38 orbital diagram for k
**This thread is no longer being updated, and has been replaced by:** # [Starship Development Thread #26](https://www.reddit.com/r/spacex/comments/q4d8u5/starship_development_thread_26/) [](/# Auto Sync Start) #### Quick Links[](https://www.flickr.com/photos/spacex/51369631902/) [^(NERDLE CAM)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_HZCh2eGWEI) ^| [^(LAB CAM)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HGb28t5TWtc&t=0s) ^| [^(SAPPHIRE CAM)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7OKb9Rc-etw&t=0s) ^| [^(SEN... I’m working through a problem set for one of my classes and so far it’s had me make the SALCs and molecular orbital diagram for NH3. Now it’s asking me to go from constructing the MO diagram to identifying the ground electronic state of the molecule. I’m guessing what I need is some kind of wave function to describe the population of each orbital in the ground state. But I’m not sure how to get there from where I am. Any tips are appreciated. I also have to work out which transitions from the ...
I am dealing with several questions that are basically all the same but the basic form of the questions are asking to build a molecular orbital diagram for an unspecified Metal-Ligand complex. ie- Using a group theory approach, develop a molecular orbital diagram for a trigonal pyramidal complex [ML4]. Consider only sigma-orbitals. Start by finding the point group (C3v), then irreducible representations [2(A1)+E], and finally draw a qualitative molecular orbital diagram. Include pictures of th...

Orbital diagram for k
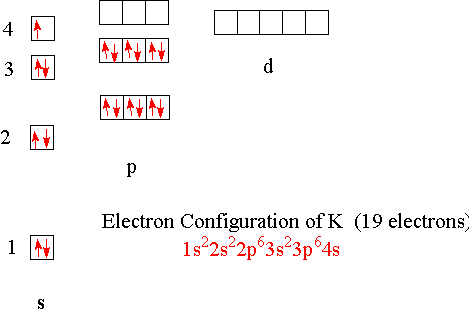
17 Dec 2014 — The full electron configuration of potassium is 1s22s22p63s23p64s1 . The noble gas notation is [Ar]4s1 . The following orbital diagram shows ...1 answer · Potassium's atomic number is 19. This means that every atom of potassium has 19 protons in its nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal ... Feb 08, 2018 · Krypton Orbital Diagram Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of krypton (atomic number: 36), the most common . Box spin diagram of outer electron orbitals for the electron configuration of the atom . 36 Krypton, Kr, [Ar]3ds24p6 = [Kr] (), [Ar]3d 4s 4p v. Hi! I'm doing some inorganic chem homework and I drew the molecular orbital diagrams for a few molecules and now I have to assign and draw the HOMO and LUMO. Does the HOMO have to be the highest totally occupied orbital or can it just be partially filled? Does the LUMO have to be totally unoccupied or can it just be partially unoccupied? Thanks in advance!
Orbital diagram for k. Click here to get an answer to your question ✍️ What is the electron configuration, orbital diagram, and noble gas notation of potassium?1 answer · Top answer: Potassium's atomic number is 19 . This means that every atom of potassium has 19 protons in its nucleus.In a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal ... Cross posted from chem help so forgive me if for some reason you’re seeing this twice now. I’m working through a problem set for one of my classes and so far it’s had me make the SALCs and molecular orbital diagram for NH3. Now it’s asking me to go from constructing the MO diagram to identifying the ground electronic state of the molecule. I’m guessing what I need is some kind of wave function to describe the population of each orbital in the ground state. But I’m not sure how to get there fro... Potassium (K) has an atomic mass of 19. Find out about its chemical and physical properties, states, energy, electrons, oxidation and more. ... Orbital Diagram. 1s ... Draw a molecular orbital diagram for He2. Use this diagram and bond order calculations to explain if He2 is more or less stable than the ions He2+ and He2−. I have done He2 and He2+ and the bond order calculations for both. I just wanted to know why you cant do the same for He2-
I need to construct the molecular orbital diagram for the hypothetical species Li4, which has the following geometrical arrangement: https://preview.redd.it/npsjre5pch571.png?width=197&format=png&auto=webp&s=c2a7948c2efa04a975bee1db722838fae7482456 The first step is to identify the point symmetry group. In this particular case, we consider that there is only one axis of rotation of order four (actually, other symmetry elements can be observed, but this is a previous consi... **This thread is no longer being updated, and has been replaced by:** # [Starship Development Thread #27](https://www.reddit.com/r/spacex/comments/qpup8z/starship_development_thread_27/) [](/# Auto Sync Start) #### Quick Links[](https://www.flickr.com/photos/spacex/51369631902/) [^(NERDLE CAM)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_HZCh2eGWEI) ^| [^(LAB CAM)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HGb28t5TWtc&t=0s) ^| [^(SAPPHIRE CAM)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7OKb9Rc-etw&t=0s) ^| [^(SEN... How then do you draw out the molecular orbital diagram for the new bond formed if you use the 2 electrons and place them in the antibonding orbital of H-Br bond? If these 2 electrons are in that antibonding orbital, what is going into the bonding orbital to form the bond between nucleophile and hydrogen atom? "Which substance would you expect to be the most magnetic: Fe, Fe+2, Fe+3? Draw the orbital diagrams for each species and use this information in your explanation of your answer. No explanation = no credit." So I was able to draw the orbital notation for each ion. I also recall that when dealing with ions for transition metals, I remove from the s subshell first. I do not understand which is the most magnetic. They all have unpaired electron shells. Is it Fe^+3 , due to the fact that it has 5...
[](/# Auto Sync Start) #### Quick Links[](https://www.flickr.com/photos/spacex/51369631902/) [^(NERDLE CAM)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_HZCh2eGWEI) ^| [^(LAB CAM)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HGb28t5TWtc&t=0s) ^| [^(SAPPHIRE CAM)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7OKb9Rc-etw&t=0s) ^| [^(SENTINEL CAM)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DC_jKgtoZOE&t=0s) ^| [^(ROVER CAM)](https://youtu.be/5HpgJJ1FwTc) ^| [^(PLEX CAM)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FcjHfaCEddA&t=0s) ^| [... [Arrow pushing mechanism for nucleophilic addition.](https://imgur.com/a/hZxwD45) So I know how to draw the nucleophilic addition mechanism and I also know the molecular orbital diagram for the carbonyl group: [https://imgur.com/a/EzB4ZKw](https://imgur.com/a/EzB4ZKw). The empty LUMO is closer to carbon and therefore the incoming nucleophile (hydride in this instance) attacks the carbon instead of oxygen. This fills the 3pi\* orbital which destructively interferes with the 3pi bonding orbital. T... I don't understand how to use the Afbau principle. At all. I have no clue. I'm assuming this is probably why I'm absolutely lost when drawing an orbital diagram, lol. The question is "write the full electron configuration and draw the orbital diagram for an atom of titanium in its ground state". I have zero clue on where to even start. I've been trying to understand orbitals for the better part of the morning, and I still have no clue what I'm doing, lmao. Please help me? If you have any resour... I have a quick question regarding the molecular orbital theory. We are doing cycloadditions right now, so we are using the HOMO/LUMO of dienes and dienophiles. I was wondering how to distinguish how many arrows a compound will have in the molecular orbital diagram? for instance 1,3-butadiene has 4 arrows in the diagram. Thanks
In my review sheet for bonding it says "Draw the orbital diagram for one of the fluorine atoms in a molecule of XeF4.". Do i just draw the diagram for the un-bonded Fluorine atom? Is it the same thing as drawing the diagram for a bonded Fluorine atom? If not, how would i write/draw the bonded Fluorine atom in XeF4?
21 Jan 2021 — As an ion potassium exists as K+, which means it loses an electron because it needs to attain stable electronic configuration and also the octet ...
The problem is draw the molecular orbital diagram for P2, P2+, P2-. Rank these in terms of increasing bond strength. Thanks in advance for the help.
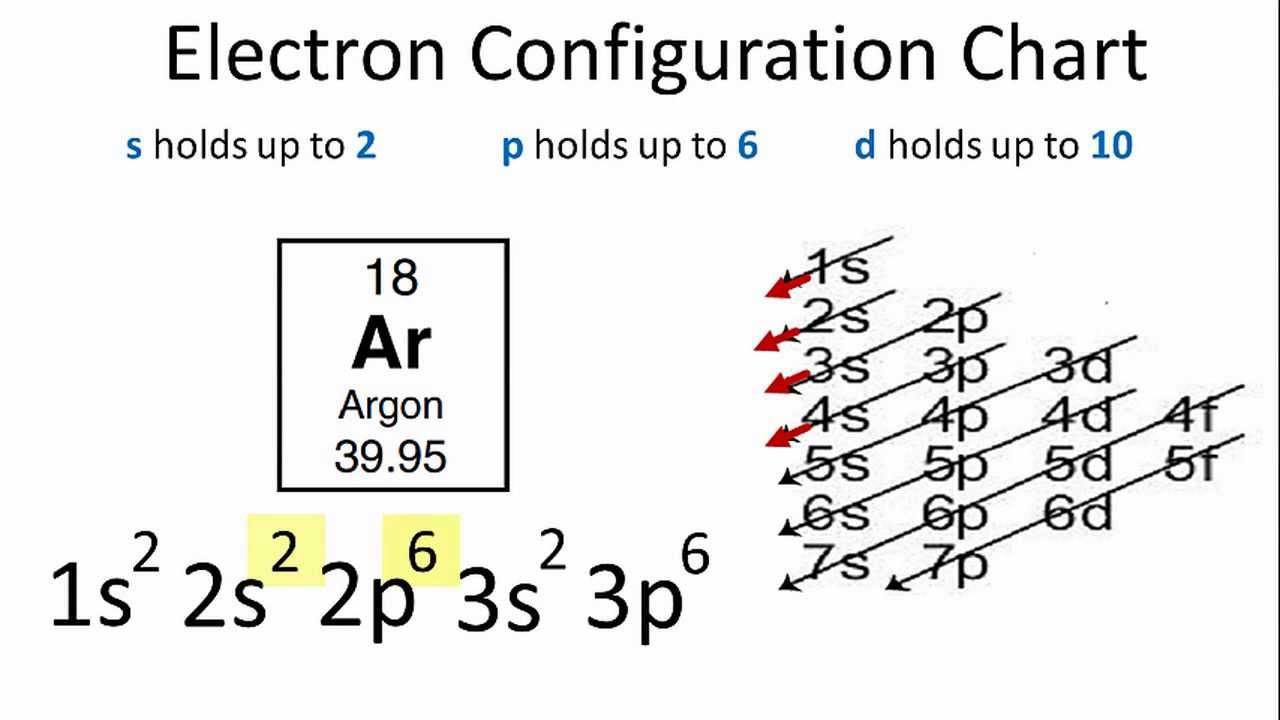
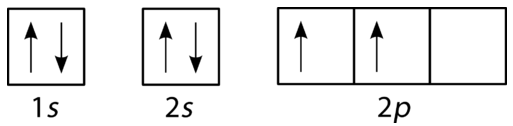
In writing the electron configuration for Potassium the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for Potassium go in the 2s orbital. The next six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons.
hey! I have a question: how do i draw a molecular orbital diagram for SO2? i only found examples for diatomic diagrams and im not sure how to do it if i have more then two atoms in the molecule.
When we draw the Lewis structure, the best structure is the one where S has the negative formal charge and each fluorine is singly bonded to the sulfur. So in my tutorial question, we are asked to draw the valence orbital diagram for F, S, S-, S*- and S hyb. So for F and S it's just the normal case. But for S-, isn't this assuming that sulfur has the negative ionic charge? I thought all it has is a negative formal charge where the formal charge does not indicate the presence of a negative ioni...
I'm working on a lab for dynamical systems that involves making an orbit diagram for fifty values of c for the quadratic family x^2 + c and then sketching the points on the orbit diagram on a piece of paper. What I want to do is somehow make a cumulative orbit diagram with every point I enter. I know nothing about Mathematica, so I'm not sure how easy or possible this is. I'll link the notebook I'm working with, I'd appreciate any suggestions or help. http://math-cs.cns.uni.edu/~ostapyuk/Orbit...
orbital diagram for potassium qaswers the bohr diagram is the diagram of the electrons on the orbital layers of the nucleus of an atom for potassium you would put 2 electrons on the first layer 8 on the second … layer and 9 on the third layer this is because the atomic number of potassium k is 19 therefore has 19 protons and 19 electrons.
I'm not sure what my Professor means when he says "Draw the orbital diagram for the hybridized Xe atom in a molecule of XeF4." and "Draw the orbital diagram for one of the fluorine atoms in a molecule of XeF4." I think i'm just confused by the wording because it seems easy but i have no idea. Could you guys explain this to me in another way? Thank you.
I have a homework problem asking me to construct the molecular orbital diagram for methylene chloride, and I am not too sure what to do next. I have determined that all of the orbitals transform as follow: C 2S=A1 C 2Pz=A1 C 2Py=B2 C 2Px=B1 2H 1S=A1+B2 2Cl 3S=A1+B1 2Cl 3Pz=A1+B1 2Cl 3Py=A2+B2 2Cl 3Px=A1+B1 My thoughts were to construct the MO for the CH2 side, then add the two chlorines from there. Let me know if you have any pointers. thank you
What would the orbital diagram for these molecules look like if they had this many electrons? ​ I'd guessed that phosphorus would have 3s(2), 3p(3), and 3d(5). The half-filled p and d orbitals would offer stability to explain why phosphorus can sometimes make 5 bonds. Alternatively I was considering 3s(2), 3p(6), and 4s(2). ​ I'd guessed that sulfur would have 3s(2), 3p(3), 3d(5), and 4s(2). Again, the half-filled p and d orbitals would offer stability. An electron from...
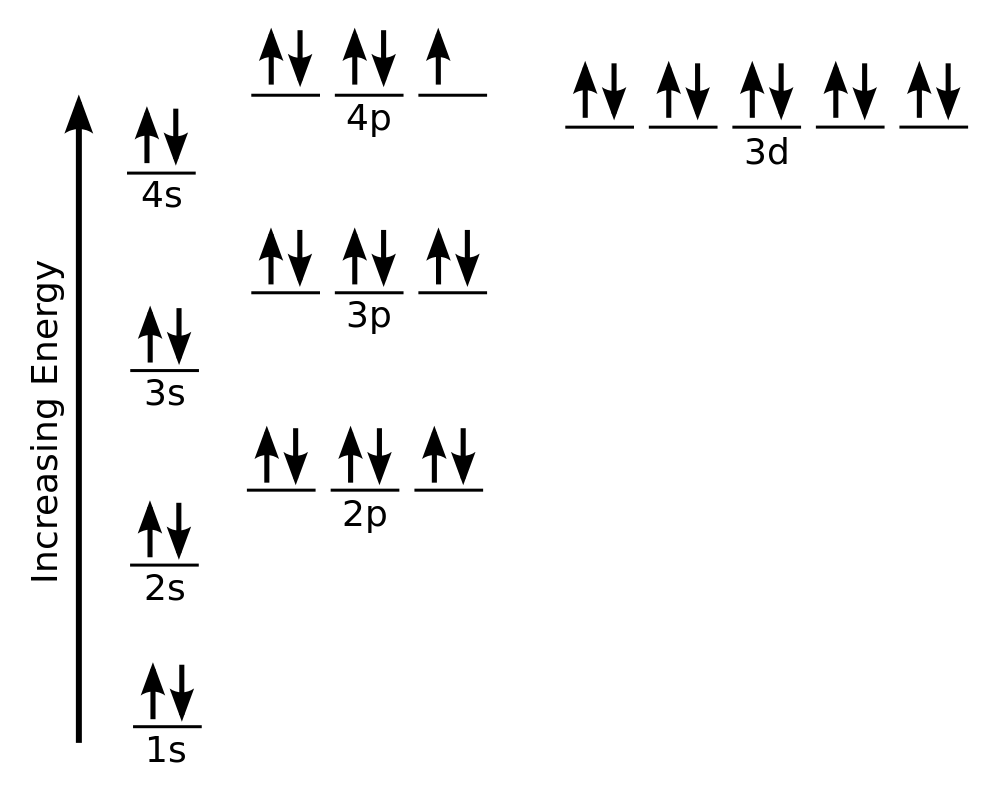
Draw the orbital energy diagram for K (potassium). Represent electrons as arrows (with up or down spin). What is the core] valence electron configuration? (type in the box below) -45 Energy 2p 2s is *** -T-5 ; Question: Draw the orbital energy diagram for K (potassium). Represent electrons as arrows (with up or down spin).
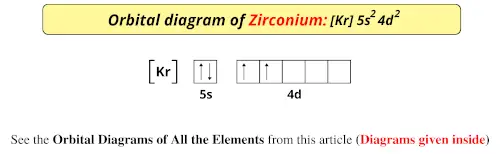
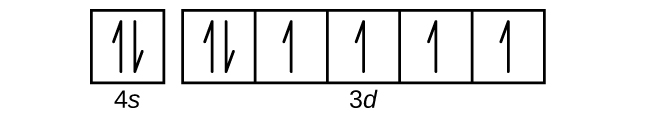
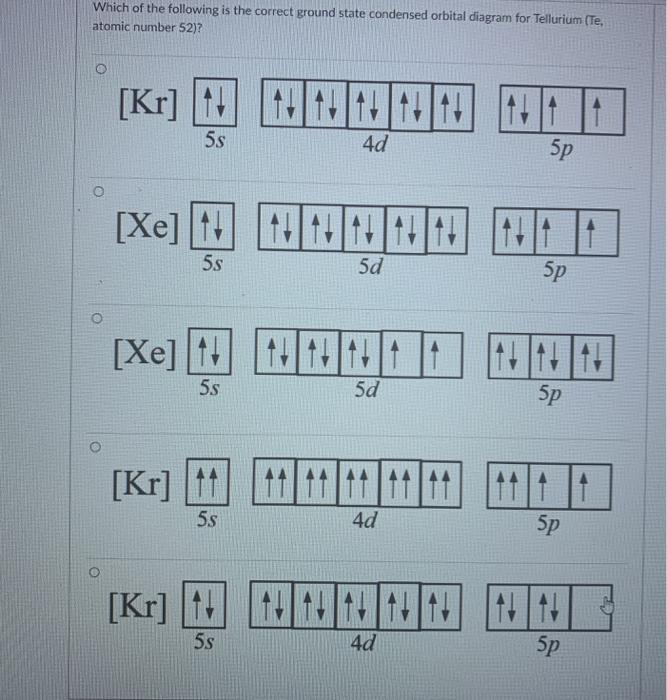
Nov 01, 2021 · Orbital diagram of Potassium (K) 20: Orbital diagram of Calcium (Ca) 21: Orbital diagram of Scandium (Sc) 22: Orbital diagram of Titanium (Ti) 23: Orbital diagram of Vanadium (V) 24: Orbital diagram of Chromium (Cr) 25: Orbital diagram of Manganese (Mn) 26: Orbital diagram of Iron (Fe) 27: Orbital diagram of Cobalt (Co) 28: Orbital diagram of ...
1 answerHint :We know that the atomic number of potassium is 19. The electronic configuration of an element describes how electrons are distributed in its atomic ...
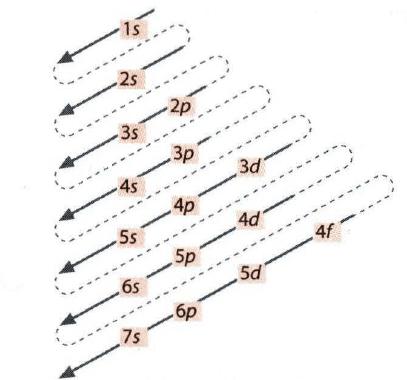
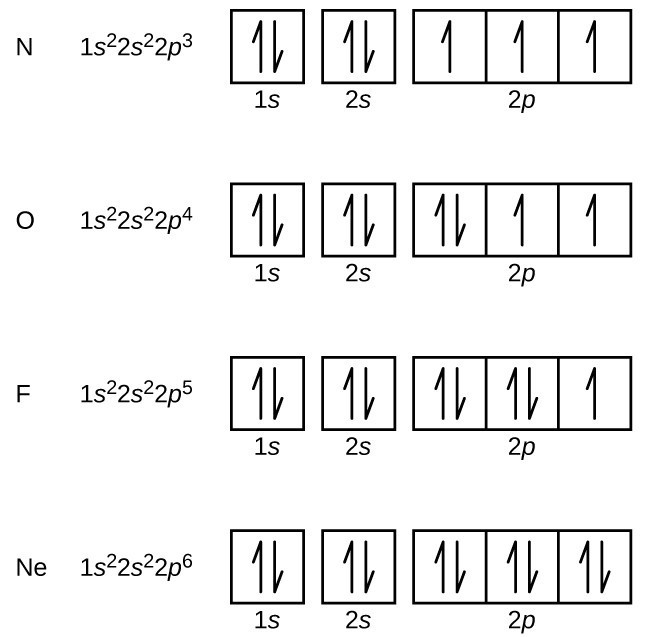
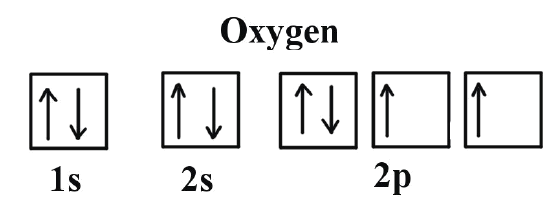
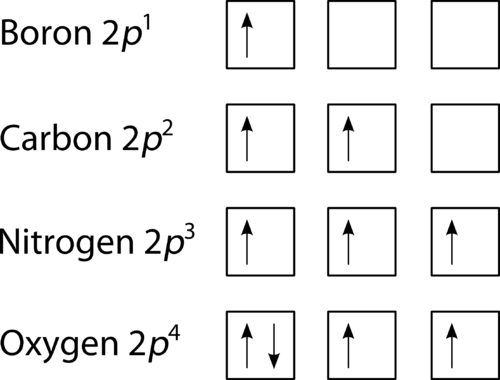
For elements 1-36, there are two exceptions to the filling order as predicted from the periodic table. Draw the atomic orbital diagrams for the two exceptions and indicate how many unpaired electrons are present. I'm not even sure where to start to be honest...
Extracted from "*Terrans: Ignoble Savages or Incredible Pioneers''* by Professor Amvir Stratmont, University of Versia publishing, 3210, 2nd edition. ​ ***Introduction*** ''For many centuries, our galaxy had enjoyed a long standing peace. Despite the odd small-scale planetary insurrection or political disturbance, order and serenity was kept by and maintained by the will of the Kachaxian Supremacy. From humble beginnings as a race of traders, the Kachax had grown to prominence d...
Hi! I'm doing some inorganic chem homework and I drew the molecular orbital diagrams for a few molecules and now I have to assign and draw the HOMO and LUMO. Does the HOMO have to be the highest totally occupied orbital or can it just be partially filled? Does the LUMO have to be totally unoccupied or can it just be partially unoccupied? Thanks in advance!
Feb 08, 2018 · Krypton Orbital Diagram Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of krypton (atomic number: 36), the most common . Box spin diagram of outer electron orbitals for the electron configuration of the atom . 36 Krypton, Kr, [Ar]3ds24p6 = [Kr] (), [Ar]3d 4s 4p v.
17 Dec 2014 — The full electron configuration of potassium is 1s22s22p63s23p64s1 . The noble gas notation is [Ar]4s1 . The following orbital diagram shows ...1 answer · Potassium's atomic number is 19. This means that every atom of potassium has 19 protons in its nucleus. In a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal ...



















0 Response to "38 orbital diagram for k"
Post a Comment