acid, C13H27COOH? (14 carbons)
40 a diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis) is shown below. Written By Tim C. Meyers. ... 19 The first round of FA bio synthesis To initiate FA bio synthesis, malonyl and All the reactions in the syn the tic process are catalyzed by a multi-enzyme complex, ...
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis 4 Fatty Acid Synthase (FAS) • FAS is a polypeptide chain with multiple domains, each with distinct enzyme activities required for fatty acid biosynthesis. •ACP: Recall that CoA is used as an activator for β-oxidation. For fatty acid biosynthesis, the activator is a protein called the acyl carrier protein (ACP).
Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. A diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis)is shown below. How many cycles of the synthesis pathway are needed to produce lauric acid, C11H23COOH? Question: A diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis)is shown below.
Reaction 1: Citrate Synthase. The first reaction of the citric acid cycle is catalyzed by the enzyme citrate synthase. In this step, oxaloacetate is joined with acetyl-CoA to form citric acid. Once the two molecules are joined, a water molecule attacks the acetyl leading to the release of coenzyme A from the complex. Figure %: Reaction 1.
The first reaction is a condensation reaction, which means that the starting molecules will have fewer carbon atoms than any of the other molecules in the pathway. Hint 2. The fatty acid synthesis pathway Use the image below to help you in arranging the individual steps of the fatty acid synthesis pathway. Hint 3.
Reaction 2: Formation of Isocitrate. The citrate is rearranged to form an isomeric form, isocitrate by an enzyme acontinase.. In this reaction, a water molecule is removed from the citric acid and then put back on in another location. The overall effect of this conversion is that the -OH group is moved from the 3′ to the 4′ position on the molecule.
A diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis)is shown below. A diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis)is shown below. How many cycles of the synthesis pathway are needed to produce lauric acid, C11H23COOH?
A diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis)is shown below. How many cycles of the synthesis pathway are needed to produce lauric acid, C11H23COOH? Solution.pdf.
Fatty acid synthesis starts with acetyl‐CoA, and the chain grows from the "tail end" so that carbon 1 and the alpha‐carbon of the complete fatty acid are added last. The first reaction is the transfer of the acetyl group to a pantothenate group of acyl carrier protein (ACP), a region of the large mammalian FAS protein.
) An acid ) A hydrox) A hydrog t happens ) The HCl m) The wate) The conc) The pH o) None of t h property mperature) High spec) High hea) High hea) A and B ) A, B, and atoms wou rus above pound tha ide ion en ion when hydr olecules s r had less f entration o f the water he above of water m for living o ific heat t of vaporiz t of fusion C ld ...
Beta Oxidation Steps. Beta oxidation takes place in four steps: dehydrogenation, hydration, oxidation and thyolisis. Each step is catalyzed by a distinct enzyme. Briefly, each cycle of this process begins with an acyl-CoA chain and ends with one acetyl-CoA, one FADH2, one NADH and water, and the acyl-CoA chain becomes two carbons shorter.




















0 Response to "36 a diagram of the reactions of the first round of fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis) is shown below."
Post a Comment