40 as the firm in the diagram expands from plant size #1 to plant size #3, it experiences
MICRO FINAL PRACTICE ch. 9 Flashcards - Quizlet The diagram above shows the short-run average total cost (ATC) curves associated with different plant size. As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size #1 to plant size #3, it experiences economies of scale econ exam #2 Flashcards - Quizlet As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size #1 to plant size #3, it experiences: economies of scale. As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size #3 to plant size #5, it experiences: diseconomies of scale. Refer to the above short-run data. The profit-maximizing output for this firm is:
Type: A... - Martinsville Indiana Computer Repair - Facebook 161. As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size #1 to plant size #3, it experiences: A) diminishing returns. B) economies of scale. C) diseconomies of scale. D) constant costs. Answer: B. Type: G Topic: 6 E: 407 MI: 163 Status: New 162. As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size #3 to plant size #5, it experiences:

As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size #1 to plant size #3, it experiences
The Shape of a Firm's Cost Curves in Long Run and Short Run The same thing is true of a firm. In the short run extra output can be produced by a firm by utilising its existing capacity (i.e., plant and machinery) more intensively. In the long run, capacity can be varied, new machines can be ordered, the size of the factory can be altered, or new factories can be set up. Long Run Industry Supply Curve (With Diagram) Now, let us suppose that there is an increase in market demand to D 1 D 1 following an increase in money income or a change in the taste of buyers. As a result, market price rises from OP to OP 1 and the firm's demand curve is now represented by P 1 = AR 1 = MR 1 line.. The firm will now expand its output to OQ 1.It will earn supernormal profit equal to the shaded area since P = LMC = MR 1 ... The above diagram shows the short run average total cost ... The above diagram shows the short-run average total cost curves for five different plant sizes of a firm. The position of these five curves in relation to one another reflects: A. economies and diseconomies of scale. B. the effect of fixed costs on ATC as output increases.
As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size #1 to plant size #3, it experiences. Long Run Average Cost Curve: Derivation, Example, Solved ... Clearly, AH > AL. Therefore, the firm chooses SAC 1. Similarly, if the firm tries to produce an output which is greater than OB but less than OD, then it chooses SAC 2 since SAC1 involves higher costs. Also, for outputs larger than OD, the firm uses SAC 3. Summing up, we can say that in the long run, the firm employs the plant yielding maximum ... Refer to the graph Which one of the following would cause ... As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size # 1 to plant size # 3 , ... 149 . As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size # 3 to plant size # 5 , ... As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size #3 to plant size #5, it experiences A. increasing returns. B. economies of scale. Solved As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size ... As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size #1 to plant size #3, it experiences #1 #5 #2 #4 #3 Average Costs ($) < 0 Output Select one: a. diminishing returns. b. economies of scope. C. economies of scale O d. diseconomies of scale. O e. constant costs. DOCX Ghulam Hassan - Home In the table below, complete the short-run supply schedule for the firm (columns 1 and 2) and indicate the profit or loss incurred at each output (column 3). Explain: "That segment of a competitive firm's marginal-cost curve which lies above its average-variable-cost curve constitutes the short-run supply curve for the firm."
ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com Refer to the diagram. This firm's average fixed costs are: a. not shown b. the vertical distance between AVC and MC c. the vertical distance between AVC and ATC d. equal to the per unit change in MC. c. the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size #1 to plant size #3, it experiences: Economics: Economies and Diseconomies of Scale Quiz - Quizizz If a firm increases its use of all factors of production but sees an increase in its average costs, this is a sign of ... As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size 1 to 3 in the LONG RUN, it experiences... answer choices . diminishing returns. PDF CHAPTER 7 THE COST OF PRODUCTION - University of Houston If the firm can produce one chair with either four hours of labor or four hours of capital, machinery, or any combination, then the isoquant is a straight line with a slope of -1 and intercept at K = 4 and L = 4, as depicted in Figure 7.5. 7.3 The Structure of Costs in the Long Run - Principles of ... Thus, the market for dishwashers will consist of 100 different manufacturing plants of this same size. If some firms built a plant that produced 5,000 dishwashers per year or 25,000 dishwashers per year, the average costs of production at such plants would be well above $500, and the firms would not be able to compete. Figure 3.
RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Economics Chapter 8 Concept of ... In this phase, the AC output of the firm is increasing because it is operating under the law of rising returns due to various internal economies. Thus, the 'U' size of short-run average cost reduction is due to non-proportional returns on the given scale of the plant. Question 11. Explain the relationship between Average and Marginal Cost ... Microeconomics (ECON-2302) Flashcards | Quizlet ~ the firm does not have sufficient time to change the size of its plant. ~ the firm does not have sufficient time to cut its rate of output to zero. ... As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size #1 to plant size #3, it experiences: ... ~ Is efficient from society's perspective because it has big plants and it uses the newest ... Production Costs & Returns to Scale Quiz - Quizizz If a firm doubles its use of inputs and finds that output increases by 50%, then it has experienced ... As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size 1 to 3 in the LONG RUN, it experiences... answer choices . diminishing returns. economies of scale. Refer to the above diagram At output level Q total cost is ... As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size #1 to plant size #3, it experiences: A) diminishing returns. B) economies of scale. C) diseconomies of scale. D) constant costs. Per unit costs are falling in the long run and we call that economies of scale due to increasing plant size.
As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size #1 to ... As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size #1 to plant size #3, it experiences economies of scale. This is explained by the fact that as the plant increases their output, the average costs of the plant decreases hence as the firm increases it size the firm becomes more efficient.
Assignment 5 (Ch 9) Flashcards - Quizlet As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size #1 to plant size #3, it experiences: economies of scale Suppose that a business incurred implicit costs of $500,000 and explicit costs of $5 million in a specific year.
As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size 3 ... 162. As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size #3 to plant size #5, it experiences: A) increasing returns. B) economies of scale. C) diseconomies of scale. D) constant costs. Answer: C. C ) diseconomies of scale . Type: G Topic: 6 E: 404 MI: 160 163. The above diagram shows the short-run average total cost curves for five ...
Type: A... - Martinsville Indiana Computer Repair - Facebook 14. As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size #3 to plant size #5, it experiences: A. increasing returns. B. economies of scale. C. diseconomies of scale. D. constant costs. 15. The short-run average total cost curve is U-shaped because: A. average fixed costs decline continuously as output increases.
Answered: Network Diagrams Exercise 1. For each… | bartleby Answered: Network Diagrams Exercise 1. For each… | bartleby. Network Diagrams Exercise 1. For each task build the relevant network diagram 2. Add the task durations for each activity 3. Conduct a forward and backward pass (calculate ES EF, LS, LF) 4. Calculate the available float for each task 5. Identify the critical path for each network.
Solved As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size ... See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size #1 to plant size #3, it experiences: diminishing returns. economies of scale. diseconomies of scale. constant costs.
Econ Final Flashcards | Quizlet As the firm in the diagram expands from plant size #1 to plant size #3, it experiences: ... The diagram shows the short-run average total cost curves for five different plant sizes of a firm. The position of these five curves in relation to one another reflects: ... In the diagram, curves 1, 2, and 3 represent: total fixed cost, total variable ...
PDF Essential Graphs for Microeconomics Theory of the Firm Short Run Cost reaches a minimum then increases (U When MC< ATC, ATC is rising Price buyers pay P S D 2 D 1 Q Price sellers receive Price w/o tax surplus D S P Q e Q e Producer surplus A tax imposed on the BUYER-demand curve moves left elasticity determines whether buyer or seller bears incidence of tax
The above diagram shows the short run average total cost ... The above diagram shows the short-run average total cost curves for five different plant sizes of a firm. The position of these five curves in relation to one another reflects: A. economies and diseconomies of scale. B. the effect of fixed costs on ATC as output increases.
Long Run Industry Supply Curve (With Diagram) Now, let us suppose that there is an increase in market demand to D 1 D 1 following an increase in money income or a change in the taste of buyers. As a result, market price rises from OP to OP 1 and the firm's demand curve is now represented by P 1 = AR 1 = MR 1 line.. The firm will now expand its output to OQ 1.It will earn supernormal profit equal to the shaded area since P = LMC = MR 1 ...
The Shape of a Firm's Cost Curves in Long Run and Short Run The same thing is true of a firm. In the short run extra output can be produced by a firm by utilising its existing capacity (i.e., plant and machinery) more intensively. In the long run, capacity can be varied, new machines can be ordered, the size of the factory can be altered, or new factories can be set up.
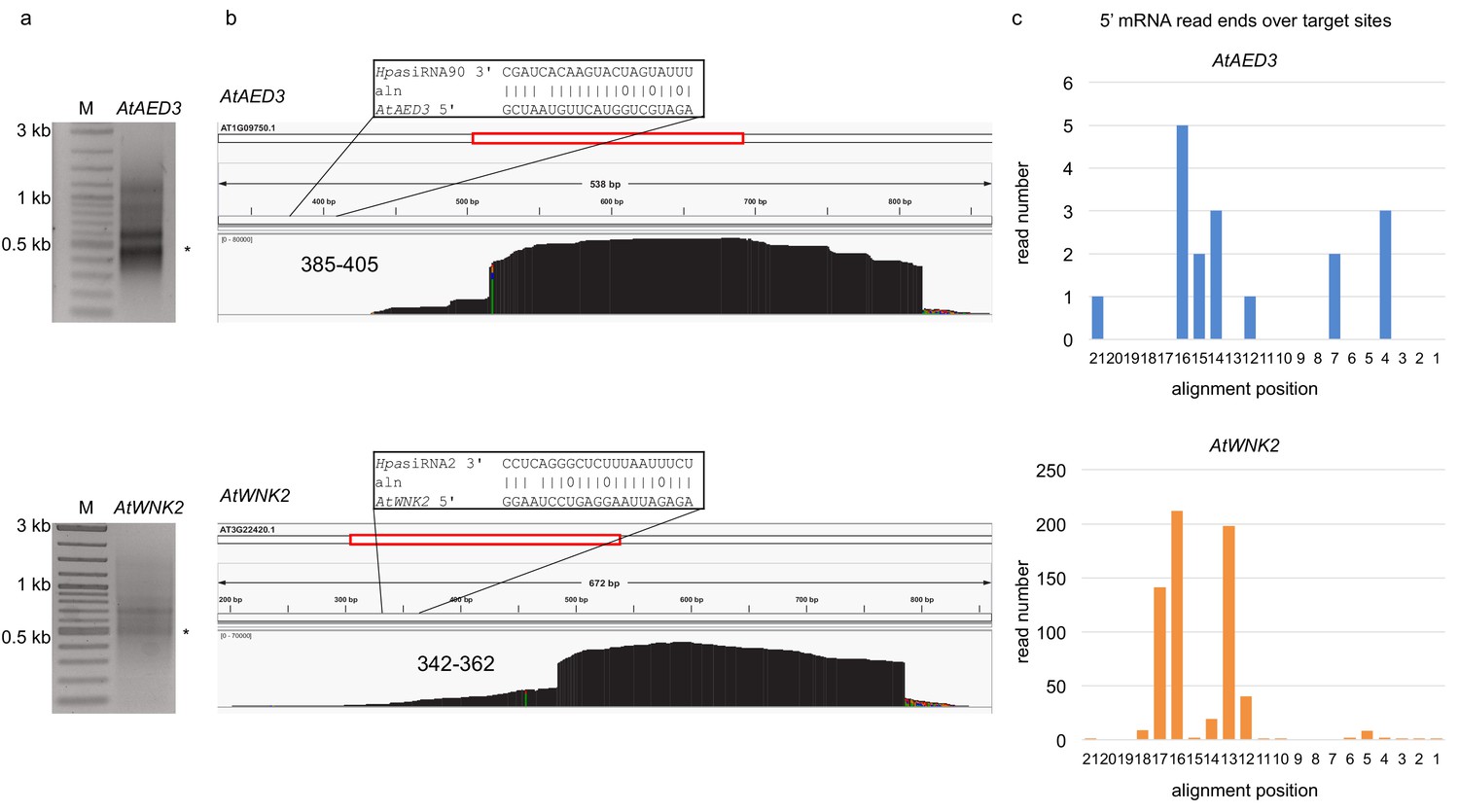








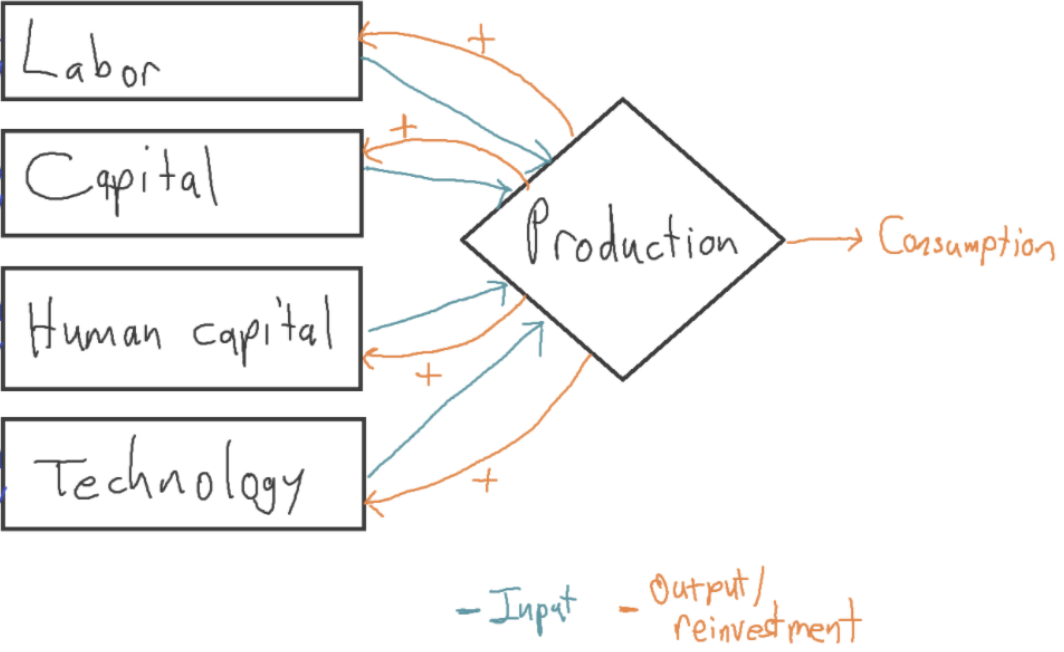

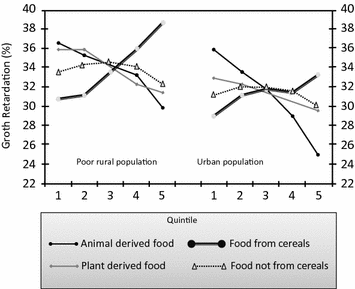
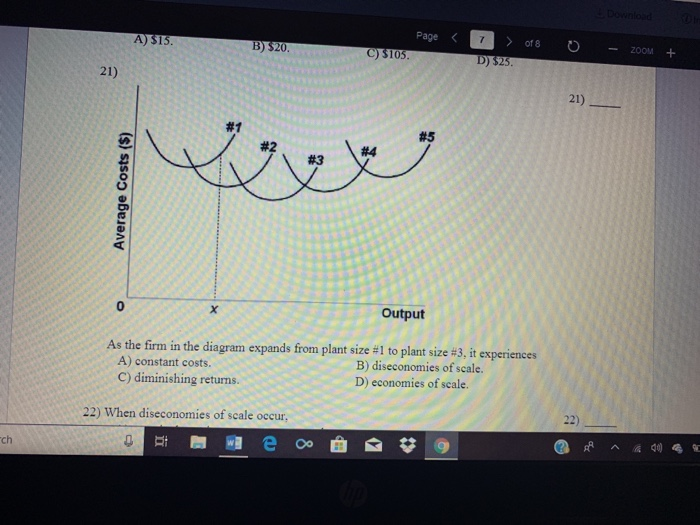

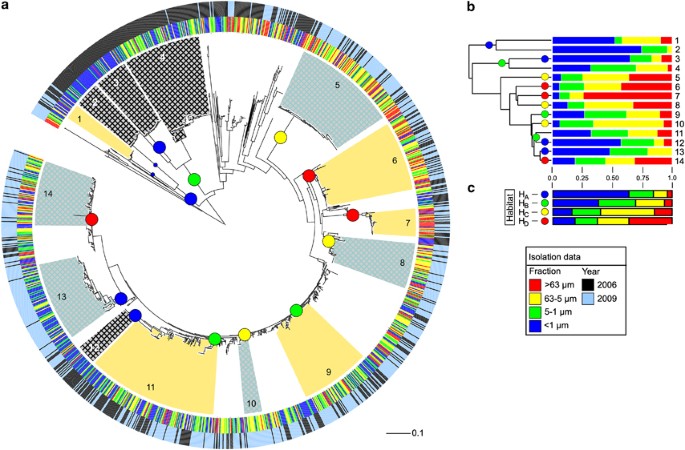




0 Response to "40 as the firm in the diagram expands from plant size #1 to plant size #3, it experiences"
Post a Comment