36 salt dissolving in water diagram
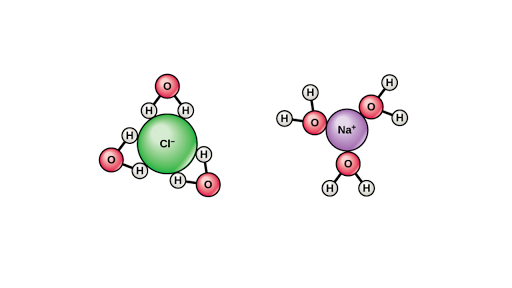
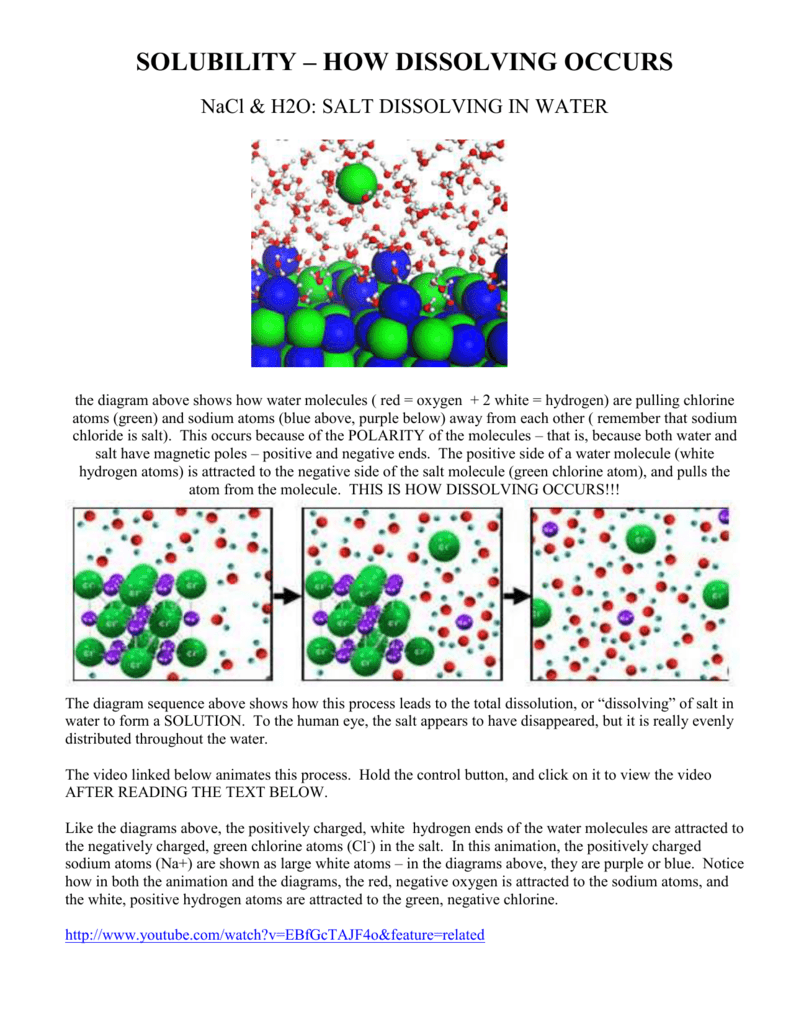
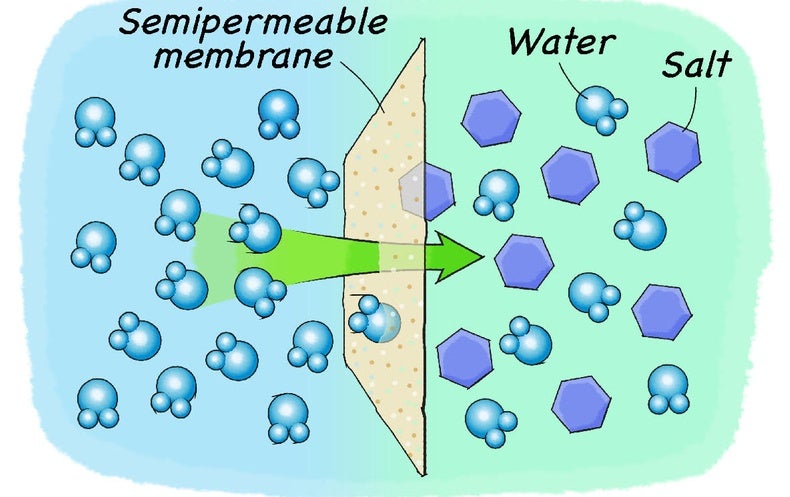
Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution. Salt such as sodium chloride dissolving in water has been considered to be an endothermic reaction. An enthalpy diagram for this process is shown below. Here, in order to break down a lattice and ...
Therefore, more sugar than salt can dissolve in a volume of water at a specific temperature. You can speed up dissolving a solid by: Heating up the solvent. The solubility of a solid solute ...
Salt dissolving in water diagram
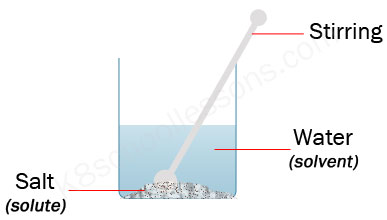
Measure out a fixed amount of water (e.g., 1 liter). Add salt one gram at a time, stirring until it completely dissolves. Repeat until no more will dissolve. With table salt and pure water, you should get around 350-360 grams of salt per liter of water to dissolve. Thanks! Dissolving a Salt Crystal: When an ionic crystal such as NaCl is placed in water, a dissolving reaction will occur. Initially, the positive and negative ion are only attracted to each other. The water molecules are hydrogen bonded to each other. If the crystal is to dissolve, these bonds must be broken. Cool water molecules are tighter together and will not allow much salt to dissolve. PROCEDURE: Students will make salt from water. In this lab ordinary table salt will be used, but in reality the "salt" in salt water consists of various other compounds as will be discussed in the post lab. Water can just take so much salt. Have the students ...
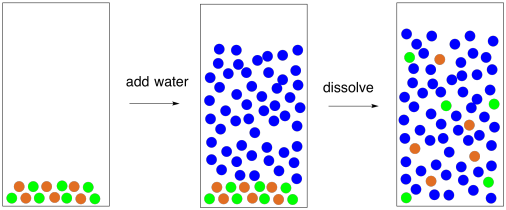
Salt dissolving in water diagram. A salt is soluble if it dissolves in water to give a solution with a concentration of at least 0.1 moles per liter at room temperature. A salt is insoluble if the concentration of an aqueous solution is less than 0.001 M at room temperature. Slightly soluble salts give solutions that fall between these extremes. Students will make a 2-D model of a salt crystal and use water molecule cut-outs to show how water dissolves salt. After seeing an animation of water dissolving salt, students will compare how well water and alcohol dissolve salt. They will relate their observations to the structure of salt, water, and alcohol on the molecular level. Objective To illustrate the point the solubility diagram for a single salt, such as potassium nitrate, is shown in Fig. 1. In this diagram, the solubility of the salt in water is given by its concentration expressed in molality (mol/kg solvent, where the solvent is water) on the ordinate axis as a function of temperature on the abscissa axis. The black ... Dissolving is an example of a reversible change. For example, when salt is mixed with water it disappears because it dissolves in the water to make salty water. But we can get the salt can back again by boiling off the water. Substances that dissolve in water are called soluble substancesOct 27, 2020.
Weigh out ~5 grams of ammonium nitrate. Record the weight of the salt. Add the salt to the water and stir to dissolve—use a stirring rod, not the thermometer to stir. Observe the temperature changes over time that occur while the salt dissolves. Record the highest or lowest temperature observed as the final temperature. Let's take the lines one at a time. The first one to look at is the one in bold green in the next diagram. This line represents the effect of increasing amounts of salt on the freezing point of water. Up to the point where there is 23.3% of salt in the mixture, the more salt the lower the freezing point of the water. Therefore, dissolving salt in water is a chemical change. The reactant (sodium chloride, or NaCl) is different from the products (sodium cation and chlorine anion). Thus, any ionic compound that is soluble in water would experience a chemical change. In contrast, dissolving a covalent compound like sugar does not result in a chemical reaction. Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution. Find out more. Adhesion/cohesion
After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution. Why is it that the dissolved salt in the water formed into salt again? Explain that as the water evaporates, water molecules go into the air. The water molecules that evaporate become a ... Answer (1 of 3): Actually, the volume decreases instead of increase (that is the intuitive result) and, makes your water super cold. LOL, right? How it works. NaCl (salt), when dissolved in water, breaks apart into two ions that I won´t write here because since I can´t format properly, they will... In the case of table salt mixed with water, Na and Cl atoms, initially bonded together in the form of a crystal, are dissolved by molecules of water. Water is a solvent. The reasons are electrostatic in nature. The cohesion of atoms and molecules derive from electrostatic links between particles that are charged or polar. Sodium chloride (NaCl) is in fact the joining of an Na+ ion and a Cl ... Explain to students that water molecules attract the sodium ions (positive) and chloride ions (negative) and pull them away from the salt crystal. The water ...18 Aug 2020 · Uploaded by American Chemical Society
Answer: Unlike what we might expect, dissolving table salt in water decreases the volume of the mixture. We have to analyse this from a micro point of view to understand this. Above is a diagram showing the general structure of water molecules in a body of water (in liquid state), the red sphe...
When table salt, sodium chloride, dissolves in water, it dissociates into its respective cations and anions, Na+ and Cl-. How does water stabilize the Na+?
Sodium chloride (NaCl) dissolves when water molecules continuously attack the NaCl crystal, pulling away the individual sodium (Na +) and chloride (Cl -) ions. This nonstop attack continuous until the whole NaCl crystal disintegrates. To understand this process at the molecular level, we must apply the three steps we previously discussed.
Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution.
If you mix two substances and the result is a homogeneous mixture, you are dealing with a solution. In the case of table salt mixed with water, Na and Cl atoms, initially bonded together in the form of a crystal, are dissolved by molecules of water. Water is a solvent. The reasons are electrostatic in nature. The cohesion of atoms and molecules derive from electrostatic links between particles ...
combining different amounts of the salt in similar amounts of water and heating the solutions until all of the solute completely dissolves. Once the solid is dissolved, the solution will be constantly stirred and allowed to cool until the temperature is low enough for the solution to become saturated.
In salt solution, salt is the solute. A solvent. is the substance that does the dissolving – it dissolves the solute. In salt solution, water is the solvent. During dissolving, particles of ...
A) coffee brewing B) water boiling C) leaves turning color in the fall D) salt dissolves in water E) None of the above are chemical changes. A physical change A) occurs when iron rusts. B) occurs when sugar is heated into caramel.
Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution.
Therefore, dissolving salt in water is a chemical change. The reactant (sodium chloride, or NaCl) is different from the products (sodium cation and chlorine anion). Thus, any ionic compound that is soluble in water would experience a chemical change. In contrast, dissolving a covalent compound like sugar does not result in a chemical reaction.
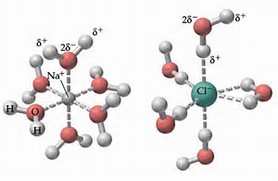
Figure 11.4. 1: The hydration of (a) a positive ion; (b) a negative ion. When ions are dissolved in water, they attract and hold several water dipoles around them shown in the circular area in the circular area in the center of each part of the diagram. The resolution of this apparent paradox lies in the interactions between ions and the ...
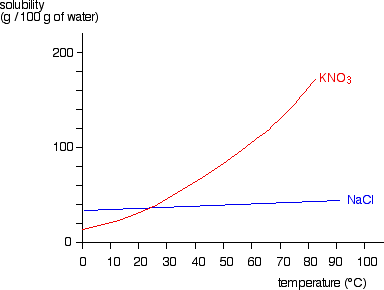
This page looks at the phase diagram for mixtures of salt and water - how the diagram is built up, and how to interpret it. It includes a brief discussion of solubility curves. Important: This page is only really designed to be an introduction to the topic suitable for courses for 16 -18 year olds, such as UK A level chemistry. If you have come to this page straight from a search engine, it ...
Water molecules pulling apart the ions (sodium and chloride) in a salt crystal, and then dissolving the salt. ... Water molecules pulling apart the ions (sodium and chloride) in a salt crystal ...
Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution.
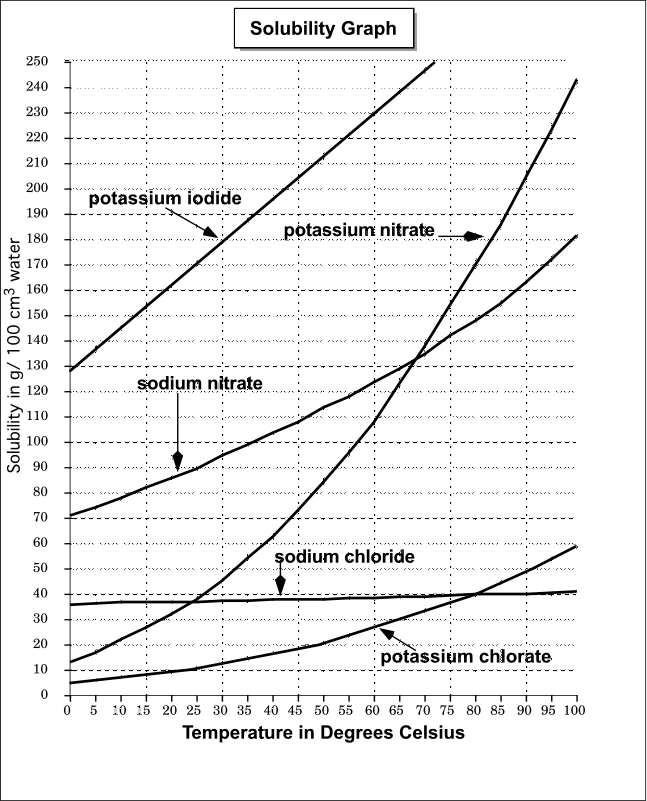
Solubility Diagram. Show all questions. 1 / 12. At approximately what temperature does the solubility of sodium chloride, NaCl, match the solubility of potassium dichromate, K 2 Cr 2 O 7? 83 ºC. 60 ºC. 50 ºC. 30 ºC. Which salt is LEAST soluble at 0 ºC?
We will first examine the process that occurs when an ionic compound such as table salt (sodium chloride) dissolves in water. Water molecules move about ...
crystals being stirred until they dissolve in the water. The end result is a solution, as all parts of the soft drink mixture look the same. Figure 8.11 is a particle diagram of wa ter particles surrounding salt particles. It illustrates how salt particles dissolve more quickly in water that is stirred compared to salt
The saturation level is only nominally dependent on the temperature of the water. At 20 °C one liter of water can dissolve about 357 grams of salt, a concentration of 26.3% w/w. At boiling (100 °C) the amount that can be dissolved in one liter of water increases to about 391 grams, a concentration of 28.1% w/w.
Cool water molecules are tighter together and will not allow much salt to dissolve. PROCEDURE: Students will make salt from water. In this lab ordinary table salt will be used, but in reality the "salt" in salt water consists of various other compounds as will be discussed in the post lab. Water can just take so much salt. Have the students ...
Dissolving a Salt Crystal: When an ionic crystal such as NaCl is placed in water, a dissolving reaction will occur. Initially, the positive and negative ion are only attracted to each other. The water molecules are hydrogen bonded to each other. If the crystal is to dissolve, these bonds must be broken.
Measure out a fixed amount of water (e.g., 1 liter). Add salt one gram at a time, stirring until it completely dissolves. Repeat until no more will dissolve. With table salt and pure water, you should get around 350-360 grams of salt per liter of water to dissolve. Thanks!

















0 Response to "36 salt dissolving in water diagram"
Post a Comment