39 energy reaction coordinate diagram
The reaction coordinate diagram for the ozone photolysis reaction is a little different from those above because this is an endothermic reaction. Together, the products O 2 and atomic O, have a higher energy than the reactant O 3 and energy must be added to the system for this reaction. The activation energy can be determined using the equation: ln (k 2 /k 1) = E a /R x (1/T 1 - 1/T 2) where. E a = the activation energy of the reaction in J/mol. R = the ideal gas constant = 8.3145 J/K·mol. T 1 and T 2 = absolute temperatures (in Kelvin) k 1 and k 2 = the reaction rate constants at T 1 and T 2.
The reaction coordinate diagram shows that the energy of activation for the reverse reaction is lowered by the catalyst as well. Enzymatic catalysis The ability of enzymes to catalyze reactions depends on their ability to interact directly and specifically with reactants The reactant of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is termed the substrate .

Energy reaction coordinate diagram
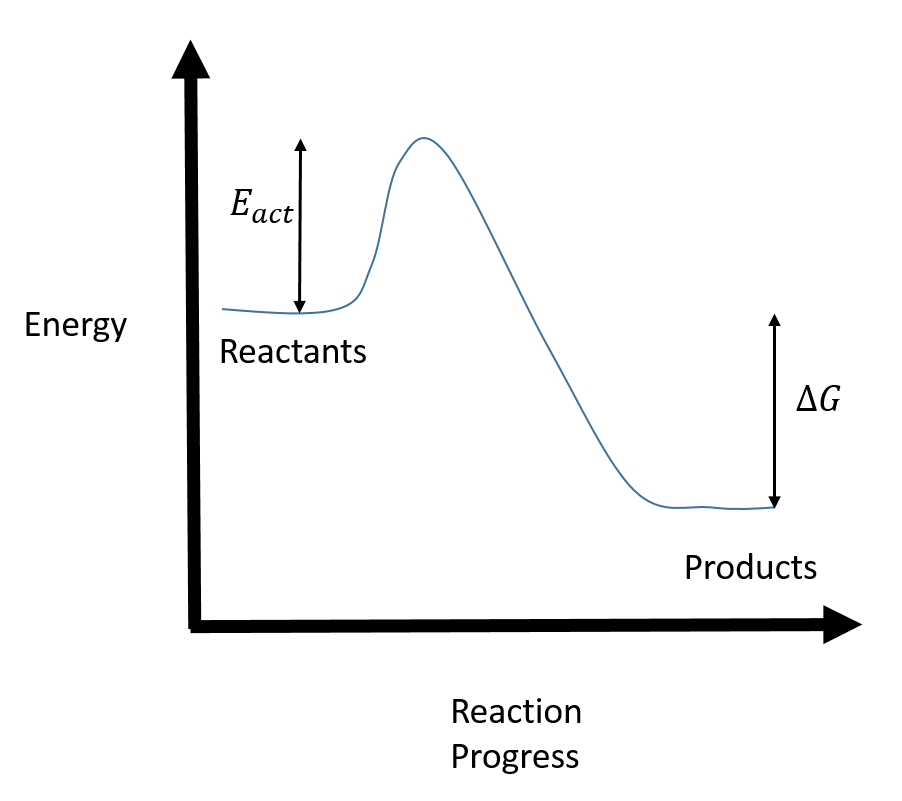
Reactivity: how fast is the reaction! (how large is the E a in the energy diagram)! Selectivity: if more than one site is available for reaction the ratio between each product obtained determines the selectivity! (the difference in E a for each competing path in the energy diagram)! This leads to an almost universal statement in organic chemistry:! Typically, we envision reactions proceeding left to right along the reaction coordinate, so often, the activation energy is only noted for the forward reaction. The activation energy on the diagram below shows the barrier to be 102.6 kJ mol-1. Barriers are measured in energy per mole (typically kJ mol-1). Reaction coordinate diagrams. The intrinsic reaction coordinate (IRC), derived from the potential energy surface, is a parametric curve that connects two energy minima in the direction that traverses the minimum energy barrier (or shallowest ascent) passing through one or more saddle point(s). However, in reality if reacting species attains enough energy it may deviate from the IRC to some extent.
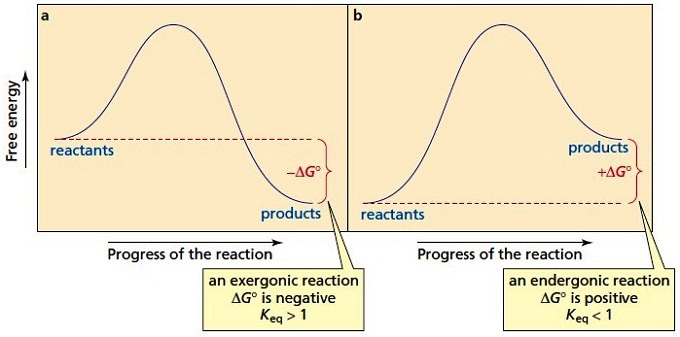
Energy reaction coordinate diagram. 1i. Draw an energy vs reaction coordinate diagram to illustrate a reaction in which the energy of the products is greater than the energy of the reactants. Label all quantities as per Fig. 1. See diagram (3) in sample exercise 14.10 on pg 595 of Brown and LeMay, 11th ed. Indian Institute of Science. I am adding here a MATLAB code for drawing free energy reaction profile. This is just for plotting del Grxn vs reaction coordinate. (A small change is needed to ... The fully filled in reaction coordinate diagram is displayed below. The arrow marked in the question represents the activation energy, which is the energy barrier that must be overcome in order for the reactants to form products. This reaction is also exothermic because the energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants. An energy diagram for an endergonic or nonspontaneous reaction is shown to the right. The energy level of the products is higher than the energy level of the. Reaction coordinate diagrams of exergonic and endergonic reactions. Exergonic and endergonic reactions are characterized by changes in. Exergonic and endergonic qualifications only apply ...
Reactants Products + Energy. Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction as above but add the activation energy, E a, for the catalyzed reaction on the appropriate curve in this diagram and label it. This is a bit more subtle since .Types of catalysts (article) | Kinetics | Khan AcademySection The Rate of a Reaction ... A reaction coordinate diagram is a graph that plots energy versus reaction progress. The amount of energy that needs to be added is called the activation energy, which is the point where the line ... A general Reaction Coordinate Diagram relating the energy of a system to its geometry along one possible reaction pathway is given in the figure below. In the figure below, the Activation Energy, Ea is that critical minimum energy in a chemical reaction required by reactants to be converted into products. the quantities, Ea; Energy Surfaces vs. Reaction Coordinate Diagrams Something that cannot be represented in the three dimensional energy surface below is the differentially populated vibrational modes of the molecules Reaction coordinate diagrams are used to simplify the situation, they represent a composite
In this video, Dr. Norris goes over practice problems in interpreting reaction energy coordinate diagrams. Reaction Coordinate Diagrams It is helpful to visualize energy changes throughout a process on a reaction coordinate diagram like this one for the rearrangement of methyl isonitrile. Reaction Coordinate Diagrams The diagram shows the energy of the reactants and products (and, therefore, E). The high point on the diagram is the transition state. Energy/Reaction Coordinate! Diagrams! Thermodynamics, Kinetics ! Dr. Ron Rusay" A Reaction Coordinate (Energy) Diagram Thermodynamic Quantities Gibbs standard free energy change (ΔGo) Enthalphy (ΔHo): the heat given off or absorbed during a reaction Entropy (ΔSo): a measure of freedom of motion ΔGo = ΔHo - TΔSo ΔG,ΔH,ΔS, ΔE are state ... Label the vertical axis "Potential Energy" and the horizontal axis "Reaction Coordinate". 2. Draw and label two short horizontal lines to mark the energies of the reactants and products. 3. Draw the energy level diagram. There must be a hump in the curve to represent the energy level of the activated complex. 4. Draw and label the activation ...
positions of atoms during a reaction. Reaction coordinate Energy Energy Diagrams 6 • Transition state ‡: - An unstable species of maximum energy formed during the course of a reaction. - A maximum on an energy diagram. • Activation Energy, ∆G‡: The difference in Gibbs free energy between reactants and a transition state.
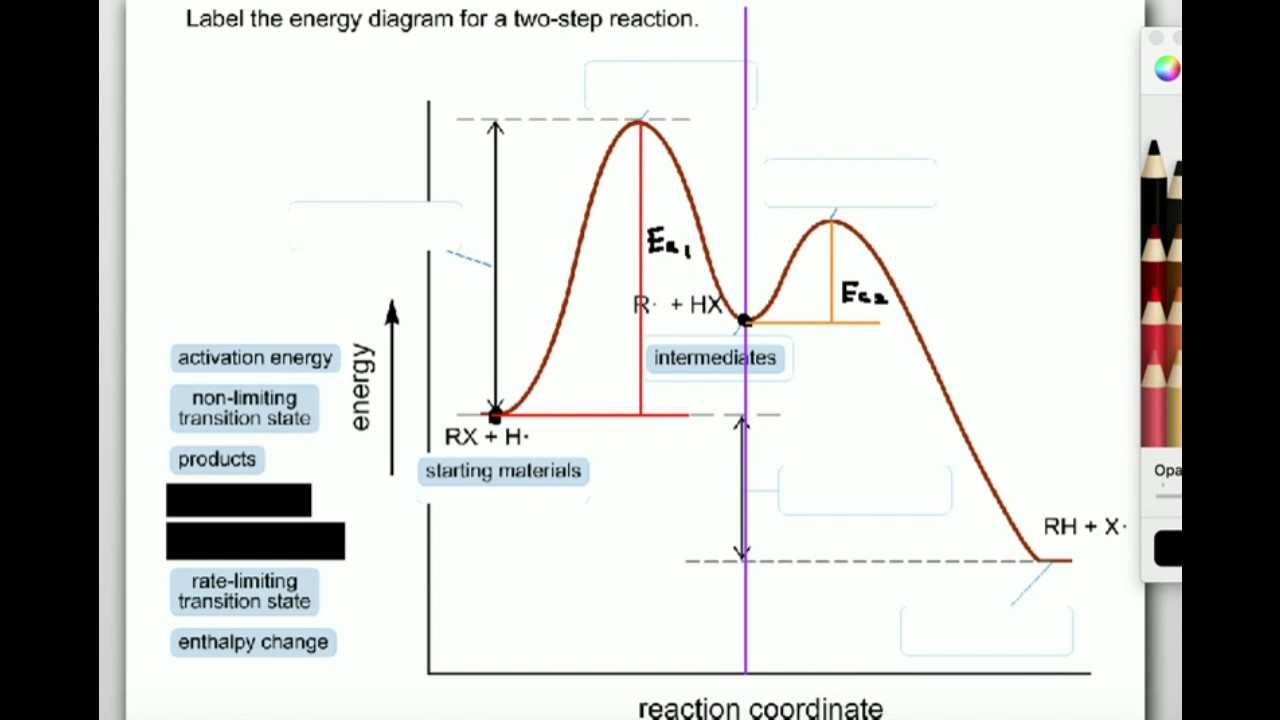
Chemistry questions and answers. Label the following reaction coordinate diagram. Energy Reactant (s) Transition State Product (s) Activation Energy (forward) Transition State Activation Energy (forward) Energy Enthalpy of Enthalpy of Reaction Product (s) Reaction AHrxn Reactant (s) Reaction Coordinate Reaction Coordinate Reset Zoom.
Consider the reaction coordinate diagram shown below. The activation energy for the forward reaction is best represented by which number shown in the diagram? 3. reaction pathway A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 potential energy
A reaction energy diagram (Figure 1) is presented on the chalk board (complete with axes labeled: potential energy vs. reaction coordinate (or reaction progress)). The activation energy, Ea, (the change in energy from reactants to the top of the "hill") is labeled. The students are taught that the species at the top of
This chemistry video tutorial focuses on potential energy diagrams for endothermic and exothermic reactions. It also shows the effect of a catalyst on the f...
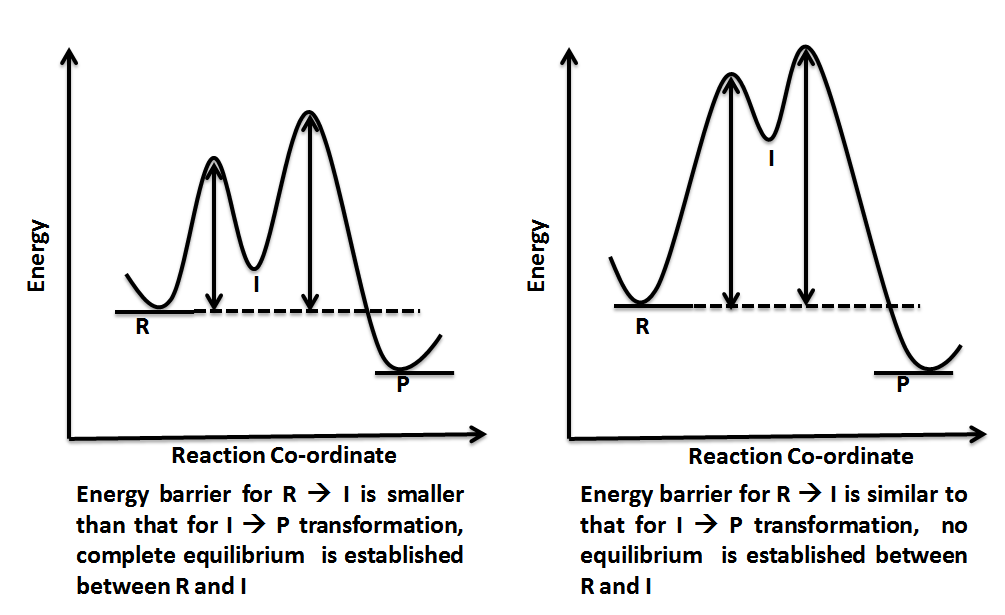
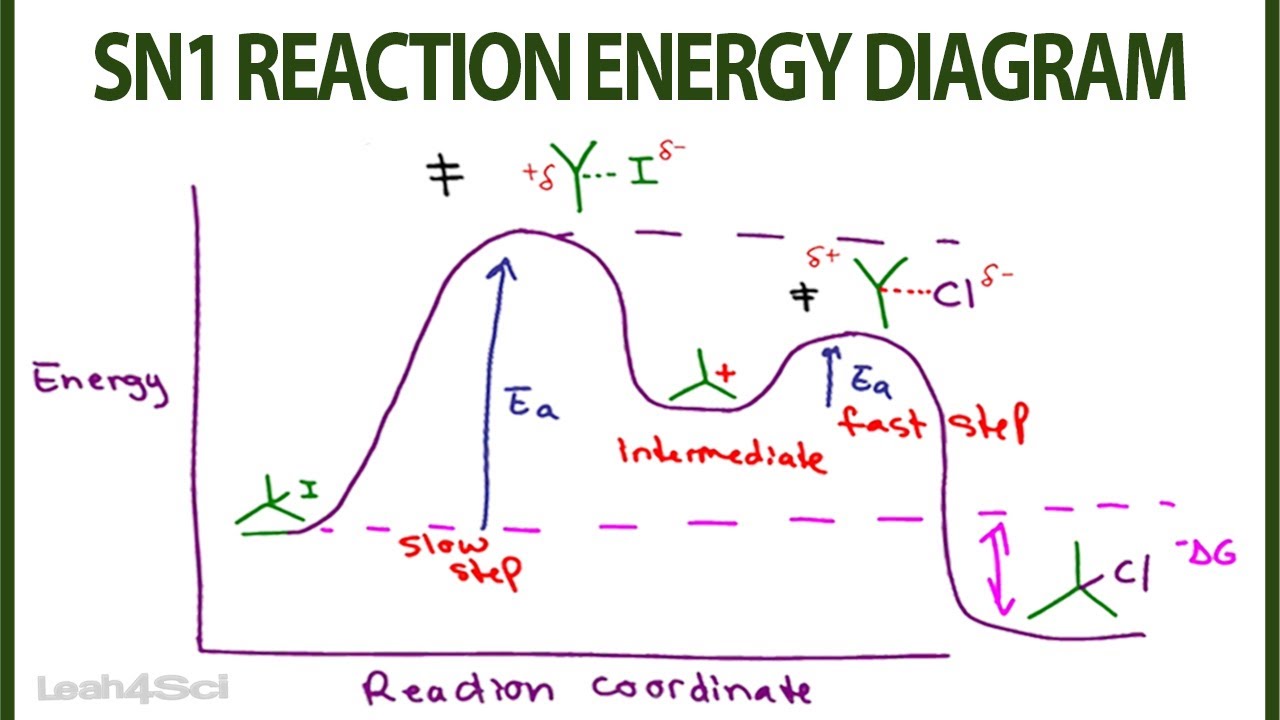
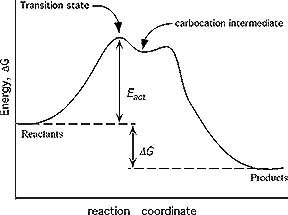
SN1 reaction The S1 reaction is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry. or process an energy profile (or reaction coordinate diagram) is a theoretical. SN1 reaction is a two step reaction as mentioned below: 1. Leaving group leaves first being solvolysed by solvent creating a carbocation intermediate. This is.
The change in the activation energy of the reaction because of the presence of an enzyme is ill minus the energy of ustrated by the energy of Transitionstateは) uncatalyzed AG of reaction reaction atalyzed ES of the reaction Reaction coordinate-→ Question: 11. Refer to the reaction coordinate diagram below.
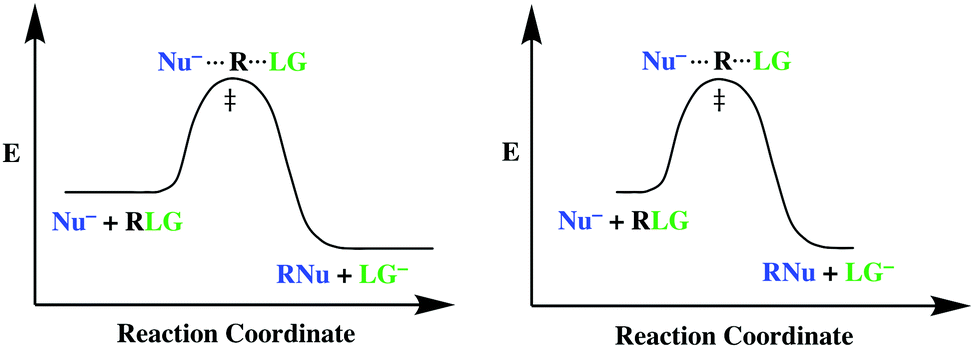
Diagram of a catalytic reaction, showing the energy niveau depending on the reaction coordinate. For a catalysed reaction, the activation energy is lower. In chemistry , a reaction coordinate [1] is an abstract one-dimensional coordinate which represents progress along a reaction pathway.
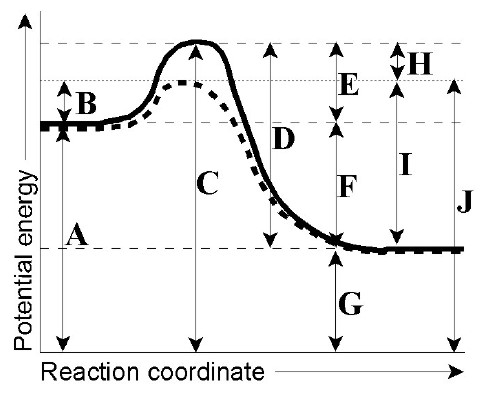
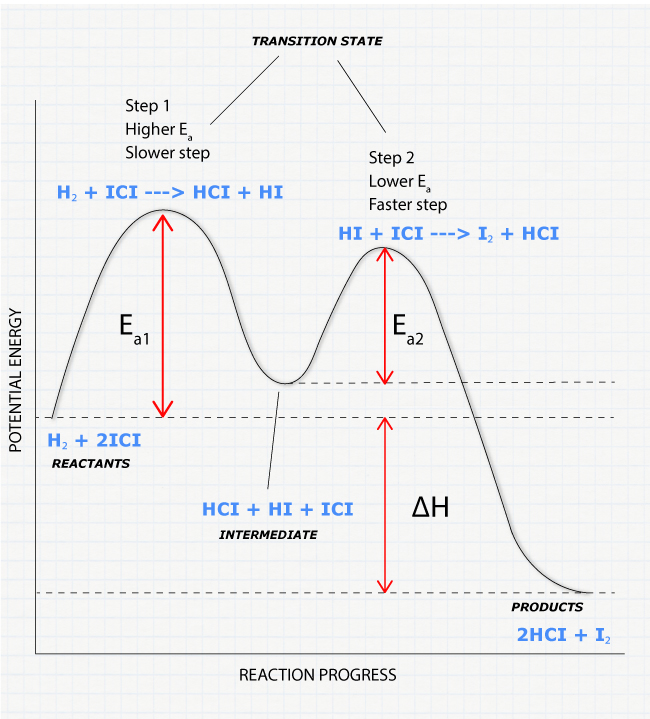
The three general rules for reaction coordinate diagrams are as follows: The number of "peaks" should be equal to the number of steps in the reaction. The height of each peak relative to the valley to its left is representative of the activation energy of that step. Larger vertical distance between peaks = greater activation energy = slower ...
For this quiz, you must be able to: Understand endothermic and exothermic reactions. Identify which points on sample reaction coordinate diagrams represent the activation energy and the change in ...
Potential Energy Diagram for E1 TS energy depends on carbocation rate-determining titi tt stability and leaving group quality. (Same as SN1.) H CH3 CH3 E transition state TS energy does not depend on the strength of the base. X H H a rate determining E - step reaction coordinate E1 and SN1 Frequently Occur Together (because they pass through a ...
Reaction coordinate diagrams. The intrinsic reaction coordinate (IRC), derived from the potential energy surface, is a parametric curve that connects two energy minima in the direction that traverses the minimum energy barrier (or shallowest ascent) passing through one or more saddle point(s). However, in reality if reacting species attains enough energy it may deviate from the IRC to some extent.
Typically, we envision reactions proceeding left to right along the reaction coordinate, so often, the activation energy is only noted for the forward reaction. The activation energy on the diagram below shows the barrier to be 102.6 kJ mol-1. Barriers are measured in energy per mole (typically kJ mol-1).
Reactivity: how fast is the reaction! (how large is the E a in the energy diagram)! Selectivity: if more than one site is available for reaction the ratio between each product obtained determines the selectivity! (the difference in E a for each competing path in the energy diagram)! This leads to an almost universal statement in organic chemistry:!

Organic Chemistry Students Interpretations Of The Surface Features Of Reaction Coordinate Diagrams Semantic Scholar
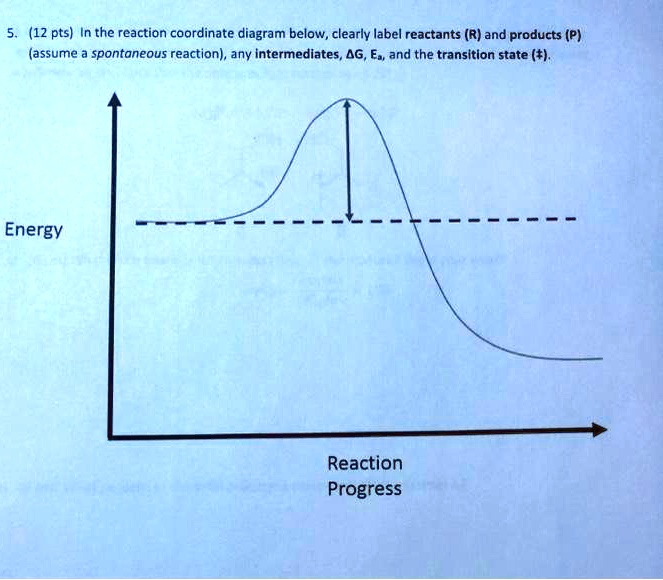
Solved 12 Pts In The Reaction Coordinate Diagram Below Clearly Label Reactants R And Products P Assume Spontaneous Reaction Any Intermediates 4g E And The Transition State T Energy Reaction Progress

Draw A Reaction Profile Diagram Of Energy Vs Reaction Coordinate For A Hypothetical Reaction Ab C Arrow A Bc In Which The Foward Reaction Has An Activation Energy Of 100

















0 Response to "39 energy reaction coordinate diagram"
Post a Comment