41 atomic force microscope diagram
Atomic Force Microscopy for Molecular Structure Elucidation Functionalizing the tip of an atomic force microscope with a CO molecule enabled atomic-resolution imaging of single molecules, and measurement of their adsorption geometry and bond-order relations. In addition, by using scanning tunneling microscopy and Kelvin probe force microscopy, the density of the molecular frontier orbitals and the ... AFM Principle - How Does an Atomic Force Microscope Work? To learn more about Atomic Force Microscopy, click through. AFM microscopes are among the best solutions for measuring the nanoscale surface metrology and material properties of samples. A conventional compound light microscope is limited to a maximum sample magnification of approximately 1000x; a quantity that is dictated by the wavelengths of ...
PDF Visualization of cell structure by atomic force microscopy light or electrons, atomic force microscopes use a very fine tip that scan the sample, producing a high resolution image of the surface. Therefore, with light and electron microscopes, internal structure of cells has been possible to analyze. On the opposite, the atomic force microscope is a surface instrument. The approach mentioned in this

Atomic force microscope diagram
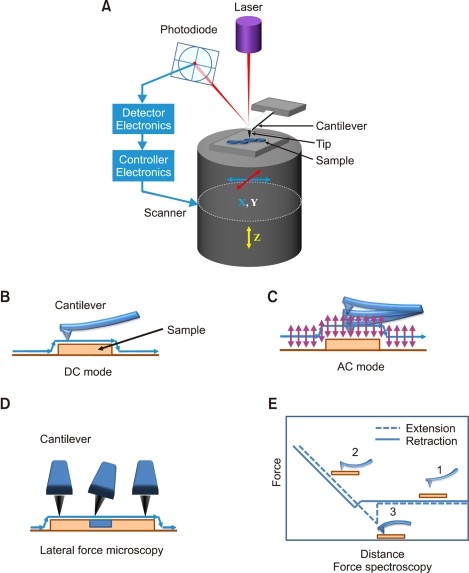
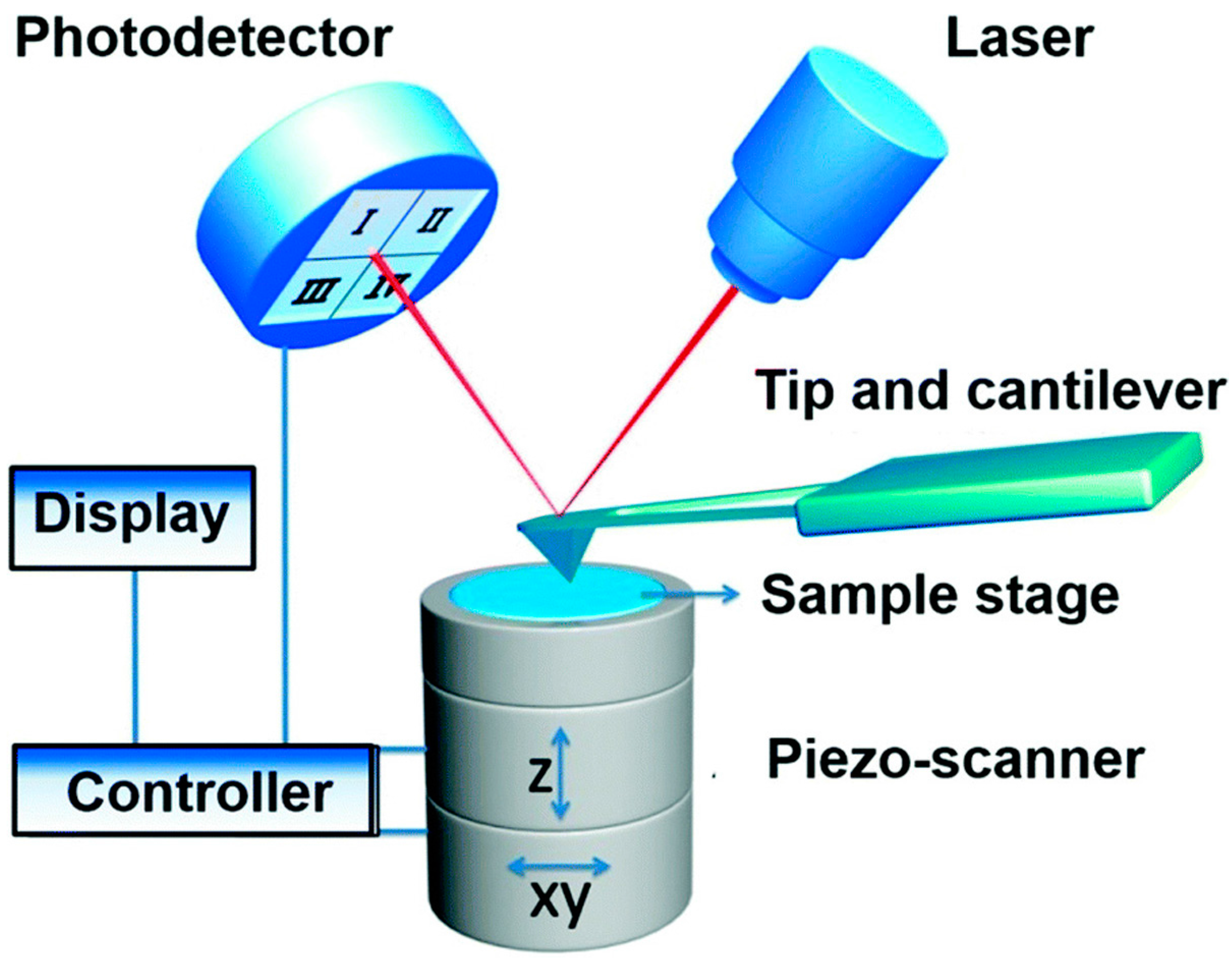
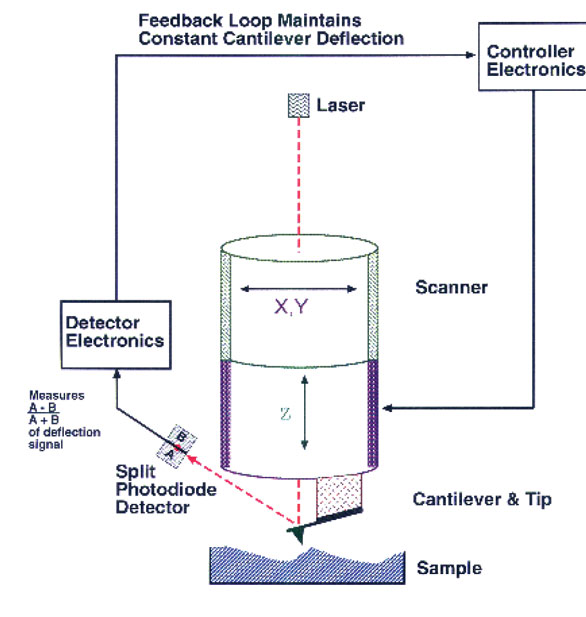
PDF Instrumentation Atomic Force Microscope Leuba, S. H. and Bustamante, C. Analysis of Chromatin by Scanning Force Microscopy. In Methods in Molecular Biology, Becker, P., Ed. 119, 143-160, 1999. piezo mirror cantilever laser AFM tip x y z photodiode position detector Dynamic mode amplitude of oscillation surface Contact mode surface The Atomic Force Microscope PDF An Introduction to Atomic Force Microscopy Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is an imaging technique used to determine topography and other properties of surfaces. It is an important tool for nanoscience. Abstract Above - our AFM setup. A photodetector records the bending of the cantilever, which reflects the topography and other surface prop erties. Automated structure discovery in atomic force microscopy Abstract. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) with molecule-functionalized tips has emerged as the primary experimental technique for probing the atomic structure of organic molecules on surfaces. Most experiments have been limited to nearly planar aromatic molecules due to difficulties with interpretation of highly distorted AFM images originating ...
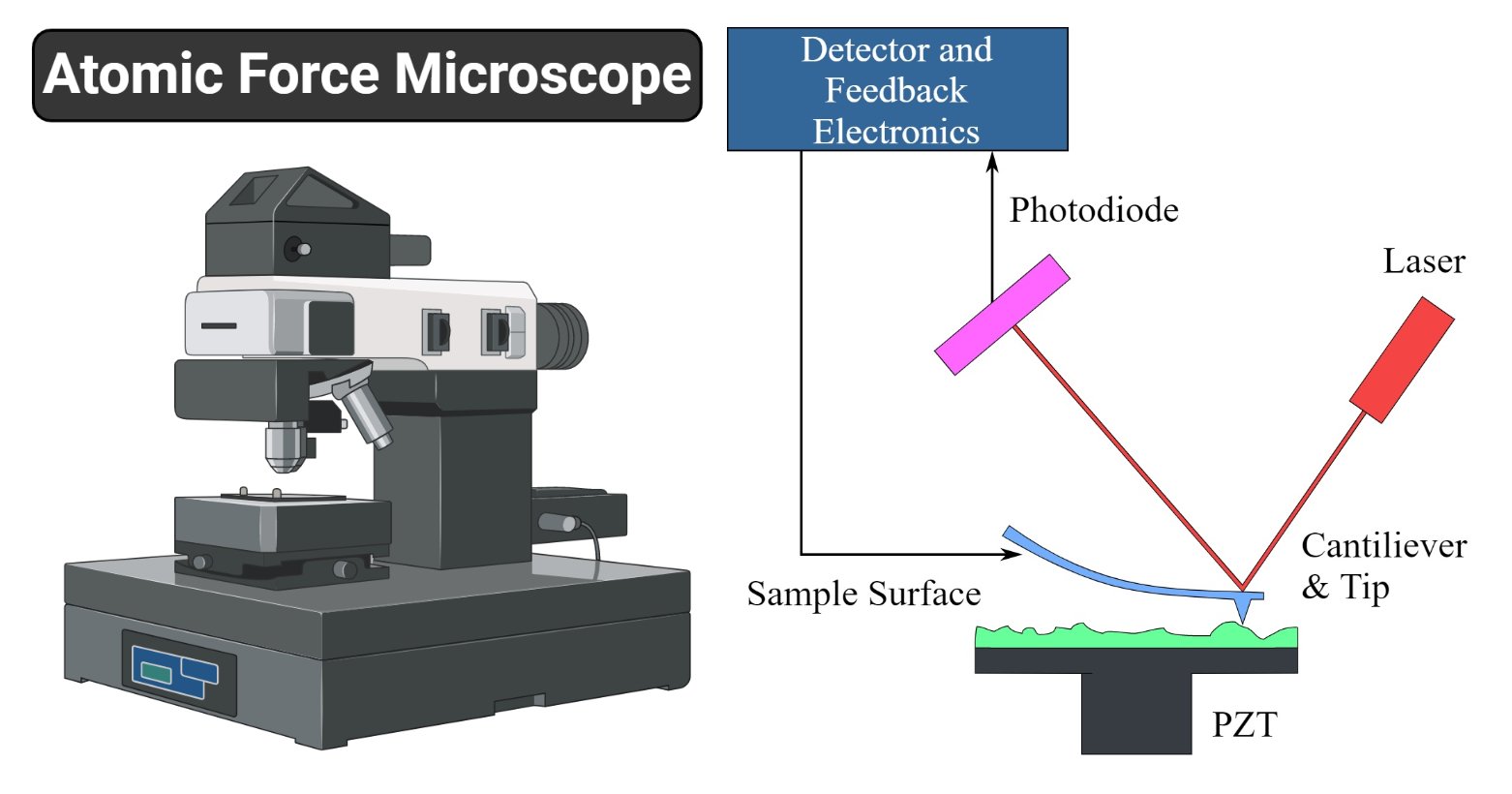
Atomic force microscope diagram. Atomic Force Microscopy. Schematic diagram of AFM and ... Download scientific diagram | Atomic Force Microscopy. Schematic diagram of AFM and three different AFM operating modes. In this paper Tapping and Contact Modes are used. from publication: A New ... Atomic Force Microscopy / Scanning Probe Microscopy An Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) provides 3-dimensional topographic information about a sample by probing its surface structure with a very sharp tip. The tip is scanned laterally across the surface, and the vertical movements of the tip are recorded and used to construct a quantitative 3-dimensional topographic map. A schematic diagram of an atomic force microscope ... Download scientific diagram | A schematic diagram of an atomic force microscope. from publication: High Performance Feedback for Fast Scanning Atomic Force Microscopes | We identify the dynamics ... Design of Atomic Force Microscope (With Diagram) In this article we will discuss about the design of atomic force microscope, explained with the help of a diagram. An atomic force microscope instead of using a lens is provided with a probe to examine the surface of a specimen with a sharp tip which may be several micrometers in and less than 10 nm in diameter at the point near field to be examined. The tip lies at the end of the lever which ...
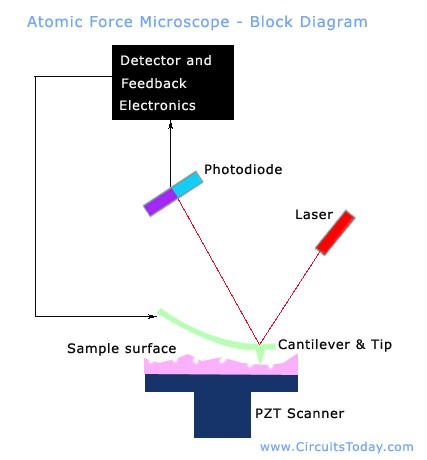
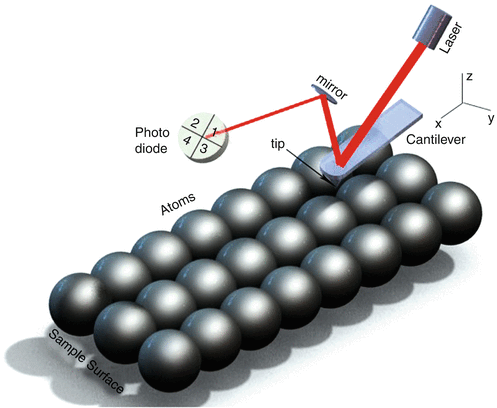
File:Atomic force microscope block diagram v2.svg ... Atomic force microscope block diagram, laser and photodiodes detection system, second position of the tip, inspired by Atomic force microscope block diagram.png: Date: 21 February 2008: Source: Own work: Author: Twisp: Other versions: Derivative works of this file: Microscopio de fuerza atomica esquema v2.svg PDF Atomic Force Microscopy: its development and applications Atomic Force Microscopy: its development and applications Dian Shi PID: A53079294 Abstract This paper reviews the invention and developments of atomic force microscopy (AFM). It starts with structure and the basic principles, then its applications and limitations are discussed. Some recent experiments using AFM are reviewed. Atomic force microscopy - Wikipedia Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the optical diffraction limit.The information is gathered by "feeling" or "touching" the surface with a mechanical probe. Piezoelectric elements that facilitate tiny but accurate and precise movements on (electronic ... Atomic Force Microscopy for Molecular Structure ... Functionalizing the tip of an atomic force microscope with a CO molecule enabled atomic-resolution imaging of single molecules, and measurement of their adsorption geometry and bond-order relations. In addition, by using scanning tunneling microscopy and Kelvin probe force microscopy, the density of the molecular frontier orbitals and the ...
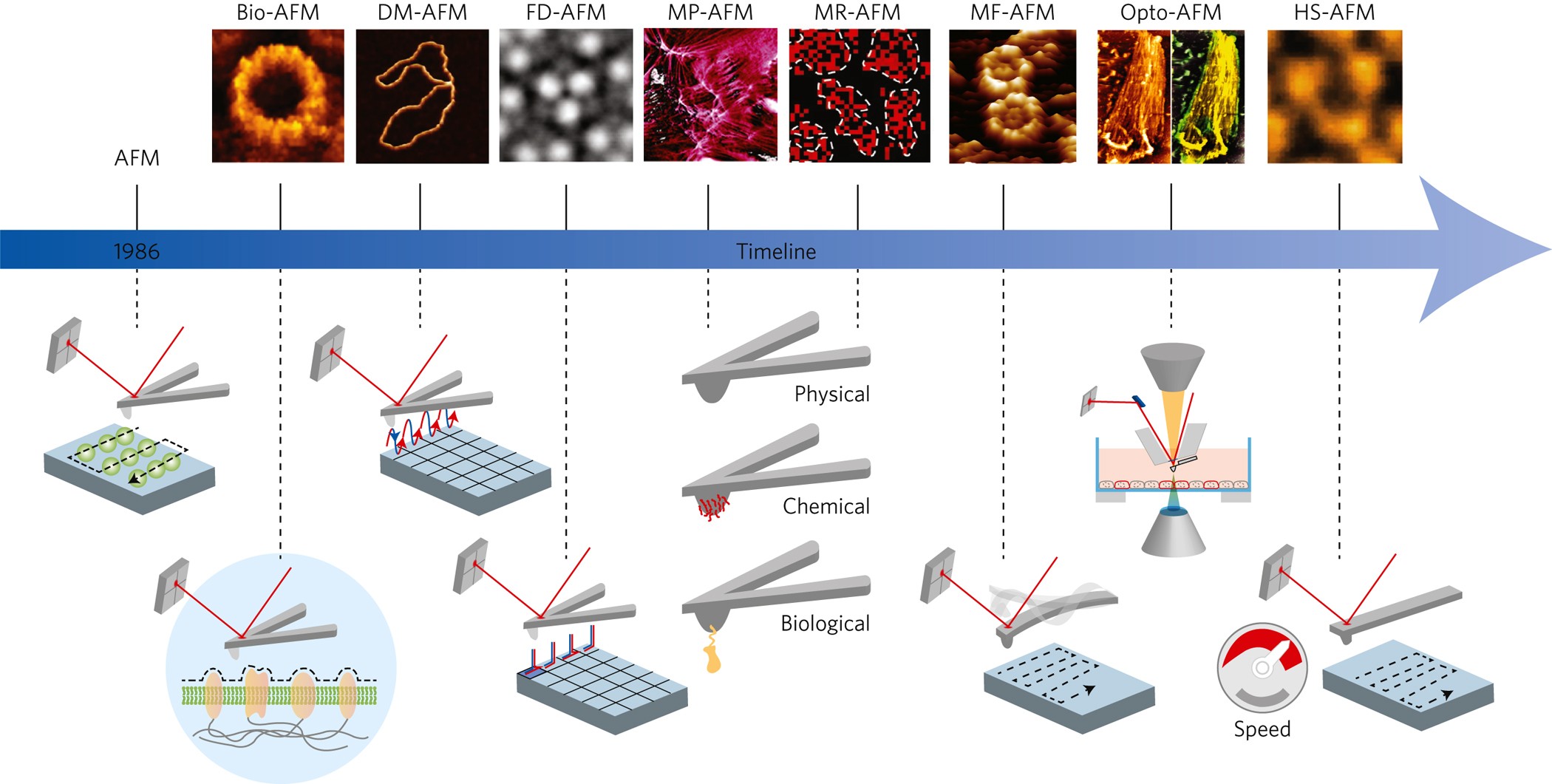
PDF Atomic Force Microscopy Basics and Applications Atomic Force Microscopy. laser beam position sensitive detector sample cantilever with tipMolecular interaction: E = F Δs E ~ eV; Δs~ Å F ~ 2.10-9N Typical AFM resolution: x-y: 1nm; z: 0.1nm Detection: - sub-Å deflection -pNforces. General AFM set-up. controller piezo ceramic sample surface laser cantilever quadrant photodiode. Advances in Atomic Force Microscopy: Imaging of Two- and ... Visualization of Hydration Layers on Muscovite Mica in Aqueous Solution by Frequency-Modulation Atomic Force Microscopy. J. Chem. Phys. 138 (18), 184704. 10.1063/1.4803742 [Google Scholar] Kuchuk K., Sivan U. (2018). Hydration Structure of a Single DNA Molecule Revealed by Frequency-Modulation Atomic Force Microscopy. PDF Lecture 10: Basics of Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) Atomic force microscopy (AFM) was developed when people tried to extend STM technique to investigate the electrically non-conductive materials, like proteins. In 1986, Binnig and Quate demonstrated for the first time the ideas of AFM, which used an ultra-small probe tip at the end of a cantilever (Phys. Rev. Letters, 1986, Vol. 56, p 930). Atomic Force Microscope Principle | AFM Scanning | How AFM ... Atomic force microscopy is arguably the most versatile and powerful microscopy technology for studying samples at nanoscale. It is versatile because an atomic force microscope can not only image in three-dimensional topography, but it also provides various types of surface measurements to the needs of scientists and engineers.
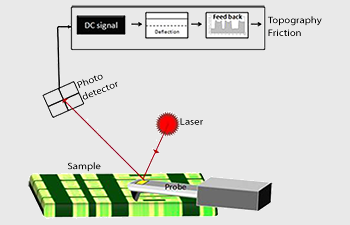
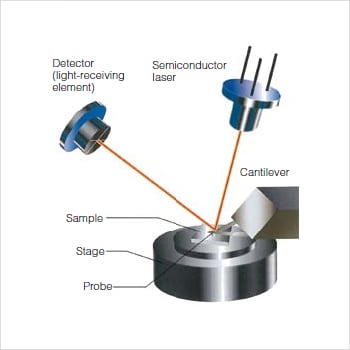
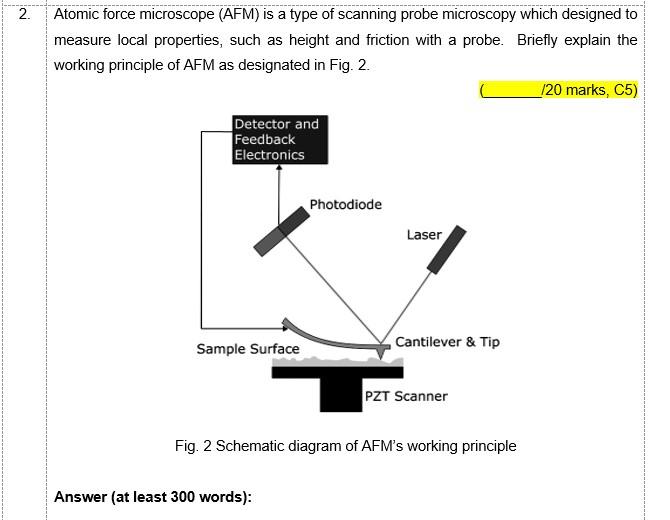
Atomic Force Microscope - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The deflections that occur in the tip, due to the interaction forces between the tip and sample surface, can be measured by focusing a laser beam onto a cantilever and detecting the reflected light from the cantilever using a position sensitive detector. Schematic diagram showing the principle of atomic force imaging is shown in Fig. 4.1a. As the tip is moved over the surface, a feedback mechanism is employed to ensure that the piezoelectric motor maintains a constant tip force or height ...
Atomic Force Microscope (AFM)- Definition, Principle ... The Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) takes the image of the surface topography of the sample by force by scanning the cantilever over a section of interest. Depending on how raised or how low the surface of the sample is, it determines the deflection of the beam, which is monitored by the Positive-sensitive photo-diode (PSDP).
Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) - Definition, Principle ... Definition of Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) The AFM, also known as the atomic force microscope (AFM) is a sort scanner probe. Its principal functions include measuring characteristics like height, magnetism and friction. Resolution is determined in millimeter. It is more precise and efficient than the optical Diffraction Limit.
Imaging DNA Structure by Atomic Force Microscopy Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a microscopy technique that uses a sharp probe to trace a sample surface at nanometre resolution. For biological applications, one of its key advantages is its ability to visualize substructure of single molecules and molecular complexes in an aqueous environment.
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Service - Creative-Biostructure In manipulation, the forces between tip and sample can also be used to change the properties of the sample in a controlled way, for example, atomic manipulation, scanning probe lithography and local stimulation of cells. Figure 1. Block diagram of atomic force microscope using beam deflection detection.
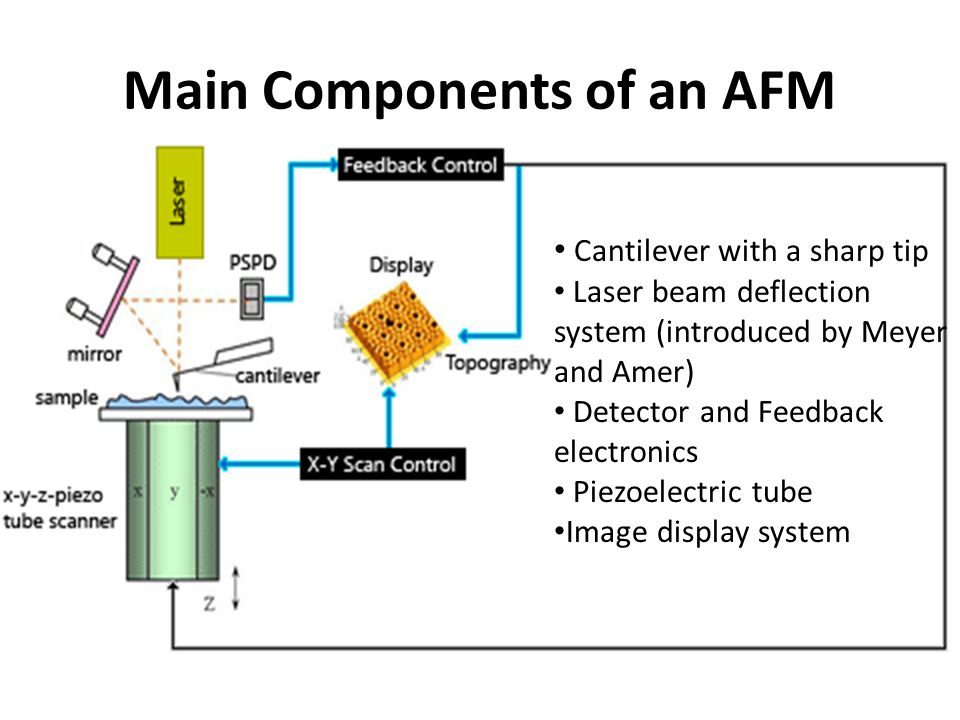
PDF Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) 1. General Principle The Atomic Force Microscope is a kind of scanning probe microscope in which a topographical image of the sample surface can be achieved based on the interactions between a tip and a sample surface. The atomic force microscope was invented by Gerd Binning et al. in 1986 at IBM Zurich based on ...
File:Atomic force microscope block diagram.svg - Wikimedia ... File:Atomic force microscope block diagram.svg. Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 646 × 599 pixels. Other resolutions: 259 × 240 pixels | 517 × 480 pixels | 647 × 600 pixels | 828 × 768 pixels | 1,104 × 1,024 pixels | 926 × 859 pixels.
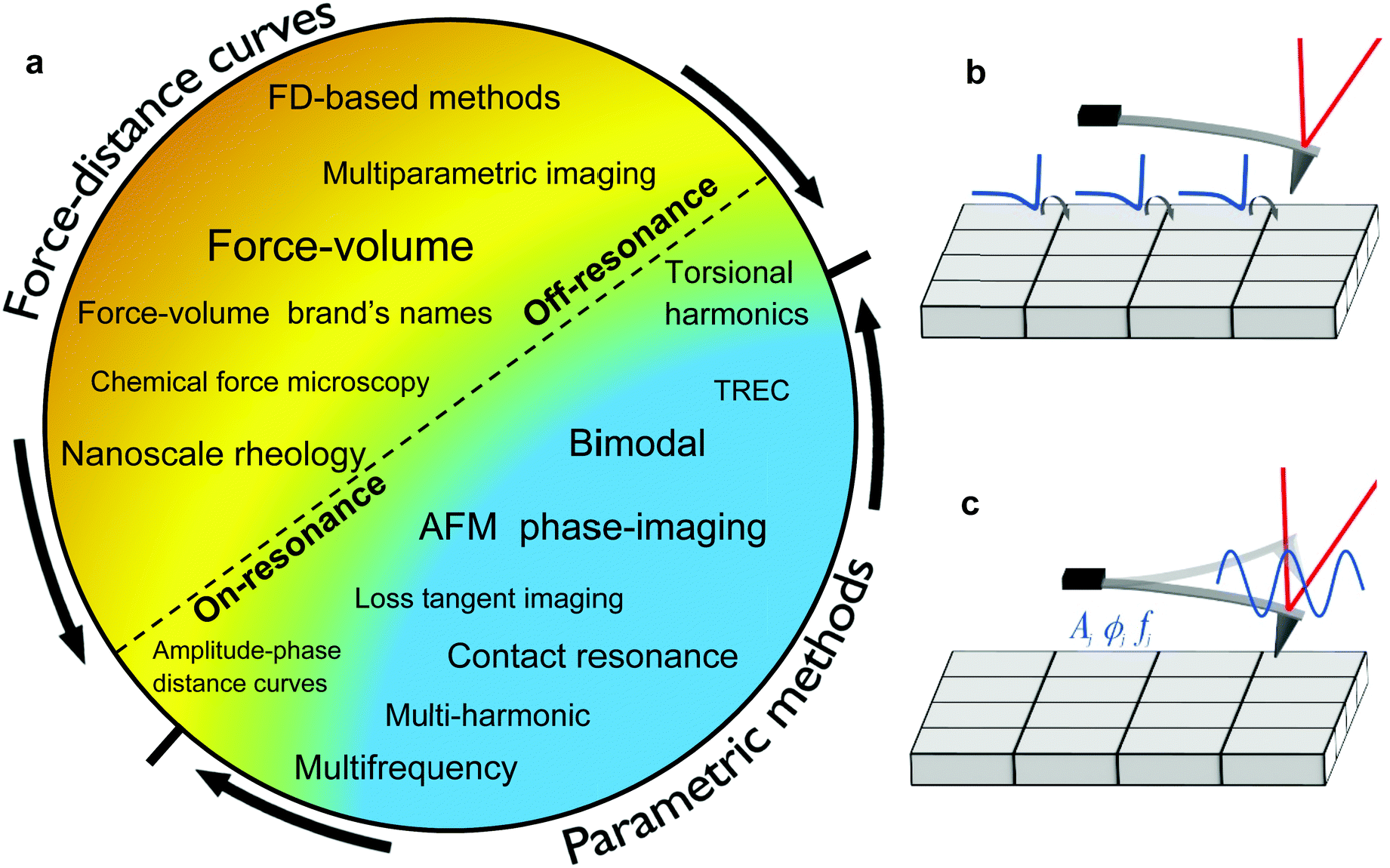
Atomic Force Microscopy - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is an influential surface analysis technique used for micro/nanostructured coatings. This flexible technique can be used to obtain high-resolution nanoscale images and study local sites in air (conventional AFM) or liquid (electrochemical AFM) surroundings. In this chapter, the principles of AFM in both air and electrolytes are reviewed and special applications of AFM for micro/nanostructured coatings are discussed.
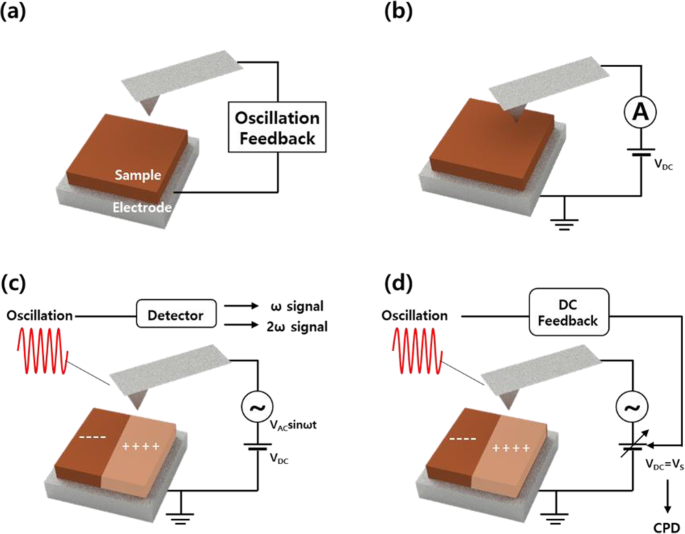
Atomic Force Microscopy Working Principle — AFM Explained ... Similarly in atomic force microscopes, depending on the different modes, there is a parameter that serves as the setpoint. For example, in static mode (contact mode) the feedback parameter is cantilever deflection, while in the most common form of tapping mode, the cantilever oscillation amplitude is the feedback parameter. The instrument is ...
Atomic-force microscopy - NIST Atomic-force microscopy enables subnanometer imaging resolution, to extract geometric parameters of reference structures that advance measurement science, and to quantify the accuracy of device design and fabrication for stakeholders. We are advancing two primary atomic-force microscopy systems. Critical-dimension atomic-force microscopy (CD-AFM) enables metrology of sidewall roughness, sidewall angle, and nanoscale width, depth, and height.
PDF Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) - nanoHUB The The microcantilevermicrocantilever--the force sensorthe force sensor. §From elementary beam theory, if E=Young's modulus, I=bh3/12 then. §δ=w(L)=F L3/(3EI), and θ=dw(L)/dx=FL2/(2EI) §Deflection and slope linearly proportional to force sensed at the tip. §k=3EI/L3is called the bending stiffness of the cantilever.
Automated structure discovery in atomic force microscopy Abstract. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) with molecule-functionalized tips has emerged as the primary experimental technique for probing the atomic structure of organic molecules on surfaces. Most experiments have been limited to nearly planar aromatic molecules due to difficulties with interpretation of highly distorted AFM images originating ...
PDF An Introduction to Atomic Force Microscopy Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is an imaging technique used to determine topography and other properties of surfaces. It is an important tool for nanoscience. Abstract Above - our AFM setup. A photodetector records the bending of the cantilever, which reflects the topography and other surface prop erties.
PDF Instrumentation Atomic Force Microscope Leuba, S. H. and Bustamante, C. Analysis of Chromatin by Scanning Force Microscopy. In Methods in Molecular Biology, Becker, P., Ed. 119, 143-160, 1999. piezo mirror cantilever laser AFM tip x y z photodiode position detector Dynamic mode amplitude of oscillation surface Contact mode surface The Atomic Force Microscope


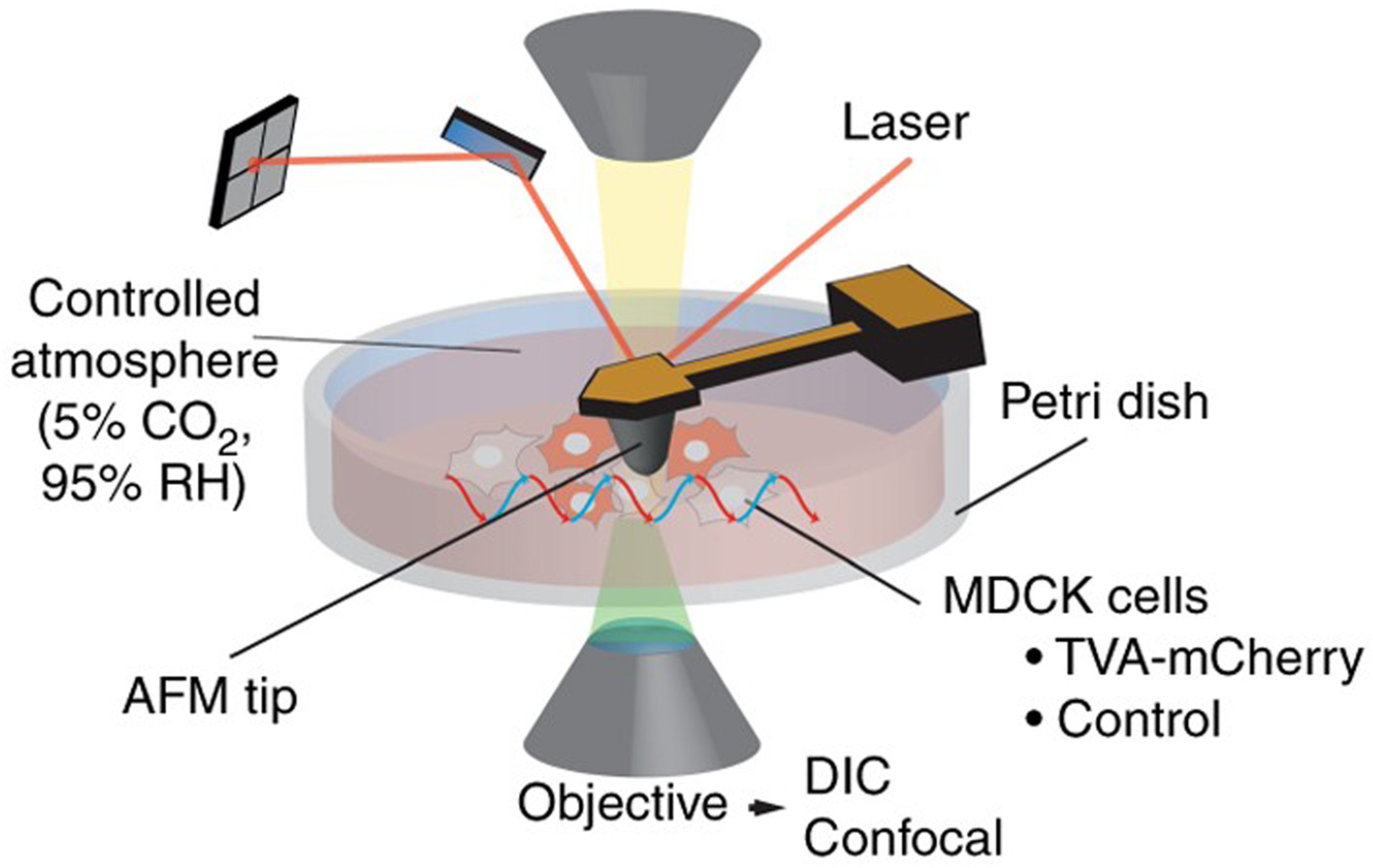

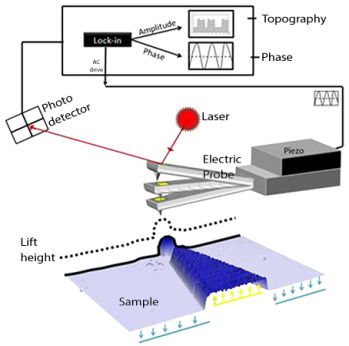
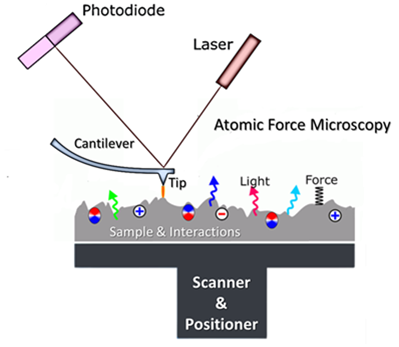
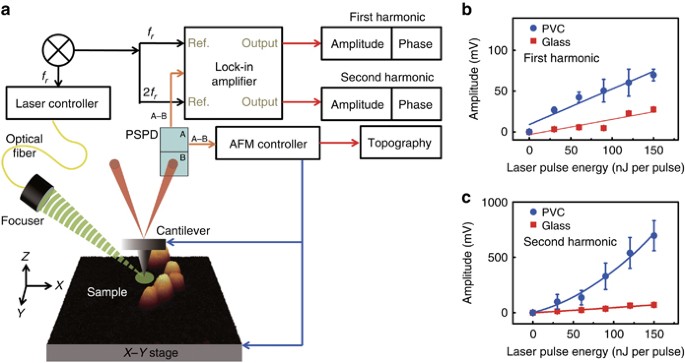



.jpg)








.jpg)


0 Response to "41 atomic force microscope diagram"
Post a Comment