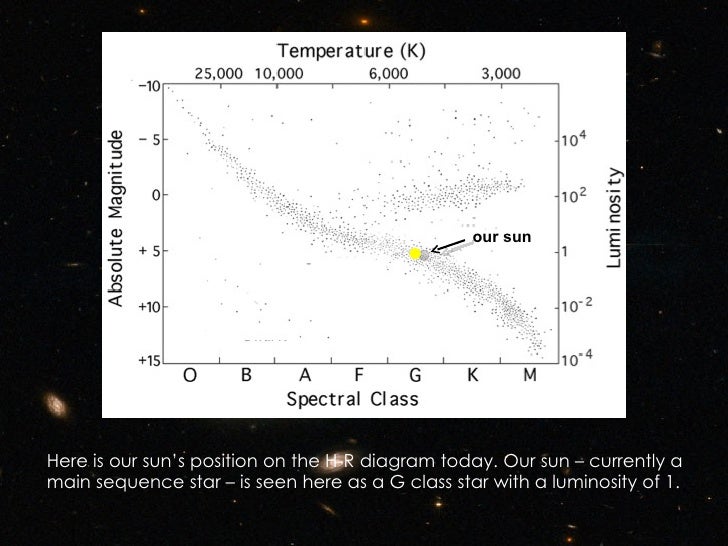
37 our sun on the hr diagram
Lets do an example and calculate the Sun's radius. Looking at the HR Diagram, we see that the Sun's luminosity is 1 L⊙ = 3.85 x 10 26 Watt and its temperature is approximately 6,000 K. To calculate its radius, we use EQ #2: 4 T4 L R R 4.17 1017 m2 R 6.46 108 m Now convert the radius from units of m to units of solar radius: How to Read the H-R Diagram. On plotting a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, the region occupied by most stars in the diagram is along a line. This line is referred to as the main sequence. The second-most concentration of stars is along a horizontal branch. Our Sun lies somewhere at the middle of the graph.
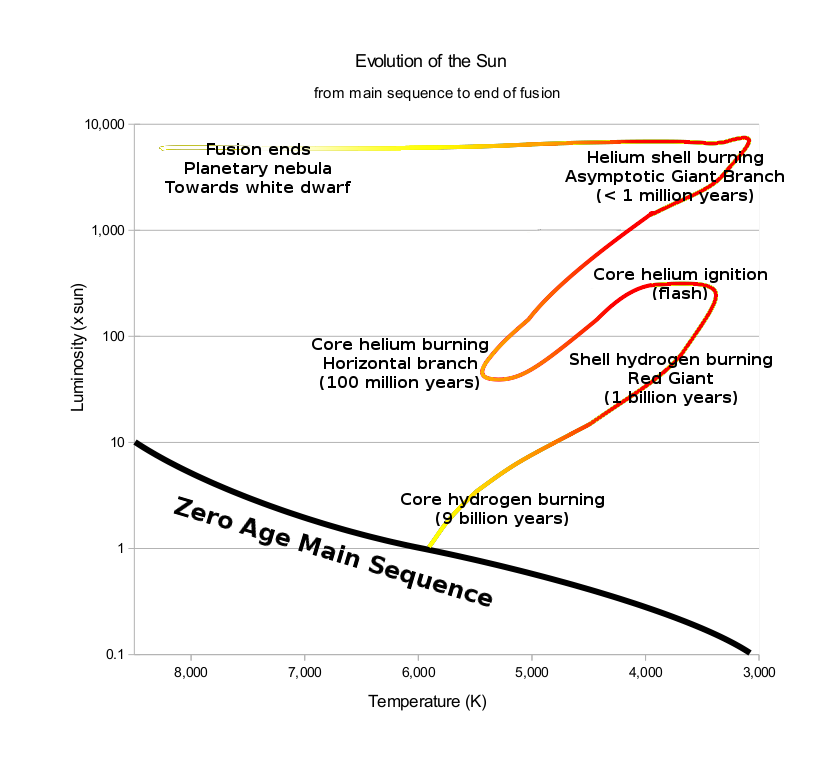
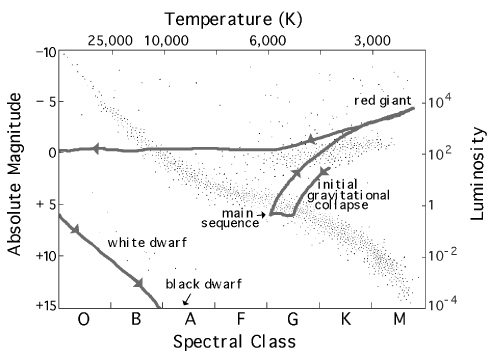
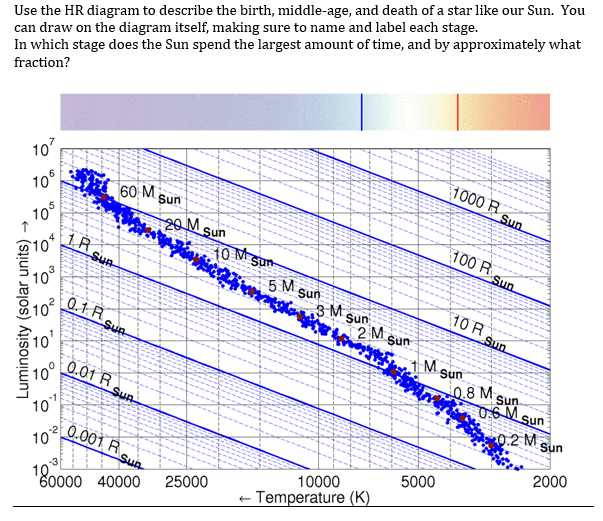
The sun was formed from a cloud of dust and gas called a nebula. This was quite cool and very dim, so would not appear on the diagram. So when the Sun was formed it just appears on the HR diagram in its current position. The Sun will follow a path during its life similar to the one on the diagram below, and you are required to know this path.
Our sun on the hr diagram
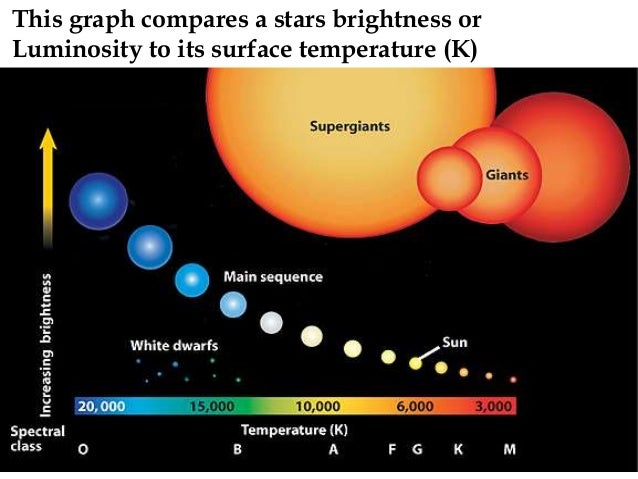
The HR diagram spans a rather large range in luminosity, from 10-4 L on the low end to as much as 10 6 L on the high end. This interactive applet might help you visualize some of the properties of the HR diagram. Star size. Of the 12 brightest stars in our sky, most are giants and supergiants. Q: Where would a star of the Sun's size, but T = 15,000 K, fall on the HR diagram? Q: Where would a star of the Sun's size, but T = 2,800 K, fall on the HR diagram? You can see that the main sequence can be explained mostly due to differences in temperature: hot stars fall on the upper left, cool stars on the lower right portion of the sequence. Earth Sciences questions and answers. 12 Question (1 point) 1st attempt Our Sun lies in the region of the H-R diagram. Choose one: subgiant white dwarf giant O main sequence 15 Question (1 point) 1st attempt Which is the correct sequence for star formation, from earliest to latest? Choose one: accretionary disk, protostar, nebula, shock wave ...
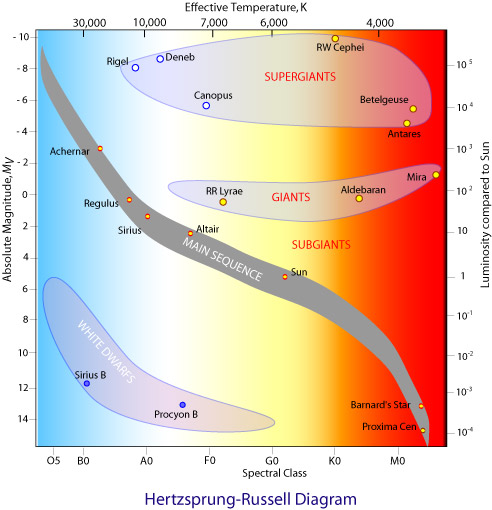
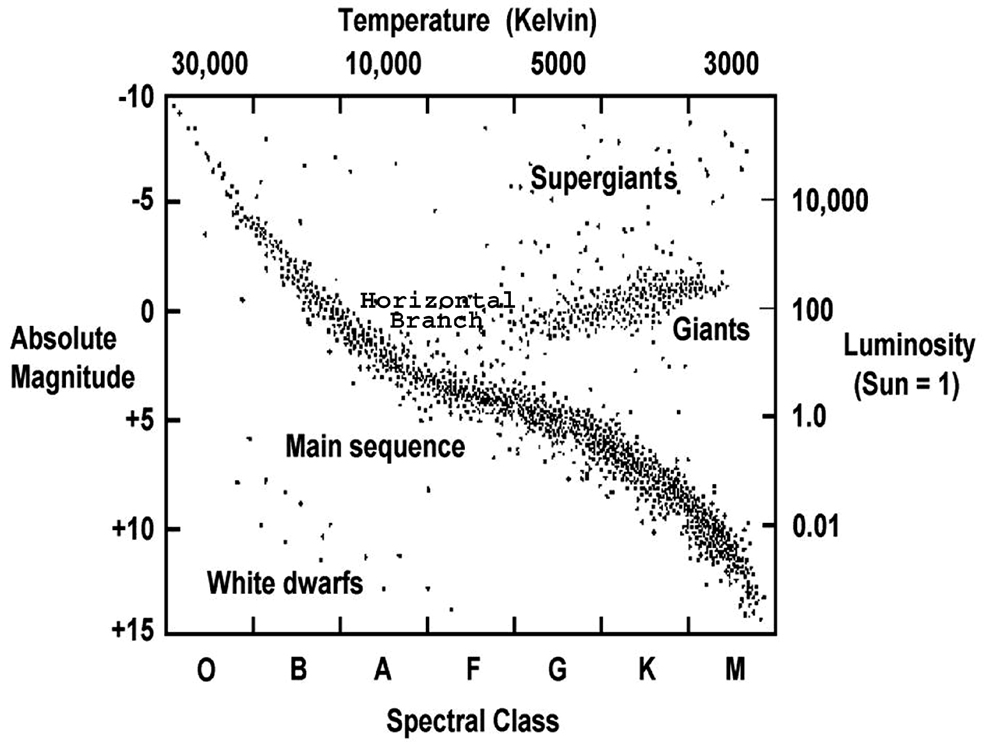
Our sun on the hr diagram. For example, the Sun is 6.96x10 8 meters in radius and has a surface temperature of 5780K. Therefore, its luminosity is 3.84x10 26 watts. On a log-log plot, the R squared term in the above equations is a straight line on an HR diagram. This means that on a HR diagram, a star's size is easy to read off once its luminosity and color are known. By definition a star of magnitude 1 is 100 × brighter than one of magnitude 6. Our Sun has an absolute magnitude of + 4.8. Possible axes for a Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Note how the temperature scale is reversed on the horizontal axis. Also take care if using magnitude to work upwards to negative values. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is one of the most important tools in the study of stellar evolution.Developed independently in the early 1900s by Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell, it plots the temperature of stars against their luminosity (the theoretical HR diagram), or the colour of stars (or spectral type) against their absolute magnitude (the observational HR diagram, also known ... Luminosity classes correspond to horizontal and diagonal bands on the HR diagram that are related to the size of a star. This somewhat qualitative classification is exhibited in the adjacent table and in the HR diagram displayed below. ... Since our Sun is a star, we can classify it according to its spectral and luminosity classes. The Sun is ...
Thus, its position on the H-R diagram, in which luminosity is plotted against temperature, also changes. As a star ages, we must replot it in different places on the diagram. Therefore, astronomers often speak of a star moving on the H-R diagram, or of its evolution tracing out a path on the diagram. In this context, "tracing out a path ... The cool supergiants in the upper corner of the H-R diagram are as much as 10,000 times as luminous as the Sun. In addition, these stars have diameters very much larger than that of the Sun. As discussed above, some supergiants are so large that if the solar system could be centered in one, the star's surface would lie beyond the orbit of ... Estimate the luminosity and temperature from the HR diagram. Note that the luminosities on the plot are displayed as a multiple of the Sun's luminosity: L ⊙ = 3.83 × 1 0 26 W. L_\odot=\SI{3.83e26}{\watt}. L ⊙ = 3. 8 3 × 1 0 2 6 W. An H-R Diagram for the Nearest Stars. In this exercise, you will make a slightly different type of H-R diagram. Instead of graphing absolute magnitude vs. b-v color, you will graph absolute magnitude vs. spectral type. Looking at a star's spectral type - defined by the peaks and valleys in its spectrum - is an another way of finding the star's ...
Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram. This diagram is called the Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram. It shows stars according to their temperature and brightness. ... Our Sun will become a red giant ... Our current telescopes and detectors are sensitive enough to take the spectrum of any (unobscured) sun-like star in the Milky Way. The HR diagram You are probably familiar with the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, or HR diagram for short. View HR-diagrams.pdf from PHYSICS AN ASTM024 at UCL. The diagram below shows a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. On this graph, the luminosity of the Sun is 1. (a) What is the correct label and suitable The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, or H-R diagram, is a plot of stellar luminosity against surface temperature. Most stars lie on the main sequence, which extends diagonally across the H-R diagram from high temperature and high luminosity to low temperature and low luminosity.
known schematic diagram combining the HR diagrams of star clusters of different ages: NGC2362 is the youngest and M67 the oldest. The pink numbers give the main sequence lifetime in years for stars at that point in the main sequence—e.g. our Sun has a main sequence lifetime of 10 Gyr. From this we see that the "double
20) All four stars in our data set live on the main sequence. Given the temperatures you already know, use the HR Diagram to determine the luminosity and radius of each star. Record this information in a table like the one below. Temperature (K) Luminosity (Lsun) Radius (Rsun) Zeta Oph Fomalhaut Sun 1 1 Proxima Centauri The mass-luminosity ...
An H-R diagram is shown in Figure 1. An H-R diagram takes a set of stars and plots their luminosities (relative to the Sun) versus their surface temperatures. Note that the temperature scale on the H-R diagram in Figure 1 runs backwards, right to left, and that the luminosity axis is highly compressed. (Historically, this was how the first H-R ...
The HR diagrams that we studied in Lesson 4 are very useful tools for studying stellar evolution. A typical HR Diagram (e.g., the one for the stars in the cluster M55, below) plots a single point per star to represent that star's color and luminosity (or brightness) as it is observed today.
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, abbreviated as H-R diagram, HR diagram or HRD, is a scatter plot of stars showing the relationship between the stars' absolute magnitudes or luminosities versus their stellar classifications or effective temperatures.The diagram was created independently around 1910 by Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell, and represented a major step towards an ...
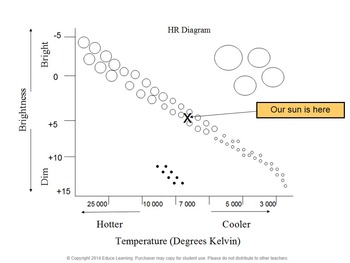
On the H-R diagram our Sun is a. - Star of average luminosity and temperature. Red giant stars are. - Close to exhausting their supply of hydrogen. The event that changes a protostar to a full-fledged star is. - Thermonuclear fusion. The longest living stars are those of. - Low mass.
A small, hot, dim star that is the leftover center of an old s…. nuclear fusion. Two or nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus. HR diagram. A graph that characterizes star by temperature and brightness. 16 Terms. Taylor_Parsons78. HR Diagram, stars, and galaxies. It shows the temperature and brightness….
Simple calculations provide a size for white dwarfs roughly that of our Earth, less than 1/100 that of the Sun. If we compare the dimmest stars on the H-R diagram we can also make some inferences. The following diagram shows the lower region of the H-R diagram.
As you can see in the HR diagram below (Fig. 6.4), the evolutionary track of a Sun-like star now moves the star back towards the Main Sequence. This region of the HR diagram is called the horizontal branch , because stars in this phase of their evolution populate a narrow, almost horizontal box that extends to hotter temperatures from the red ...
Solved Locate The Sun On The H R Diagram How Will The Sun S Luminosity And Temperature Change As It Ages How Will These Changes Affect Its Positi Course Hero
Our Sun is a G2V star and will thus appear in the centre of the HR diagram.
Earth Sciences questions and answers. 12 Question (1 point) 1st attempt Our Sun lies in the region of the H-R diagram. Choose one: subgiant white dwarf giant O main sequence 15 Question (1 point) 1st attempt Which is the correct sequence for star formation, from earliest to latest? Choose one: accretionary disk, protostar, nebula, shock wave ...
Q: Where would a star of the Sun's size, but T = 15,000 K, fall on the HR diagram? Q: Where would a star of the Sun's size, but T = 2,800 K, fall on the HR diagram? You can see that the main sequence can be explained mostly due to differences in temperature: hot stars fall on the upper left, cool stars on the lower right portion of the sequence.
The HR diagram spans a rather large range in luminosity, from 10-4 L on the low end to as much as 10 6 L on the high end. This interactive applet might help you visualize some of the properties of the HR diagram. Star size. Of the 12 brightest stars in our sky, most are giants and supergiants.
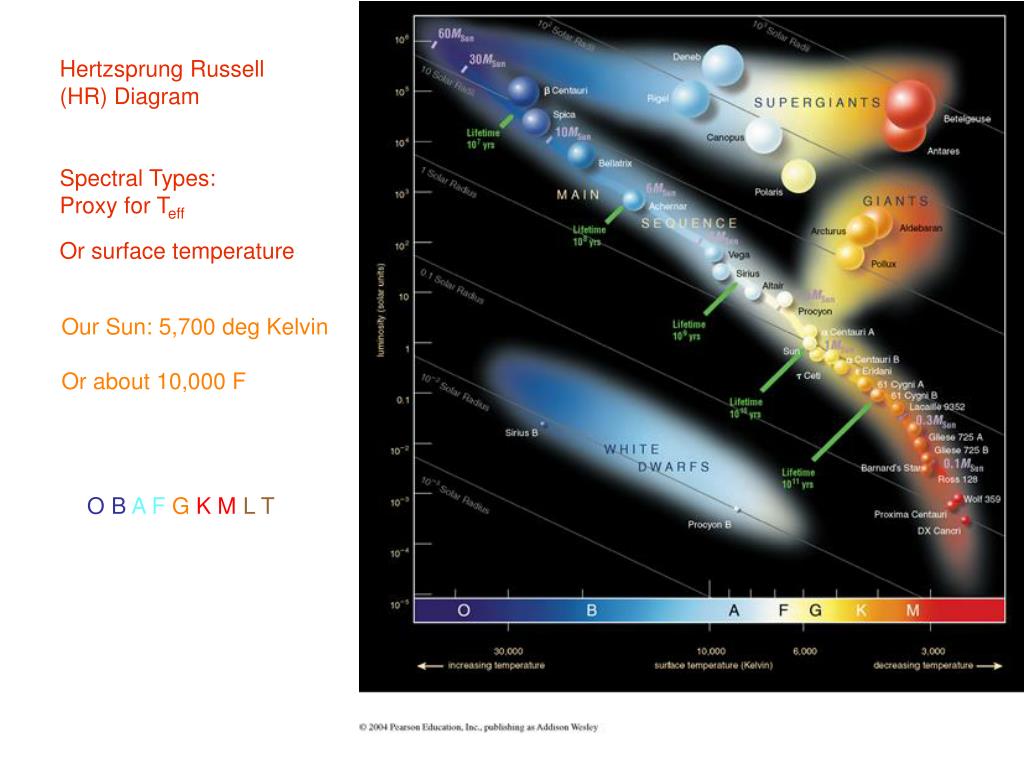
Ppt Hertzsprung Russell Hr Diagram Spectral Types Proxy For T Eff Or Surface Temperature Powerpoint Presentation Id 5915385

















0 Response to "37 our sun on the hr diagram"
Post a Comment