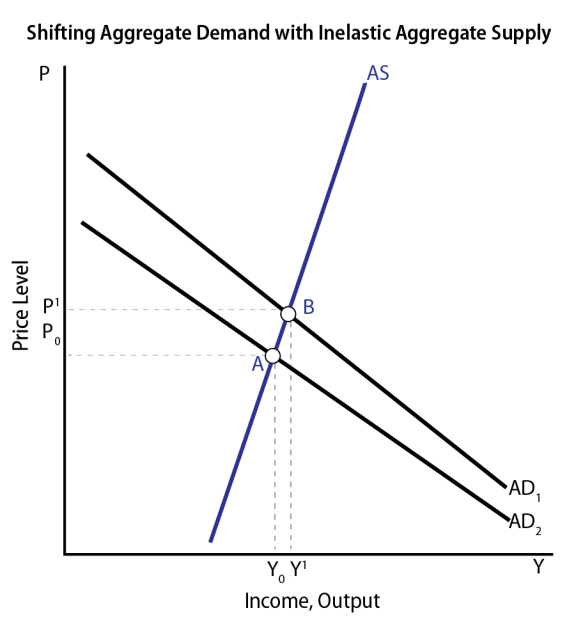
37 In A Diagram Of Aggregate Demand And Supply Curves, The Gdp Gap Is Measured As The
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves the GDP ... 26. In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the a) Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output. b) Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. AGGREGATE OUTPUT, PRICES AND ECONOMIC GROWTH - Coggle Diagram Inflationay gap: an increase in aggregate demand curve that results in an equilibrium at a level of GDP > than full employment GDP in the short run competition among producers for workers, raw materials and enery may shift the SRAS curve to the left , returning the economy to full employment GDP but at a price level that is higher
Chapter 11 - Macroeconomics Flashcards - Quizlet In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output If the recessionary GDP gap is $500, then the proper fiscal stimulus when faced with an upward-sloping AS curve is to Shift the AD curve rightward by more than $500

In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the gdp gap is measured as the
11.3 The Expenditure-Output (or Keynesian Cross ... - OpenStax The aggregate expenditure schedule shows how total spending or aggregate expenditure increases as output or real GDP rises. The intersection of the aggregate expenditure schedule and the 45-degree line will be the equilibrium. Equilibrium occurs at E0, where aggregate expenditure AE0 is equal to the output level Y0. The aggregate demand-aggregate supply (AD-AS) model ... Two axes: a vertical axis labeled "Price level" or "PL" and a horizontal axis labeled "real GDP." A downward sloping aggregate demand curve labeled "AD." An upward sloping short-run aggregate supply curve labeled "SRAS." - An equilibrium price level and real GDP. These should be labeled as indicated in the question. In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves the AD ... In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the AD shortfall is measured as the A . Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. B. Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output. C .
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the gdp gap is measured as the. Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply - CAS The Aggregate Demand Curve (AD) represents, in that sense, an even more appropriate model of aggregate output, because it shows the various amounts of goods and services which domestic consumers (C), businesses (I), the government (G), and foreign buyers (NX) collectively will desire at each possible price level. In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the AD ... In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the AD shortfall is measured as the: a. Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. b. Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output. c. Aggregate Demand Definition - investopedia.com Aggregate demand eventually equals gross domestic product (GDP) because the two metrics are calculated in the same way. As a result, aggregate demand and GDP increase or decrease together. Article ... Unit 15 Inflation, unemployment, and monetary policy - CORE In the boom shown, the upward shift in the aggregate demand curve reduces the unemployment rate, which in turn creates a bargaining gap of 1%. In the recession shown, the downward shift in the aggregate demand curve increases the unemployment rate, which in turn creates a bargaining gap of 0.5%.
28.4 Monetary Policy and Economic Outcomes - Principles of ... Figure 2. Expansionary or Contractionary Monetary Policy. (a) The economy is originally in a recession with the equilibrium output and price level shown at E 0.Expansionary monetary policy will reduce interest rates and shift aggregate demand to the right from AD 0 to AD 1, leading to the new equilibrium (E 1) at the potential GDP level of output with a relatively small rise in the price level. The Keynesian Theory Associated with this level of real GDP is an aggregate expenditure curve, AE 1. Now, suppose that autonomous expenditure declines, from A 1 to A 3, causing the AE curve to shift downward from AE 1 to AE 3. This decline in autonomous expenditure is also represented by a reduction in aggregate demand from AD 1 to AD 2. Aggregate Supply / Aggregate Demand Model Aggregate Demand Definition Aggregate demand is the demand of all products in an economy - OR the relationship between the Price Level and the level of aggregate output (real GDP) demanded. Be able to define: Aggregate Demand Real Domestic Output (RDO) which can be measured by real GDP real GDP Price Level Economic Growth | Explainer | Education | RBA Aggregate demand (AD), like GDP(E), refers to the total level of spending in the economy. Consequently, when aggregate demand is measured it is the same as GDP(E). Aggregate demand includes household spending (also called consumption, C), investment by businesses and households (I), spending by the government (G) and net spending from overseas ...
Aggregate demand - Economics Help Lower GDP, therefore consumers will have less money to spend. Fall in AD. In this diagram, we see a fall in AD. This causes a fall in real GDP and a fall in the price level (P1 to P2) In this diagram, the fall in AD has mainly caused a fall in the price level, with little change in real GDP. Components of AD. Components of aggregate demand as % How To Draw Inflation Adjustment Line? - lietaer.com Aggregate demand curves allow economic policymakers to observe each economy's demand at a specific price level for a specific amount of goods (and services) and services. Value measured by the level of actual GDP are taken as a horizontal axis to reflect the quantity of goods and services. Is Ia A Model? Solved In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves ... In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the: a. Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output. b. Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. What Is The Meaning Of The 45 Line In The 45 Line Diagram Whereas in the Keynesian cross model aggregate demand depended only on national income, now it depends as well on the interest rate. The interest rate is the cost of capital to the firm. What is equilibrium GDP? An economy is said to be at its equilibrium level of income when aggregate supply and aggregate demand are equal.
Aggregate Demand (AD) Curve - CliffsNotes An example of an aggregate demand curve is given in Figure . The vertical axis represents the price level of all final goods and services. The aggregate price level is measured by either the GDP deflator or the CPI. The horizontal axis represents the real quantity of all goods and services purchased as measured by the level of real GDP.
29 In A Diagram Of Aggregate Demand And Supply Curves The Gdp ... Dec 29, 2019 · In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves the gdp gap is measured at the horizontal distance between the equilibrium and the full employment output if the multiplier equals 2 and the ad shortfalls is 6 million then the desired fiscal stimulus is. In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves the gdp gap is measured as the. In a ...
Inflationary and Deflationary Gap (With Diagram) If aggregate demand exceeds the aggregate value of output at the full employment level, there will exist an inflationary gap in the economy. Aggregate demand or aggregate expenditure is composed of consumption expenditure (C), investment expenditure (I), government expenditure (G) and the trade balance or the value of exports minus the value of ...
Aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves (article ... Aggregate supply, or AS, refers to the total quantity of output—in other words, real GDP—firms will produce and sell. The aggregate supply curve shows the total quantity of output—real GDP—that firms will produce and sell at each price level. The graph below shows an aggregate supply curve.
24.2 Building a Model of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply The intersection of the aggregate supply and aggregate demand curves shows the equilibrium level of real GDP and the equilibrium price level in the economy. At a relatively low price level for output, firms have little incentive to produce, although consumers would be willing to purchase a high quantity.
Fiscal Policy Practice (test practice) Flashcards | Quizlet In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the GDP gap is measured as the A) Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. B) Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output.
PDF Chapter 33 Aggregate Demand And Aggregate Supply At Read PDF Chapter 33 Aggregate Demand And Aggregate Supply At ... production of the U.S. economy as measured by real GDP has grown by about __ percent per year. 3. Aggregate demand ... Indian Demand- Supply Gap ... Page 1/2. Read PDF Chapter 33 Aggregate Demand And Aggregate Supply At
How Are Aggregate Demand and GDP Related? Aggregate Demand and GDP GDP, AD, and Keynesian Economics Potential Issues Gross domestic product ( GDP) is a way to measure a nation's production or the value of goods and services produced in an...
The Model of Aggregate Demand and Supply (With Diagram) Aggregate Demand: The term aggregate demand (AD) is used to show the inverse relation between the quantity of output demanded and the general price level. The AD curve shows the quantity of goods and services desired by the people of a country at the existing price level. In Fig. 7.2 the AD curve is drawn for a given value of the money supply M.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the AD ... In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the AD shortfall is measured as the: (Points: 1) A - Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. B - Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output.
In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves the AD ... In a diagram of aggregate demand and supply curves, the AD shortfall is measured as the A . Vertical distance between the equilibrium price and the price at which the aggregate demand would intersect aggregate supply at full employment. B. Horizontal distance between the equilibrium output and the full-employment output. C .
The aggregate demand-aggregate supply (AD-AS) model ... Two axes: a vertical axis labeled "Price level" or "PL" and a horizontal axis labeled "real GDP." A downward sloping aggregate demand curve labeled "AD." An upward sloping short-run aggregate supply curve labeled "SRAS." - An equilibrium price level and real GDP. These should be labeled as indicated in the question.
11.3 The Expenditure-Output (or Keynesian Cross ... - OpenStax The aggregate expenditure schedule shows how total spending or aggregate expenditure increases as output or real GDP rises. The intersection of the aggregate expenditure schedule and the 45-degree line will be the equilibrium. Equilibrium occurs at E0, where aggregate expenditure AE0 is equal to the output level Y0.

0 Response to "37 In A Diagram Of Aggregate Demand And Supply Curves, The Gdp Gap Is Measured As The"
Post a Comment