41 ethene molecular orbital diagram
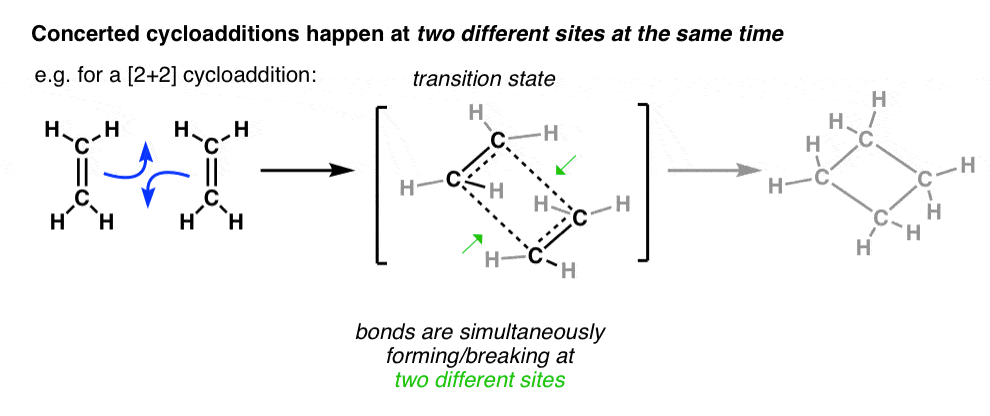
also intraorbital, 1836, from intra- "within" + orbit (n.) + -al (1). Additionally, as the molecular orbitals don't have matching symmetries, one of the ethene molecules needs to be excited by UV light, so one electron can enter the pi* orbital. So basically the HOMO of excited ethene A (pi*) and the LUMO of ethene B (also pi*)can form two sigma bonds needed for the cyclobutane, in addition to the already ...
1540s, "of or pertaining to the eye socket;" 1839 with reference to heavenly bodies; from orbit (n.) + -al (1).
Ethene molecular orbital diagram
The other sp2 hybrid orbitals form sigma bonds between C and H, therefore, leading to C-H single bonding structure. C2H4 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram. The molecular orbital theory is a concept of quantum mechanics where atomic linearly combines to form molecular orbitals and we describe the wave nature of atomic particles. Construct the molecular-orbital energy level diagrams of (a) ethene and (b) ethyne on the basis that the molecules are formed from the appropriately hybridized CH2 or CH fragments. (For clarity, you may omit the orbitals involved in the carbon-hydrogen bonds and only show the orbitals involved in the carbon-carbon bonds.) Ethene vs. ammonia. Postby Ella Bogomilsky 2B » Mon Nov 15, 2021 3:09 am. In ammonia, the 5 valence electrons on nitrogen all go into the hybridized orbitals. In ethene, the 4 valence electrons on carbon go into the hybridized orbitals, and one goes into the unhybridized p orbital. Why does this happen?
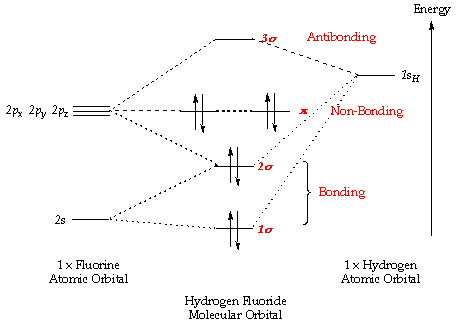
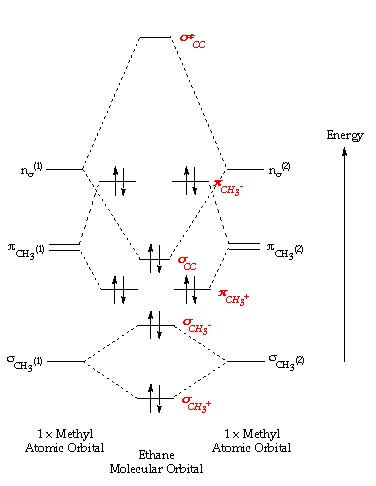
Ethene molecular orbital diagram. The hybrid orbitals are more prominent outward so that their ability to overlap is stronger than that of normal orbitals. Molecular Formula: A chemical formula is a brief way of expressing the number and type of atoms that make up a particular chemical compound. Here one s orbital and two p orbitals of C-atom undergo sp 2 hybridization forming a total of three sp 2 orbitals.The third 2p orbital remains unhybridised. In ethene the two carbon atoms form a σ bond by overlapping one sp 2 orbital from each carbon atom. The π bond between the carbon atoms perpendicular to the molecular plane is formed by unhybridized 2p z -2p z overlap. The molecular orbital is formed from the combination of atomic orbitals, which must have nearly the same energy and are symmetrical about the molecular axis. To understand the MO diagram of ethane, we consider it as a homonuclear diatomic A2 molecule. Molecular orbital s of H. The simplest neutral molecule is molecular hydrogen, H 2, which consists of two electrons and two protons. The molecular orbital Hamiltonian in this case is the same as it is for the molecular hydrogen ion and the molecular orbital s are the same as for the molecular ion. H H2 mo =− ℏ2 2me ∇2− e2 4πϵ0|. Hi ...
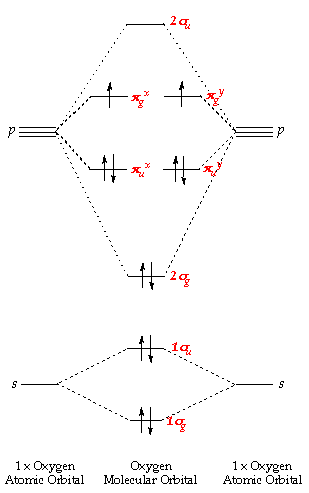
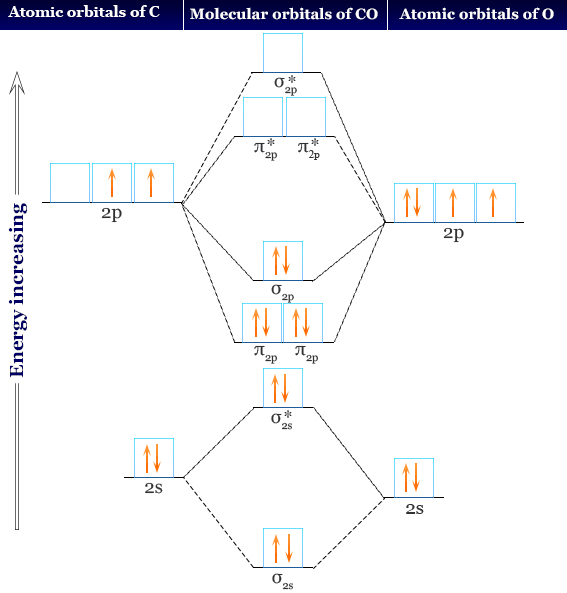
A molecular orbital diagram for oxygen may be seen by Clicking Here. A cartoon of the p and π orbitals of a double bond may be examined by Clicking Here. A model of the π orbitals of ethene may be examined by Clicking. FREE Expert Solution. We're being asked to complete the molecular orbital diagram of CN- and then determine the bond order. Molecular orbitals are obtained by combining the atomic orbitals on the atoms in the molecule. One of the molecular orbitals in this molecule is constructed by adding the mathematical functions for the two 1s atomic orbitals that come together to form this molecule. ... The π orbital of ethylene has two orbital lobes (one shown in the red and ... 21.E: Resonance and Molecular Orbital Methods (Exercises) Exercise 21-1 Determine which of the following structures can be represented by one or more specific electron-pairing schemes similar to the Kekulé structures of benzene: Exercise 21-2 Calculate the heat of formation of 1,3-butadiene in the gas phase at 25o from the bond energies in ... We start with two atomic orbitals: one unhybridized 2p orbital from each carbon. Each contains a single electron. In MO theory, the two atomic combine ...
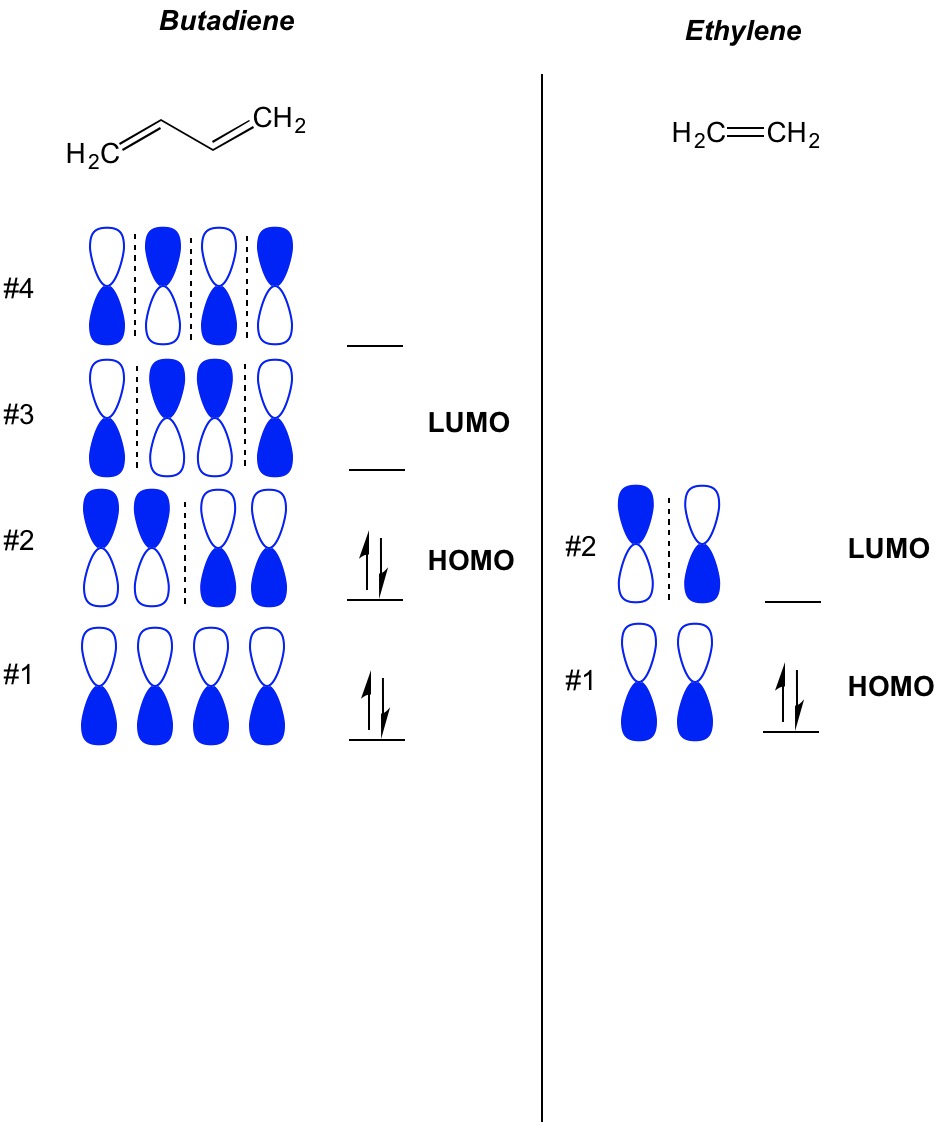
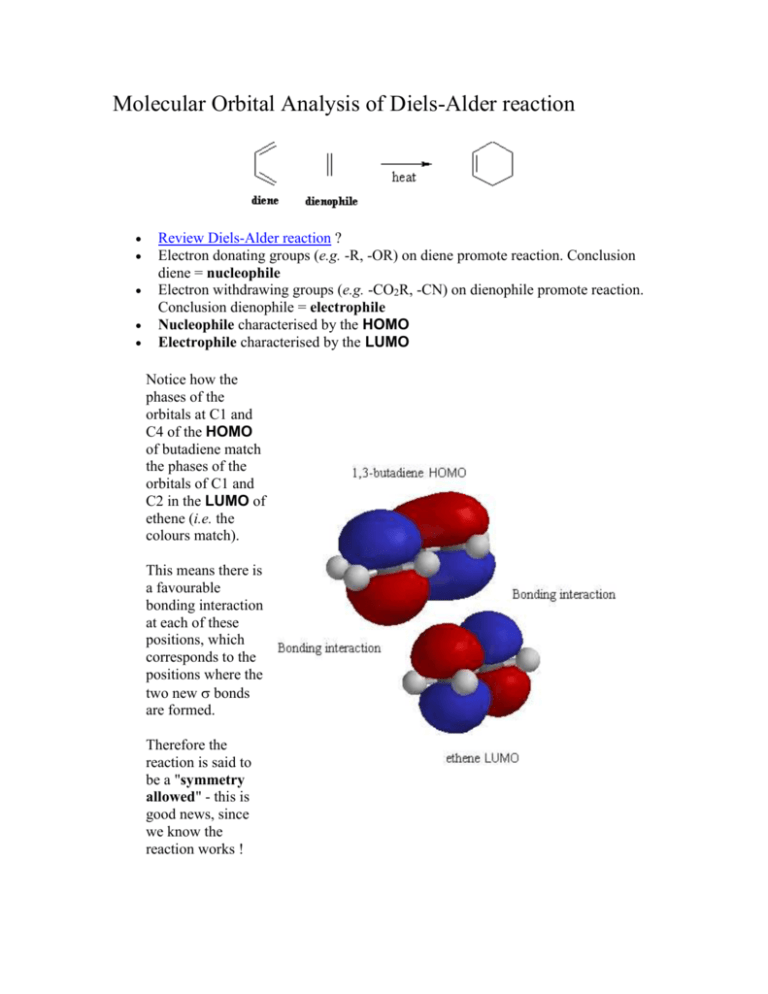
"the property of certain compounds by virtue of which they differ in molecular weight and chemical properties though formed from the same elements in the same proportion," 1866, from polymer + -ization. Molecular Orbitals - Double Bonds, Ethene. Electronic Configuration of Atoms (Part 1) Next Top. ABPI. The Association of the British Pharmaceutical. Industry is a company limited by guarantee registered. in England and Wales(registered number 09826787) 7th Floor Southside, ... For the ethene orbital energy diagram these are shown as pCC for the HOMO, and p*CC for the LUMO. An important property of the ethene molecule, and alkenes ... Molecular Orbital Analysis of Ethene Dimerisation the reaction is said to be a "symmetry forbidden" – interestingly, this reaction is rare and very slow !24 pages
"relating to or consisting of molecules," by 1815, from molecule + -ar or else from French moléculaire or Modern Latin molecularis. Molecular biology is attested by 1950.
1610s, "an illustrative figure giving only the outlines or general scheme of the object;" 1640s in geometry, "a drawing for the purpose of demonstrating the properties of a figure;" from French diagramme, from Latin diagramma "a scale, a musical scale," from Greek diagramma "geometric figure, that which is marked out by lines," from diagraphein "mark out by lines, delineate," from dia "across, through" (see dia-) + graphein "write, mark, draw" (see -graphy). Related: Diagrammatic; diagrammatically. The verb, "to draw or put in the form of a diagram," is by 1822, from the noun. Related: Diagrammed; diagramming.
Q.2. The outer orbitals of C in ethene molecule can be considered to be hybridized to give three equivalent sp² orbitals. The total number of sigma (s) and pi (p) bonds in ethene molecule is (a) 1 sigma (s) and 2 pi (p) bonds (b) 3 sigma (s) and 2 pi (p) bonds (c) 4 sigma (s) and 1 pi (p) bonds (d) 5 sigma (s) and 1 pi (p) bonds
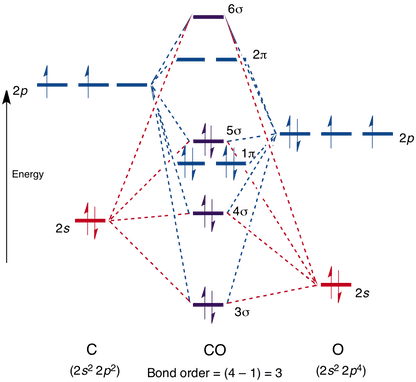
Answer: a. Explanation: When a molecule's bond order is equal to zero, the molecule cannot exist. The formula for finding out bond order is \ (\frac {1} {2}\) (NB - NA). So NA - NB = 0, that is NA = NB. Where NA as the number of anti-bonding molecular orbitals and NB as the number of bonding molecular orbitals. 3.
1868, from normal (in reference to molecular structure) + epinephrine.
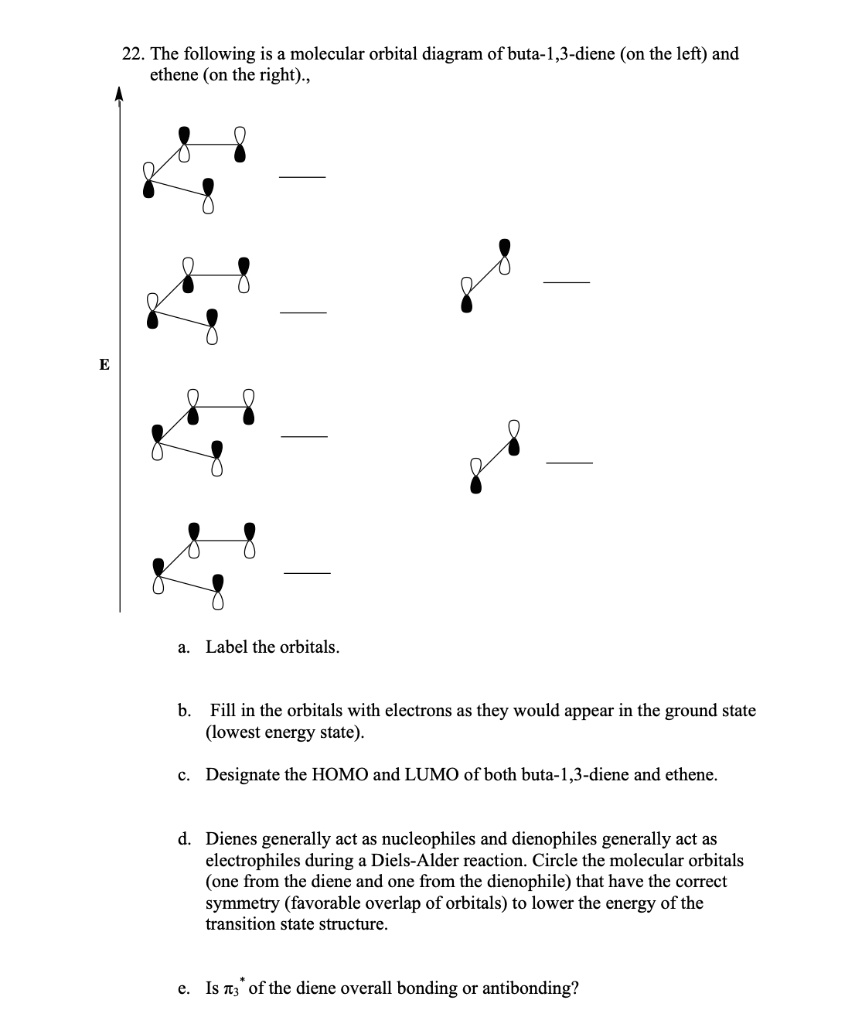
To treat the π -electron system of 1,3-butadiene by simple MO theory, we combine the four p carbon orbitals of an atomic-orbital model, such as 17, to obtain four molecular orbitals: Figure 21-8). Therefore the delocalization energy is ( 4 α + 4.48 β) − ( 4 α + 4 β) = 0.48 β or 9 kcal, assuming that β = 19 kcal.
How to draw Molecular orbital Diagram for Fluorine. How to draw Molecular Orbital Diagram of N2 . How to draw molecular orbital diagram for oxygen atom / ion . How to draw molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen. How to draw molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen and helium. Difference between the Molecular orbital structure of ethene and ethyne
Ethane Formula: We all know that natural gas used as fuel for warming up our homes and for cooking, consists of methane, but do we know Ethane also forms a part of this natural gas. It is the second-largest percentage in natural gas. Ethane is a colourless, odourless, and flammable gas with a chemical formula of \({{\rm{C}}_2}{{\rm{H}}_6}\). CLEAR YOUR CONCEPTUAL DOUBTS ON ETHANE
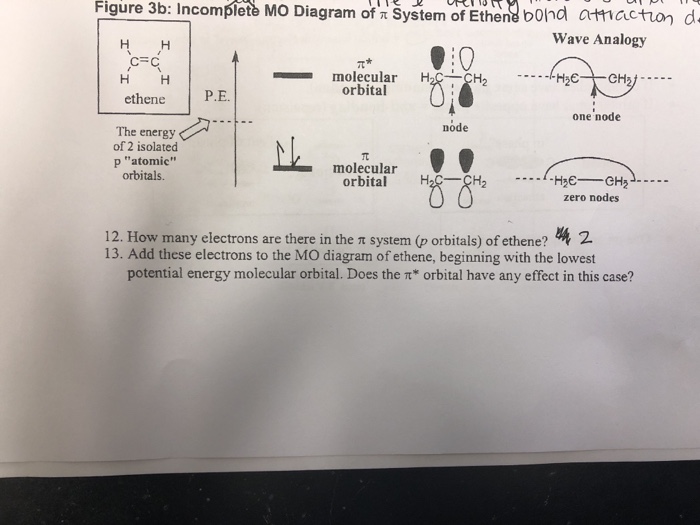
Molecular orbitals for ethene (ethylene) In the bonding pi orbital, the two shaded lobes of the p orbitals interact constructively with each other, as do the two unshaded lobes (remember, the arbitrary shading choice represents mathematical (+) and (-) signs for the mathematical wavefunction describing the orbital).
"pertaining to schemes," 1701, from Latin stem of scheme (n.) + -ic. Noun meaning "diagram" is first attested 1929. Related: Schematical (1670s).
Pi Molecular Orbitals of Ethylene ... In ethylene there are two adjacent carbon atoms involved in the pi system and the combination of a p orbital from each of ...
Figure 7.3. 1: Bonding in Ethylene. (a) The σ -bonded framework is formed by the overlap of two sets of singly occupied carbon sp2 hybrid orbitals and four singly occupied hydrogen 1 s orbitals to form electron-pair bonds. This uses 10 of the 12 valence electrons to form a total of five σ bonds (four C-H bonds and one C-C bond).
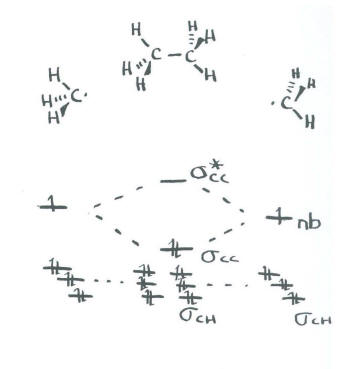
ular orbitals (SOMOs) and orbitalrelaxation (i.e.,charge trans-fer and polarization). Figure 1. a) sp3-, sp2-, and sp-hybridizedC@Hbonds of ethane, ethene, and ethyne, and b) sp3-, sp2-, and sp-hybridized C@Cbonds of propane,propene, and propyne, where the bond of interest is showninblack (sp3), blue (sp2), and red (sp). c) Schematic molecular ...
c) Schematic molecular orbital diagram of the formation of a generic R n C−X electron-pair bond and interaction with a closed-shell orbital that leads to (steric) Pauli repulsion. Not unexpectedly, our DFT computations reproduce the aforementioned trend of a shortening of the C−H and C−C bond lengths as we go along sp 3 to sp 2 to sp ...
The diagram to the right shows the relative energies of the atomic p orbitals, the resulting π molecular orbitals and the electron configuration. (The same ...
Re: Ethene sp^2 Hybridization. A good bookkeeping strategy would be to acknowledge the number of regions of electron density around an atom. In your case for ethene, , a carbon atom has three regions of electron density (a single bond, a single bond, and a double bond). Since there are three regions of electron density, if we were to apply ...
also sub-orbital, 1803 of the eye; 1959 of a planet, from sub- + orbital (adj.). Related: Suborbitally.
Example: Cyclohexane. Create models of aromatic molecules. Example: Benzene. Display Surface topology of molecules. Example: Molecular surface and Dot surface. Create models of Atomic orbitals s, p, d and f. Create models of Molecular Orbitals sp3, sp2 and sp. Create molecular orbitals for methane molecule. Create molecular orbitals for ethene ...
Molecular orbitals like atomic orbitals obey Aufbau principle for filling of electrons. Answer: C ( Bonding molecular orbital has higher energy than antibonding molecular orbital. Question 26: The conditions for the combination of atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals are stated below.
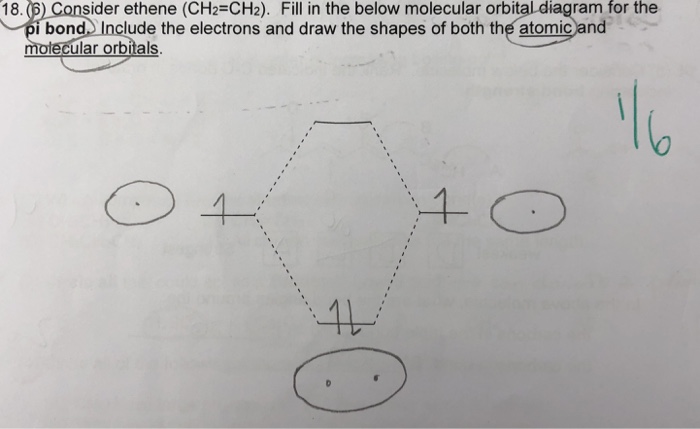
Sigma (σ) bonding molecular orbital - Shared electron density is directly between ... Problem 6 – Use ethene (H2C=CH2) as a model to draw an MO diagram for ...13 pages
Draw a complete MO diagram for all the bonds in ethene. What can we say, at this point, about the relative energy levels of the orbitals in this molecule ...40 pages
unit of molecular quantity, 1902, from German Mol coined 1900 by German chemist Wilhelm Ostwald, short for Molekül (see molecule).
Figure 10.5.5 : Schemetic representation of the \(\pi\) molecular orbitals framework for ethylene . Notice that the antibonding molecular orbital has one more node than the bonding molecular orbital as expected since it is higher in energy.
Ethylene is the simplest molecule that has a double bond. As we saw from the valence bond model, we should find the presence of a σ-bond framework, ...
C2H4 Lewis Structure, Molecular Structure, Hybridization, Bond Angle and Shape. The chemical formula C2H4 represents Ethylene. This molecule is also represented by H2C=CH2, clearly showing the alkene nature of the compound. An alkene is a hydrocarbon with a Carbon-Carbon double bond. C2H4 exists as a colorless gas and is flammable.
b) A molecular orbital is singly occupied. c) An example is oxygen molecule. d) Repelled by the magnetic field. Answer: Repelled by the magnetic field. 48. Combination of two atomic orbitals results in the formation of two molecular orbitals namely. a) one bonding and one non-bonding orbital. b) two bonding orbitals. c) two non-bonding orbitals
Molecular orbital theory. How to draw Molecular orbital Diagram for Fluorine. How to draw molecular orbital diagram for oxygen atom / ion . How to draw molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen. How to draw molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen and helium. Difference between the Molecular orbital structure of ethene and ethyne
1918 (Venn's diagram is from 1904), named for English logician John Venn (1834-1923) of Cambridge, who explained them in the book "Symbolic Logic" (1881).
Ethene vs. ammonia. Postby Ella Bogomilsky 2B » Mon Nov 15, 2021 3:09 am. In ammonia, the 5 valence electrons on nitrogen all go into the hybridized orbitals. In ethene, the 4 valence electrons on carbon go into the hybridized orbitals, and one goes into the unhybridized p orbital. Why does this happen?
Construct the molecular-orbital energy level diagrams of (a) ethene and (b) ethyne on the basis that the molecules are formed from the appropriately hybridized CH2 or CH fragments. (For clarity, you may omit the orbitals involved in the carbon-hydrogen bonds and only show the orbitals involved in the carbon-carbon bonds.)
The other sp2 hybrid orbitals form sigma bonds between C and H, therefore, leading to C-H single bonding structure. C2H4 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram. The molecular orbital theory is a concept of quantum mechanics where atomic linearly combines to form molecular orbitals and we describe the wave nature of atomic particles.













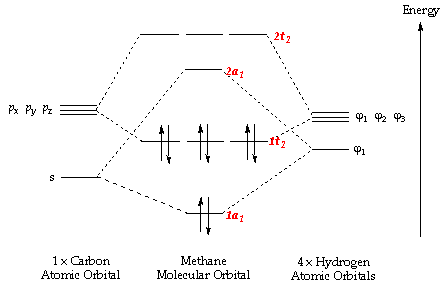

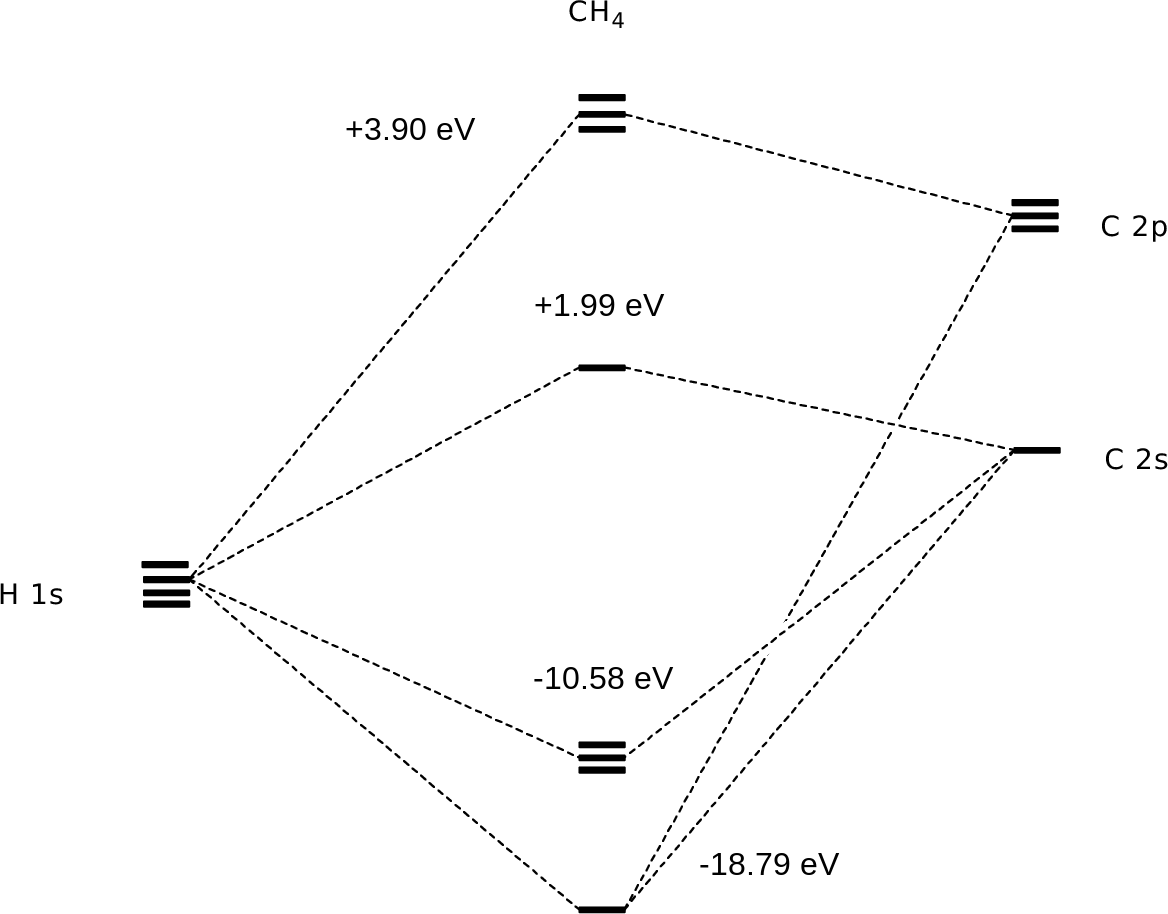

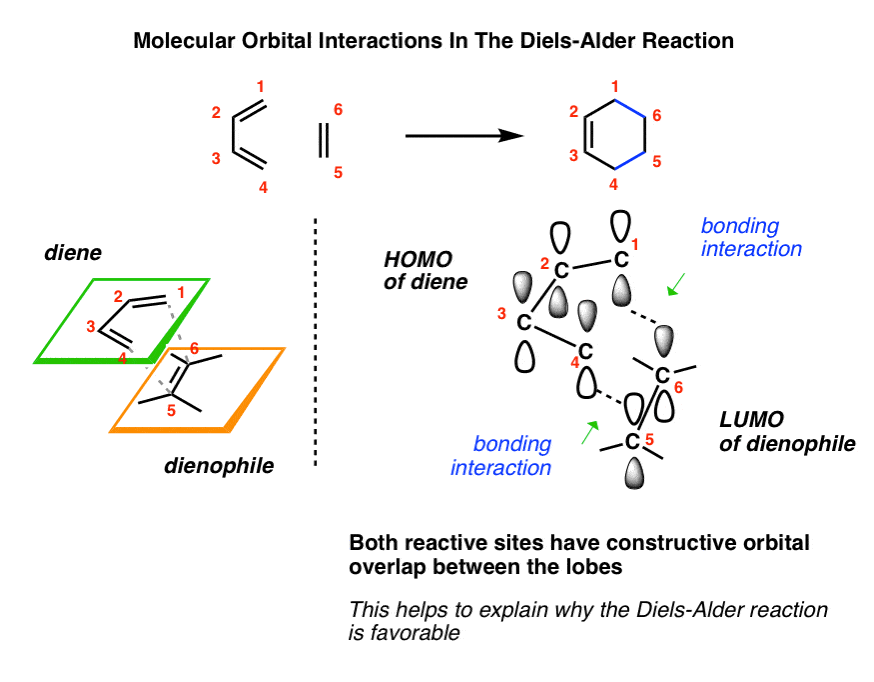

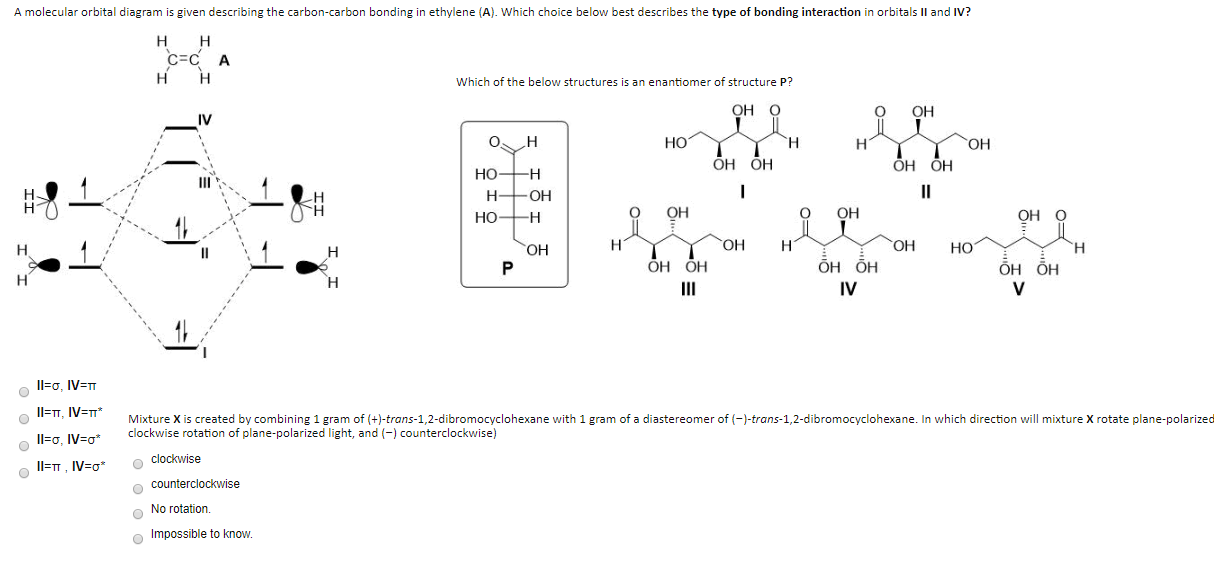
0 Response to "41 ethene molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment