37 which diagram shows a homologous chromosome pair that has homozygous alleles?
24. The diagram below shows two sets of homologous chromosomes in pea plants. The longer pair carries the gene for pea flower color, where P= purple and p= white. This pea plant is heterozygous, for pea flower color. a. In the figure above, write in the alleles for pea flower color on chromosome pair number one. b. A heterologous chromosome is a chromosome that contains different set of genes for a given trait. Homozygous means that the organism has two copies of the same allele for a gene. Heterozygous means that an organism has two different alleles of a gene.
Which diagram shows a homologous chromosome pair that has homozygous alleles? D Which is the cell structure that is made of DNA that gives the master instructions for the cell?
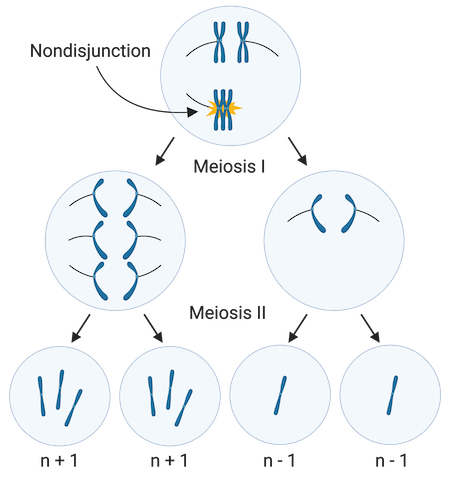
Which diagram shows a homologous chromosome pair that has homozygous alleles?
2.The diagram below represents a pair of homologous chromosomes. Which allelic combination represents the ... homozygous genes. ... gene-chromosome theory. 9.According to the gene-chromosome theory, the two alleles associated with a single trait are located at (1) corresponding positions on homologous chromosome (2) corresponding positions on ... The diagram shows a cell cycle. ... €€€€Figure 1 shows one pair of homologous chromosomes. ... The locus of this pair of alleles is shown in Figure 1 . Label two chromosomes on Figure 2 to show the location of the B allele and the location of the b allele. (1) It's really hard for me to grasp how autosomal or gonosomal inheritance would look like on a molecular DNA level. What is the difference between a recessive gene and a dominant gene DNA wise? And how does a gene "know" if it needs to be active or not.
Which diagram shows a homologous chromosome pair that has homozygous alleles?. We have been going in circles with this question. Our DNA has 2 copies of a gene, 1 on each chromosome. If you have an allele of a particular gene, would that mean you'd have 4 copies of the same gene? So confused. Help! Below is a picture of a karyotype, which is a graphic of sorted images showing every chromosome within a cell. Like the one below, most karyotypes show the homologous chromosomes next to each other. Realistically, unless they are lined up during cell division, these homologous chromosomes are randomly distributed throughout the nucleus. with the chromosomes of each homologous pair tangled together. There are thus four chromatids in each pair of chromosomes (N.B. and so only half as many 'sets' visible in diagrams). 2. Portions of each chromatid may break off and reattach to an adjacent chromatid on the homologous chromosome. The places Which diagram shows a homologous chromosome pair that has homozygous alleles? D Karyotypes can be studied to determine an organism's chromosomal makeup and to detect genetic defects.
loci on this pair of homologous chromosomes); same thing as three pairs of alleles (2) Medelian Genetics Genes Units of information about specific traits Passed from parents to offspring Each has a specific location (locus) on a chromosome Alleles Different molecular forms of a gene found on homologous chromosomes Arise by mutation I probably have a very wrong idea of how genome sequencing works, since I cannot find the answer to my question anywhere When we sequence our whole genome, we get some results like this: AATGCCCGAGAGCATTTC.. 1. From here, where is its complementary DNA strand's sequence? Is it simply now shown? 2. How do we know from what nucleotide to what nucleotide is chromosome 1,2,3, etc? 3. This is my biggest question. Where is the sequence of the homologous chromosome representednin this result? If ... So I'll give you a little backstory to help understand why it's such a mystery yet somehow I do know about it. When my mom and dad were pregnant with me in '89 my mom was in her later 30s and so for safety they had a prenatal screening done on me as a fetus. The results were abnormal and displayed a trisomy on one of my chromosome pairs. My mom was freaked out and quite frankly was opting for a possible abortion at that point since she wasn't ready to necessarily take care of a special needs c... A couple of homologous chromosomes, or homologs, are a set of one maternal and one paternal chromosome that pair up with each other inside a cell during fertilization.Homologs have the same genes in the same loci where they provide points along each chromosome which enable a pair of chromosomes to align correctly with each other before separating during meiosis.
Jun 12, 2018 · The right answer is C (see the images): An organism is heterozygous for a gene when it has two different alleles of that gene on the same locus for each of its homologous chromosomes. An allele is a variable version of the same gene or genetic locus, that is to say, a varied form that can be distinguished by variations in its nucleotide sequence. Alleles can exist in different forms and diploid organisms typically have two alleles for a given trait. These alleles are inherited from parents during sexual reproduction. Upon fertilization, alleles are randomly united as homologous chromosomes pair up. A human cell, for example, contains 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 chromosomes. Homozygous is a word that refers to a particular gene that has identical alleles on both homologous chromosomes. It is referred to by two capital letters (XX) for a dominant trait, and two lowercase letters (xx) for a recessive trait. My textbook is giving me two definitions **1st def**: "random orientation of homologous chromosomes at the metaphase plate in meiosis 1." **2nd def**: "alleles for one gene separate into gametes independently of alleles of any other gene (only if genes are on non-homologs or very far apart on same chromosome)." It seems to me that the 1st definition is talking about alleles on homologs themselves and how there's 50% chance that gamete will get paternal and maternal allele of a gene. And I'm g...
The following diagram depicts two diploid cells, one from a male and one from a female of the same species. In each cell, two pairs of homologous chromosomes are shown. The larger chromosomes have different alleles of Gene A, and the smaller chromosomes have different alleles of Gene B.
The statement that alleles on homologous chromosomes determine traits, correctly describes the mechanism of inheritance.; Homologous chromosomes are defined as a pair of chromosomes which have the genes arranged on them in the same order however the alleles may be different.; The chromosome pair of homologous chromosomes is formed because a diploid organism has one paternal and one maternal ...
Justin is looking at two chromosomes that have identical alleles for a particular trait. These chromosomes would be considered chromosomes. homozygous. Which diagram shows a homologous chromosome pair that has heterozygous alleles? C (Aa)
homozygous. Which is the cell structure that is made of DNA that gives the master instructions for the cell? chromosome. Which term describes the chromosomal abnormality of having three copies of a single chromosome? trisomy. Having the ability to roll or curl the tongue up along both sides to form a tube is a dominant trait.
Chromosomes Pre-Test answer keys. D (aa) Which diagram shows a homologous chromosome pair that has homozygous alleles? petit arm (short arm) Consider the chromosome. mc001-1.jpg.
[This](https://www.snpedia.com/index.php/Rs1801133\(T;T\)) is what I'm talking about. First let me say that I'm going to doc thursday to get blood levels of homocysteine, B12, and folate checked. But if they come back as expected (high homocysteine, low b12 and folate) I will start taking methylfolate. What scares me and what I also want to correct is: "Carriers of the MTHFR risk allele had detectable brain volume deficits, in the white matter, of up to 2–8% per risk T allele locally at baseli...
Since the Human CYP2D6 Isoform is the most important cytochrome p450-isoform in the synthesis of both serotonin and dopamine, through 5-methoxytryptamine O-demethylation for serotonin and hydroxylation of tyramine for dopamine, and I have null enzyme activity is this an avenue for exploration in why i might be experiencing treatment resistant depression for the last 2-3 years? It is certainly the reason for why none of the anti-depressants and ssri’s i tried over those 2ish years never gave any ...
Answer (1 of 2): Homologous chromosomes are pair of chromosomes obtained from each parent (male and female). The genes are similar in homologous chromosomes. · Alleles are alternate form of genes. · One form is designated as dominant and the other as recessive. If both alleles are same, i.e d...
Nov 27, 2017 · Homologous chromosomes are those chromosomes that are similar in length, centromere location and, gene position. The position of a gene on each homologous chromosomes are same, however, it may contain different alleles. One of the homologous pairs of a gene is derived from the mother and other from the father.
The Punnett square diagram shows all combinations of alleles that are inherited, and marks the resulting phenotype for eye color. Given that brown eye color is the dominant allele, and that 3 out of 4 possibilities result in at least one brown eye color allele being inherited, the probability that the offspring will have brown eyes is 75%.
* A) The crossover would have to occur between the A locus and the centromere and involve two homologous (non-sister) chromatids. * B) The crossover would have to occur between the A locus and the end of the chromosome and involve two homologous (non-sister) chromatids. * C) The crossover would have to occur on the same chromosome arm as the A locus and involve two homologous (non-sister) chromatids. * D) The crossover would have to occur on the same chromosome as the A locus and involve two hom...
Homologous chromosome pairs contain the same genes, but the alleles that each contains can differ. For example, the homologues of chromosome pair #1 may contain a gene for hair color, but that gene on the paternal homologue (the one you inherited from your father) may contain the allele for red hair, while the maternal homologue (that you ...
A plant geneticist has two pure lines, one with purple petals and one with blue. She hypothesizes that the phenotypic difference is due to two alleles of one gene. To test this idea, she aims to look for a 3 : 1 ratio in the $$ F_2. $$ She crosses the lines and finds that all the $$ F_1 $$ progeny are purple.
Genes for smooth wrinkled seeds are alleles of each other and occupy the same locus on homologous chromosomes. Homologous and Heterologous Chromosomes: The term homozygous and heterozygous were coined by Bateson and Saunders (1902) for the types of symbolised gene combinations.
[https://i.imgur.com/HWK4LdO.jpg](https://i.imgur.com/HWK4LdO.jpg) I'm going to be tutoring a grade 11 high school biology student in Canada forgive me for any limited understanding of genetics or biology , I have completed a minor in immunology, but I would like to still fill in any gaps in my understanding and I would like to be well-prepared to tutor the student I just wanted to understand/further elucidate: According to the very first imgur link , it shows two homologous chromosomes th...
What is the difference between homozygous and homologous? Homozygous individuals will have the same colour allele on a homologous pair of chromosomes, either RR or rr, and Heterozygous individuals will hold different alleles on a homologous pair of chromosomes like Rr. Let us discuss what these pairs are and the difference between them.
A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair comes from each gene. 6. A cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes is haploid. 7. The gametes of sexually reproducing organisms are haploid. 8. If an organism's haploid number is 6, its diploid number is 3. Phases of Meiosis
The genes are on different pairs of chromosomes. Allele A produces a pink anthocyanin pigment in the spines. Allele B has no effect by itself, but increases the colour produced by allele A to give red spines. Alleles a and b have no effect on spine colour. In the absence of anthocyanin, the spines are green.
Answers: 1 to question: Which diagram shows a homologous chromosome pair that has homozygous alleles? A chromosome is labeled Upper A a. A chromosome is labeled a a. 2 chromosomes are labeled Upper A and a. 2 chromosomes are labeled a and a.
The cells in diploid organisms contain sets of homologous chromosomes, which are paired chromosomes that have the same genes at the same positions along each chromosome pair. Although homologous chromosomes have the same genes, they may have different alleles for those genes. Alleles determine how particular traits are expressed or observed.
thank you for your time and help
Doesn't make any sense because when the chromosome is separated during Anaphase I, it takes both genes with it (like linked genes). So how does that mean independent assortment of the two genes?
The image below shows a simple organism. This organism is diploid, but only has a 1 pair of chromosomes. These are homologous chromosomes, because they carry the same genes. However, they can carry different alleles of each gene, shown by their internal pattern. This organism can reproduce asexually, simply by duplicating the DNA and dividing ...
Like, for example, the tall gene in tomato plants that causes the expression of a more effective giberrellin- wouldn't having twice the amount of the hormone that makes the plant tall result in a taller tomato plant? Are plants that are homozygous for the tall gene taller than heterozygous plants? This is a simple example to try to explain what my question is, but I'm really thinking about human enzymes. If having increased amounts of vitamins can make such a difference in energy levels, etc, ho...
Just wanting to check whether I'm understanding this correctly. A diploid cell (which resulted from mitosis) has two pairs of each of the 23 types of chromosomes, and a haploid cell (from meiosis) has only one chromosome of each of the 23 types, is that correct? Any help is appreciated!
It's really hard for me to grasp how autosomal or gonosomal inheritance would look like on a molecular DNA level. What is the difference between a recessive gene and a dominant gene DNA wise? And how does a gene "know" if it needs to be active or not.
The diagram shows a cell cycle. ... €€€€Figure 1 shows one pair of homologous chromosomes. ... The locus of this pair of alleles is shown in Figure 1 . Label two chromosomes on Figure 2 to show the location of the B allele and the location of the b allele. (1)
2.The diagram below represents a pair of homologous chromosomes. Which allelic combination represents the ... homozygous genes. ... gene-chromosome theory. 9.According to the gene-chromosome theory, the two alleles associated with a single trait are located at (1) corresponding positions on homologous chromosome (2) corresponding positions on ...
0 Response to "37 which diagram shows a homologous chromosome pair that has homozygous alleles?"
Post a Comment