38 arterial blood gas diagram
An arterial blood gas is a laboratory test to monitor the patient's acid-base balance. It is used to determine the extent of the compensation by the buffer system and includes the measurements of the acidity (pH), levels of oxygen, and carbon dioxide in arterial blood. Unlike other blood samples obtained through a vein, a blood sample from an ...
Taking an arterial blood gas (ABG) involves using a needle and syringe to directly sample blood from an artery (typically the radial artery). Below is a step-by-step guide to taking an arterial blood gas sample in an OSCE setting, with an included video demonstration.
Press Release Arterial Blood Gas Sampling System Market Competition, Opportunities and Challenges 2022-2027 Published: Nov. 10, 2021 at 10:38 p.m. ET

Arterial blood gas diagram
the policy authorizing arterial line sampling may do arterial line sampling. Physician's Orders Sampling will be done at the physician's order or as per the specific ICU protocol. (RT and/ or RN are capable of drawing a blood gas from an arterial line.) Indications Arterial blood gas values may be indicated before and after the start or
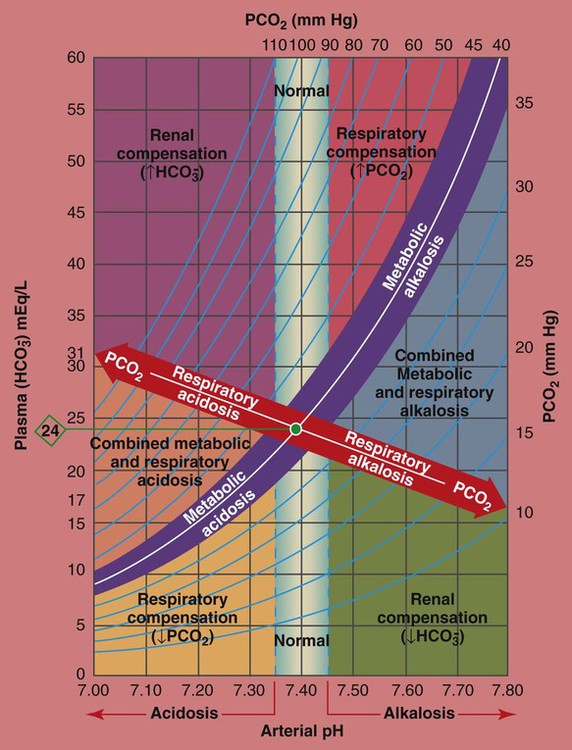
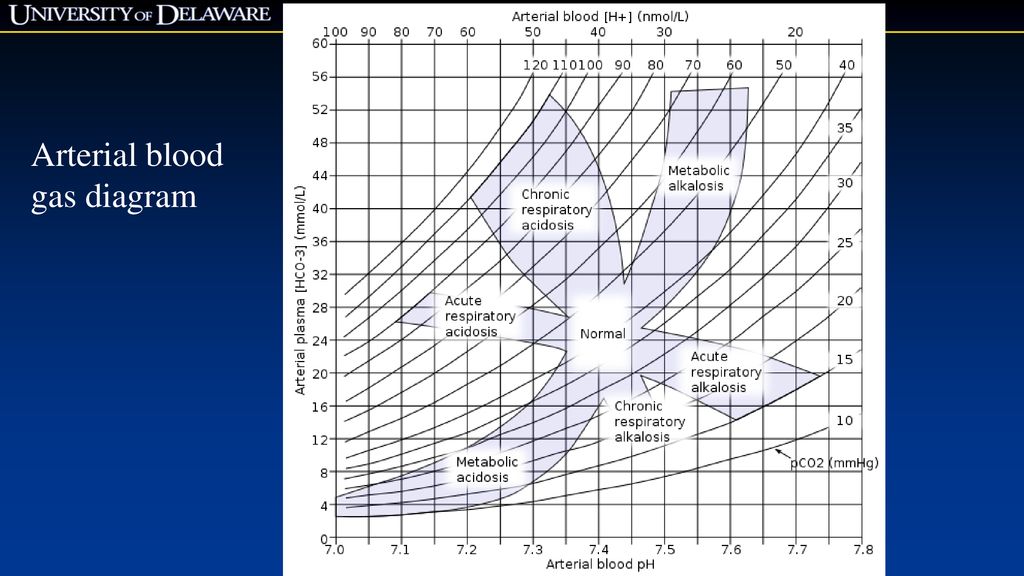
A simple diagram for arterial blood gas tensions was constructed from values obtained from normal volunteers at rest, during voluntary breath-holding and during maximal voluntary hyperventilation. Thus, an appropriate arterial oxygen tension (PaO 2) was established for any physiologic level of alveolar ventilation, as reflected by the arterial ...
Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs) David A. Kaufman, MD Chief, Section of Pulmonary, Critical Care & Sleep Medicine Bridgeport Hospital-Yale New Haven Health Assistant Clinical Professor, Yale University School of Medicine (Section of Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine) Introduction: Interpreting an arterial blood gas (ABG) is a crucial skill for physicians, nurses, respiratory ...
Arterial blood gas diagram.
A "blood gas analysis" can be performed on blood obtained from anywhere in the circulatory system (artery, vein, or capillary). An arterial blood gas (ABG) tests explicitly blood taken from an artery. ABG analysis assesses a patient's partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) and carbon dioxide (PaCO2).
We collected quantitative indices of nocturnal hypoxemia, patient demographics, medications, pulmonary function tests, as well as arterial blood gas (ABG) data from the night of the PSG.
Arterial blood collection: sampling and storage - part 2 of 2. by S. B. Blonshine. Quality assurance Blood gases/acid-base. The collection of arterial specimens with glass syringes and immediate storage in iced water was the accepted industry standard for many years. Practice has changed over the past several years to blood gas sample ...
Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: Example Set 1. Case A. A patient is brought back to the floor from the operating room on a patient controlled analgesia (PCA) pump with hydromorphone. The patient hits his PCA button several times in the first hour. Shortly thereafter, the nurse walks in the room and finds him somnolent and difficult to arouse.
expired air, arterial blood, or venous blood, can be plotted on this diagram. It will be appreciated at the end of this discussion that 1) there are certain physical limits to what combinations of O 2 and CO 2 can exist in the alveolus and, therefore, the blood; and 2) even if arterial blood gases are the only available
Laboratory determination of blood gas analysis (1) The pH of blood : heparinized whole arterial blood ( or heparinized capillary blood ) is used. The pH determination is performed immediately after collection of blood .The blood can be stored at 0-4 ⁰ C up to 2-3 hrs,without significant change in pH .
Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis is an essential part of diagnosing and managing a patient's oxygenation status and acid-base balance. The usefulness of this diagnostic tool is dependent on being able to correctly interpret the results. Arterial blood gas diagram. An arterial blood gas (ABG) tests explicitly blood taken from an artery.
Lactate is produced via pyruvate metabolism under anaerobic or aerobic glycolytic conditions. In the presence of adequate oxygen and mitochondrial capacity, pyruvate is normally converted to acetyl CoA which then enters the Krebs cycle. In the absence of oxygen or in the presence of excessive glycolysis, pyruvate is shunted into lactate ...
Specimen Collection - Arterial Blood Gas The primary responsibility of a phlebotomist is to collect blood for laboratory analysis, which is necessary for diagnosis and care of the patient. Collection of a quality specimen is the first step in providing an accurate test result.
An Arterial Blood Gas Diagram for Clinical Use* Edward E. Mays, Lt Col, USA, MC, F.C.C.P. o o A simple diagram for arterial blood gas tensions was constructed from values obtained from normal volunteers at rest, during voluntary breath-holding and during maximal voluntary hyperventilation. Thus, an appropriate arterial oxygen
Arterial Blood Flow Chart Artery Lateral Femoral Circumflex. Author: Tim Plagge Created Date: 4/24/2012 6:44:50 AM ...
Mar 25, 2015 - ABG Fishbone Diagram This is the 13th in the series of fishbones on ABG Interpretation for for nurses. Overview of Arterial Blood Gases diagram Acidotic Alkalotic PCO2 HCO3 PH Balances. The main key is to identify that PCO2 is Respiratory and HCO3 is Metabolic I am working on this for my class all of this can be shared.
An arterial blood gas (ABG) test measures the amounts of arterial gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide.An ABG test requires that a small volume of blood be drawn from the radial artery with a syringe and a thin needle, but sometimes the femoral artery in the groin or another site is used. The blood can also be drawn from an arterial catheter.. An ABG test measures the blood gas tension ...
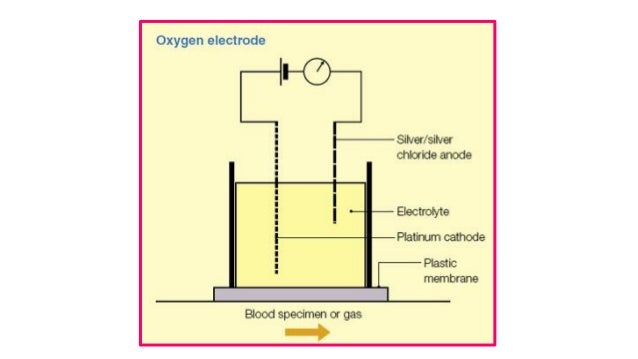
Arterial oximetry, or co-oximetry, is carried out by most modern arterial blood gas analysis equipment. SaO 2 is measured using a cuvette with a defined light path and up to six light sources of differing wavelengths to distinguish oxyhemoglobin, deoxyhemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin, methemoglobin, and other abnormal hemoglobin saturation levels ...
An arterial blood gases (ABG) test is a blood test that measures the acidity, or pH, and the levels of oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from an artery. The test is used to check the function of the patient's lungs and how well they are able to move oxygen into the blood and remove carbon dioxide.
The process of analysis and monitoring of arterial blood gas (ABG) is an essential part of diagnosing and managing the oxygenation status and acid-base balance of the high-risk patients, as well as in the care of critically ill patients in the Intensive Care Unit. ... Flow diagram showing approach to hypoxemic respiratory failure ...
The pH, base excess and pCO 2 (acid-base status) of arterial blood flowing through the umbilical cord provides valuable objective evidence of the metabolic condition of neonates at the moment of birth; a notion that has assured a role for the blood gas analyzer in hospital delivery suites in cases of suspected fetal distress/asphyxia.. The intended purpose of this review article is to detail ...
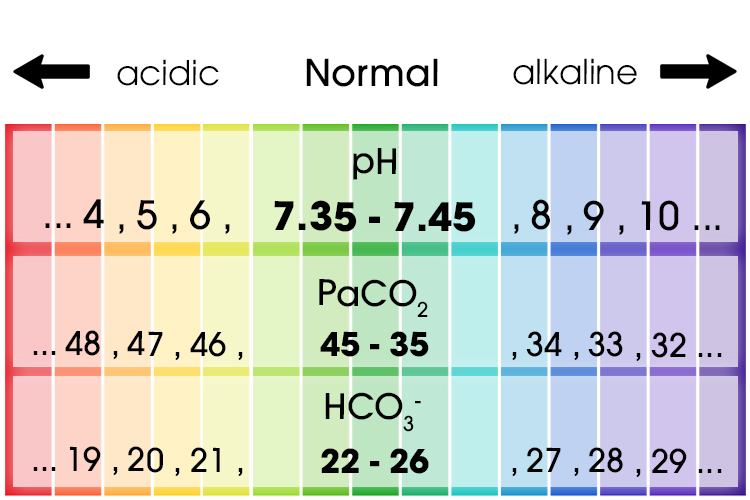
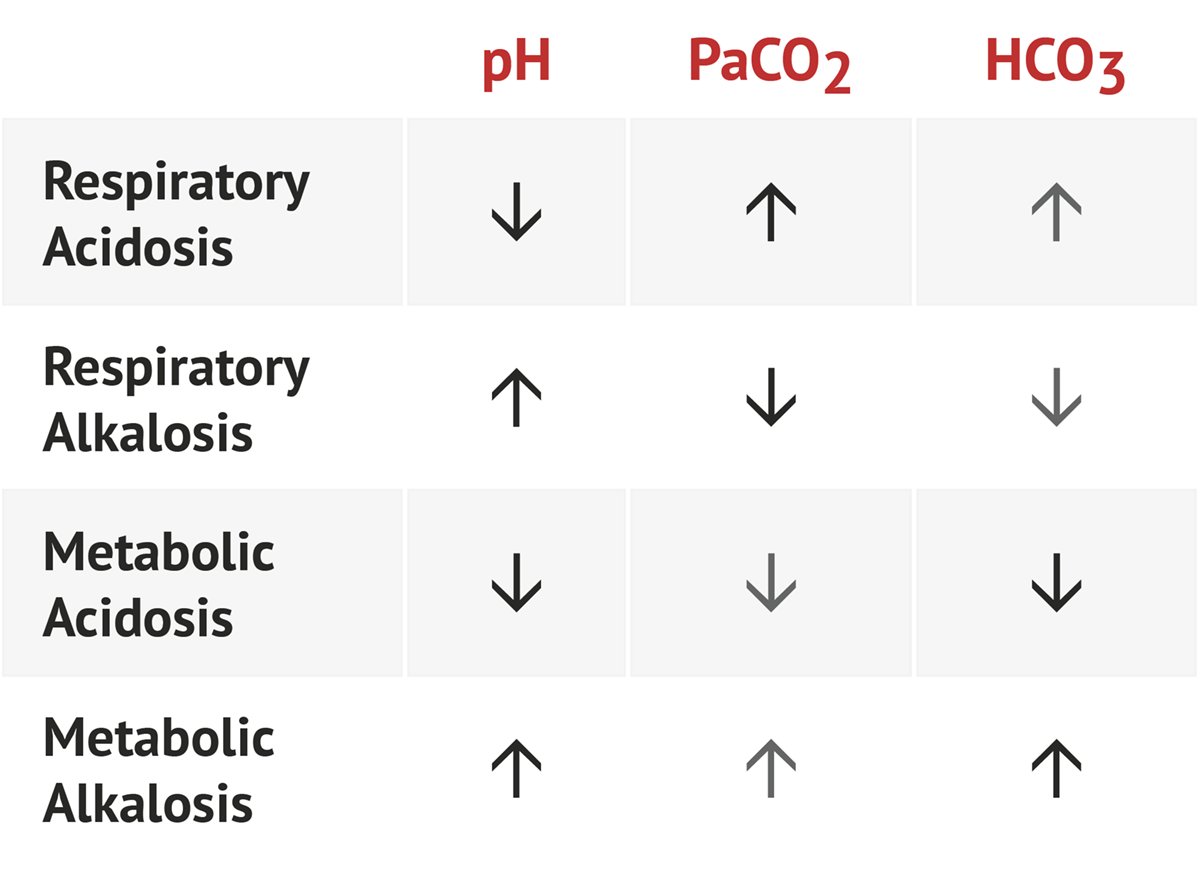
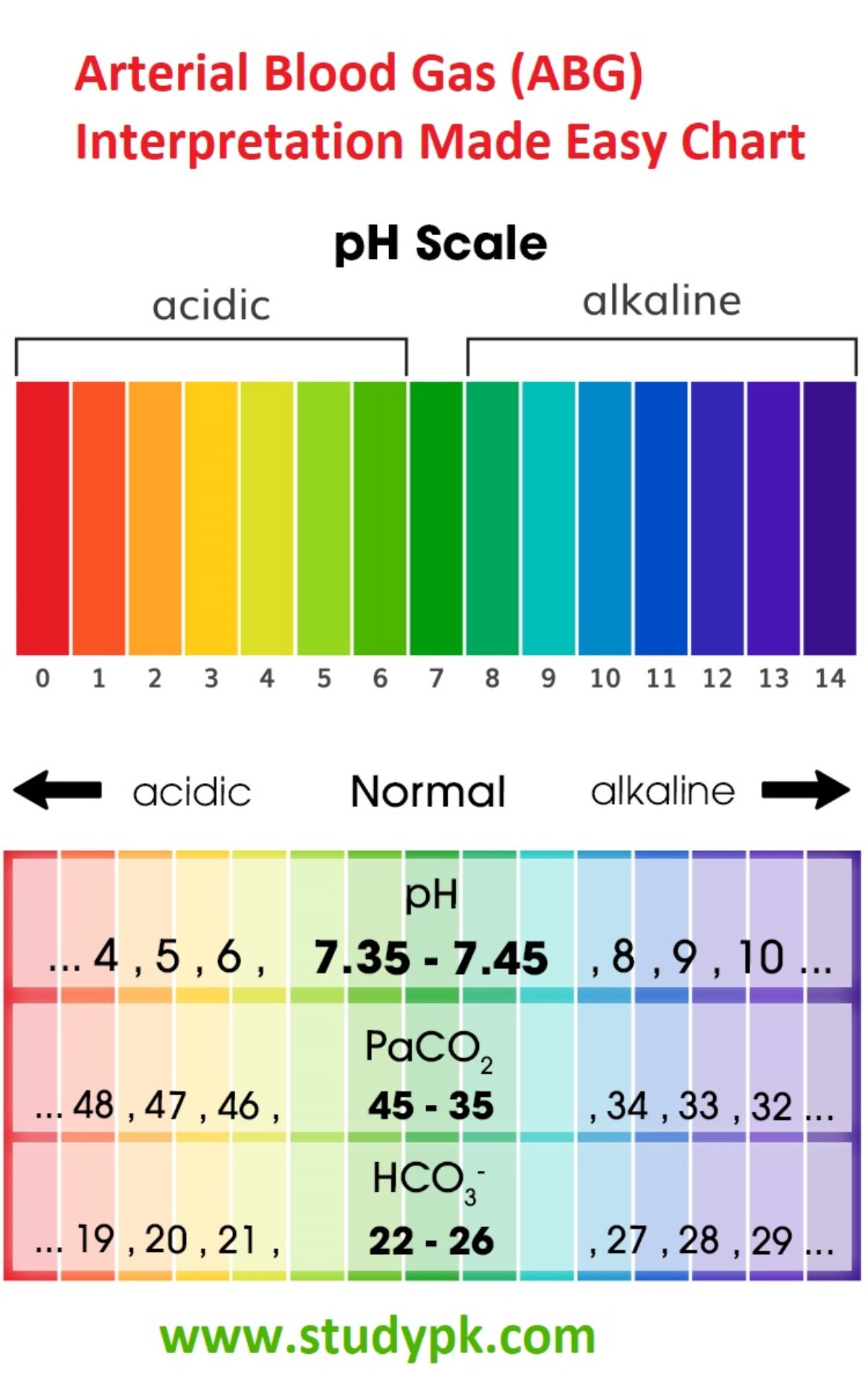
Components of the Arterial Blood Gas The arterial blood gas provides the following values: pH Measurement of acidity or alkalinity, based on the hydrogen (H+) ions present. The normal range is 7.35 to 7.45 Remember: pH > 7.45 = alkalosis pH< 7.35 = acidosis PO2 The partial pressure of oxygen that is dissolved in arterial blood.
The alveolar-arterial gradient is a comparison of the partial pressure of Oâ‚‚ in the alveoli and in arterial blood. ... based on the patient's inspired FiOâ‚‚ and the PCOâ‚‚ from their blood gas result, while the arterial value is the PaOâ‚‚ from the patient's blood gas result. ... Quick diagrams to have the answers, fast ...
A simple diagram for arterial blood gas tensions was constructed from values obtained from normal volunteers at rest, during voluntary breath-holding and during maximal voluntary hyperventilation. Thus, an appropriate arterial oxygen tension (PaO2) was established for any physiologic level of alveolar ventilation, as reflected by the arterial carbon dioxide tension (PaCO2).
Label the diagram showing the three forms in which CO2 is transported in the blood. Analyze the graphs, which demonstrate the effects of acute exercise on arterial blood gases and pH. Then, determine whether the statements are true or false.
The Davenport diagram shows that shifts in pH at various levels of arterial carbon dioxide tension (P a CO 2) with, A, normal bicarbonate concentrations, B, increased carbonic acid levels, C, decreased carbonic acid levels in the blood. The line connecting the points is the buffer line for arterial blood.
The Importance of Arterial Blood Gas Analysis. 1. Oxygen. 3. Carbon Dioxide and Respiratory Failure. 4. Bicarbonate and Metabolic Imbalance. 5. Respiratory and Metabolic Compensation.




![PDF] Arterial blood gas analysis. | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/1a0a3209910a5b74141239a24ee0c9fad8459240/5-Figure1-1.png)





















0 Response to "38 arterial blood gas diagram"
Post a Comment