35 car free body diagram
Free Auto Repair Diagrams. Below we provide access to three basic types of diagrams that will help in the troubleshooting and diagnosis of an automotive related problem. Wiring diagrams are one of the most common these days with all the added electronics. The bells and whistles tend to break the most often.
Free Body Diagrams, Net Force
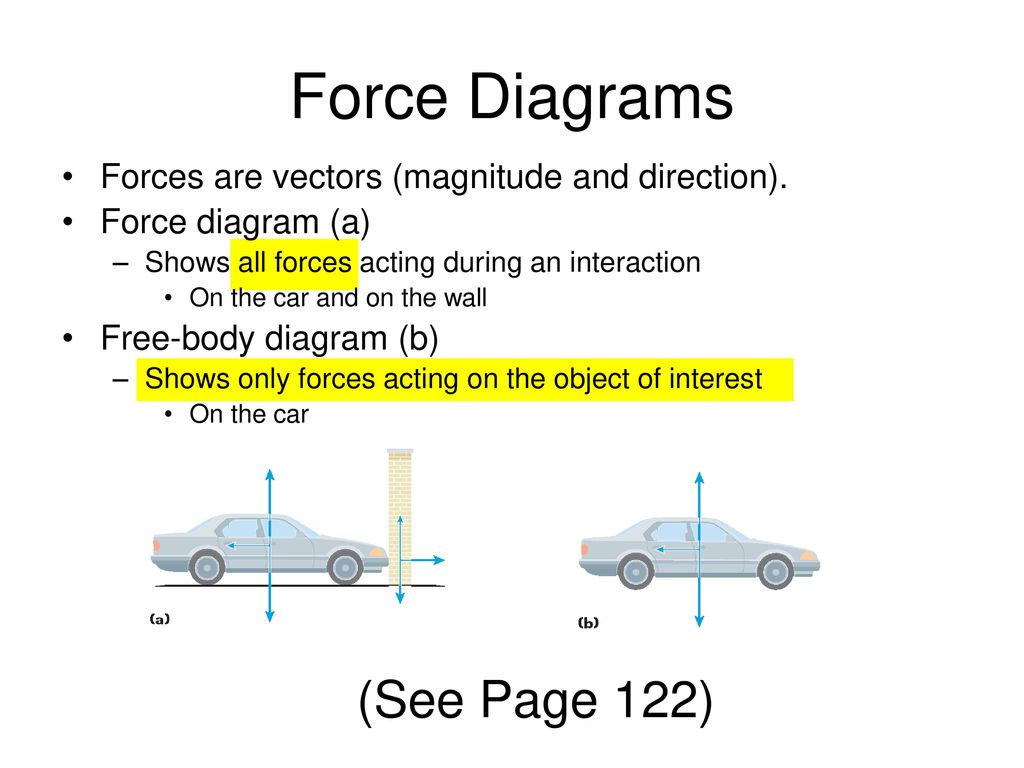
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
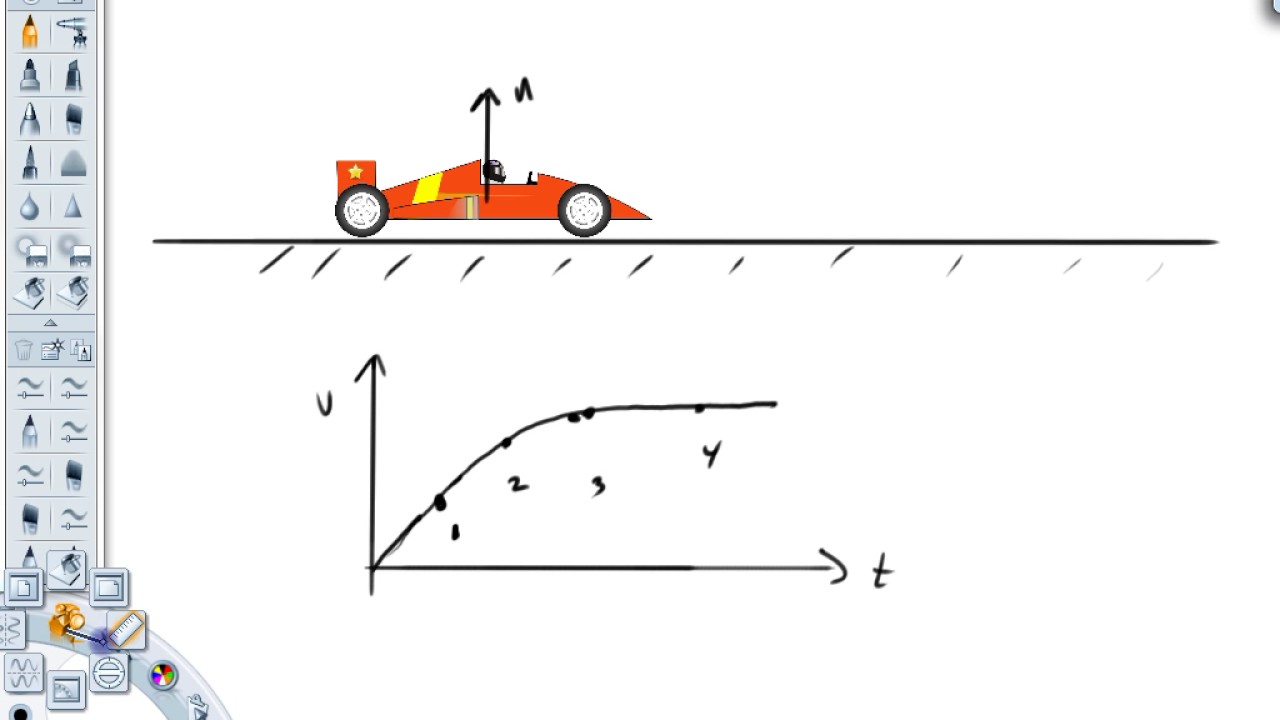
Car free body diagram
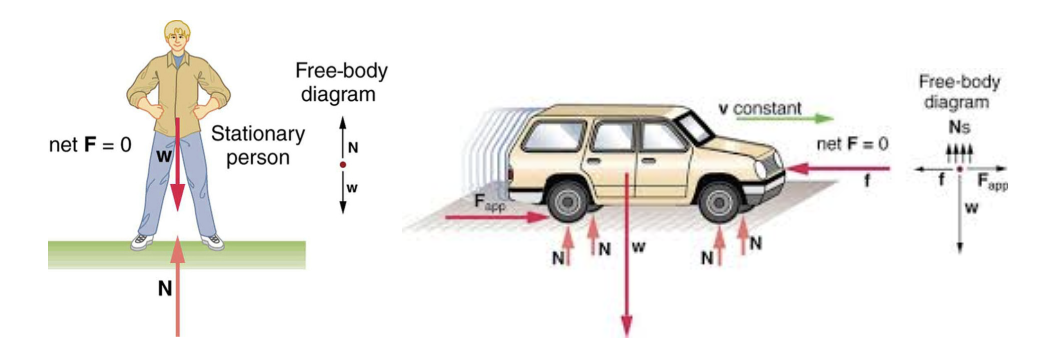
The free body diagram of a car traveling at a constant speed consists mainly of five forces, when considered in an actual situation. These vectors are that of friction, gravity, normal force, air resistance, and engine driving force. In a hypothetical situation without external forces (friction and air resistance), only the three remaining ...
FBD of Newton's 3rd Law. The following FBD is a representation of Newton's Third Law. This diagram is a representation of a dancer as he or she balances. Whether it be two feet on the floor, one foot on the floor or on pointe, force normal is equal to the force of Earth. This is the case because of Newton's Third Law, which states that there ...
A free body diagram models the forces acting on an object. The object or 'body' is usually shown as a box or a dot. The forces are shown as thin arrows pointing away from the centre of the box or ...
Car free body diagram.
A free-body diagram for the car on the banked turn is shown at left. The banking angle between the road and the horizontal is (theta). The normal force, N, has been resolved into horizontal and vertical components (the blue vectors). In the vertical direction there is no acceleration, and: so:
Car suspension model Mass - spring - viscous damper system Model Force balance Free body diagram F K0 Mg Free body diagram (no motion) F K0 Mg force due to spring in equilibrium force because spring changes length during motion force due to viscous damping System ODE : 8 m d 2 x < = F. K +F. v (2. nd . order ordinary > dt. 2 =) m d. 2. x ...
The free body diagram helps you understand and solve static and dynamic problem involving forces. It is a diagram including all forces acting on a given object without the other object in the system. You need to first understand all the forces acting on the object and then represent these force by arrows in the direction of the force to be drawn.
The car with a mass of m moves along a road. The system was initially at rest. Equation of motion was driven from the free body diagram, and since the value of spring constant (k), damping constant (b) was given, the natural frequency and damping coefficient was calculated.
Free Body Diagrams Practice Problems Construct free-body diagrams for the various situations described below. 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. 2. A girl is suspended motionless from a bar which hangs from the ceiling by two ropes. Diagram the forces acting on the girl. 3. An egg is free-falling from a ...
Image: Quarter-car Xcos block diagram model The road input u is modeled as a step input, with a rising edge and falling edge. v1 is the vertical translational speed of the body of the vehicle and v2 is the vertical translational speed of the wheel.
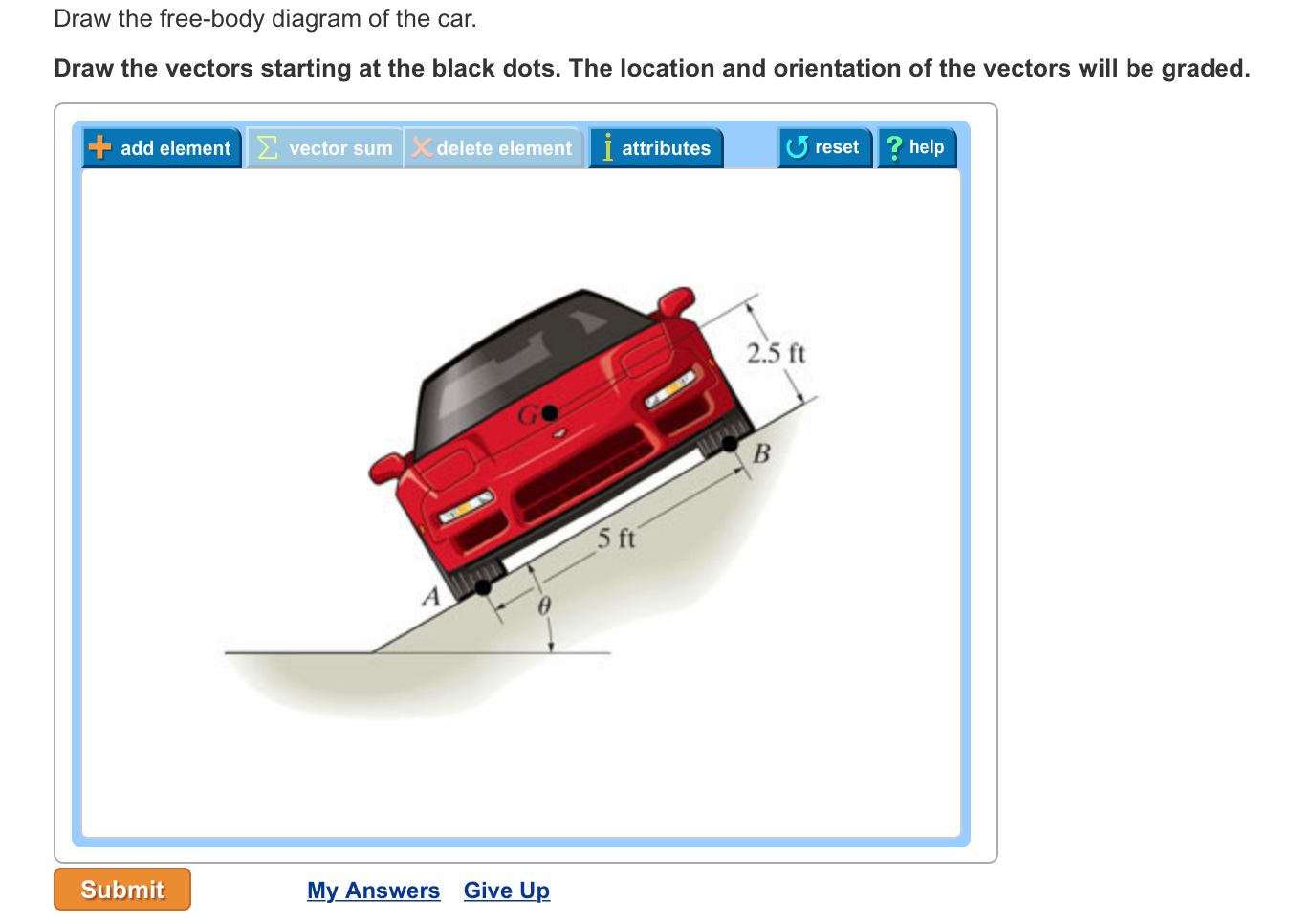
Draw A Free-body Diagram for the Car. drawing free body diagrams physicsclassroom an example of a free body diagram is shown at the right the free body diagram above depicts four forces acting upon the object objects do not necessarily always have four forces acting upon them there will be cases in which the number of forces depicted by a free body diagram will be one two or three solved draw ...
Free body analysis of car braking on all wheels. For a car of mass M, CofG at height h above ground, setback l from the front axle, calculate the vertical reaction at the front and rear wheels and hence the torque provided by those wheels. ... Free body diagram of car decelerating ...
I make a free-body diagram for a car that accelerates to the right. I make a free-body diagram for a car that accelerates to the right.
Free wiring diagrams for your car or truck. Including lighting, engine, stereo, hvac wiring diagrams. Get your Free Automotive Wiring Diagrams Sent right to you, Free Wiring Schematics
A car pushes a block across the floor. (assume that it is moving from left to the right) Draw a free body diagram for the car showing: Force by block on car. Force of friction. Force of Gravity. Normal force. Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution Normal force Straight up, gravity straight down.
R5Improve their ability to draw free body diagrams. R5Be able to identify errors in diagrams and correct them. R5Recognize free body diagrams as representations of forces, and connect them with real-world objects and phenomena. Motivation R5Free body diagrams are a key problem-solving strategy for physics and engineering students.
Free-Body Diagram Example Problem 2 A car with a mass of 1050 [kg] travels around a curve of radius 300 [m] banked at a 14˚ angle. Find the maximum speed the car can take this curve without assistance from friction. Find the centripetal force on the car.
Free Body Diagram. W is the car's weight, R 1 and R 2 are the rolling resistance of the tires, N 1 and N 2 are the reaction forces (balancing out the car's weight). Note: steel wheels (like on trains) have less rolling resistance, but are way too slippery on the road! Calculations.
A free-body diagram can be drawn very simply, with squares and arrows, or you can make it much more complex. The only requirement is that you or someone else looking at it should be able to understand what the diagram is telling. A free-body diagram (FBD) is a representation of a certain object showing all of the external forces that acts on it.
Free Body Diagram 1. Vehicle fixed co-ordinate system: It is defined with reference to a right-hand orthogonal coordinate system which originates at CG and travels with the vehicle x - forward y- lateral z- downward p- roll velocity q- pitch velocity R - yaw velocity 1. Earth fixed co-ordinate system: Vehicle altitude and trajectory
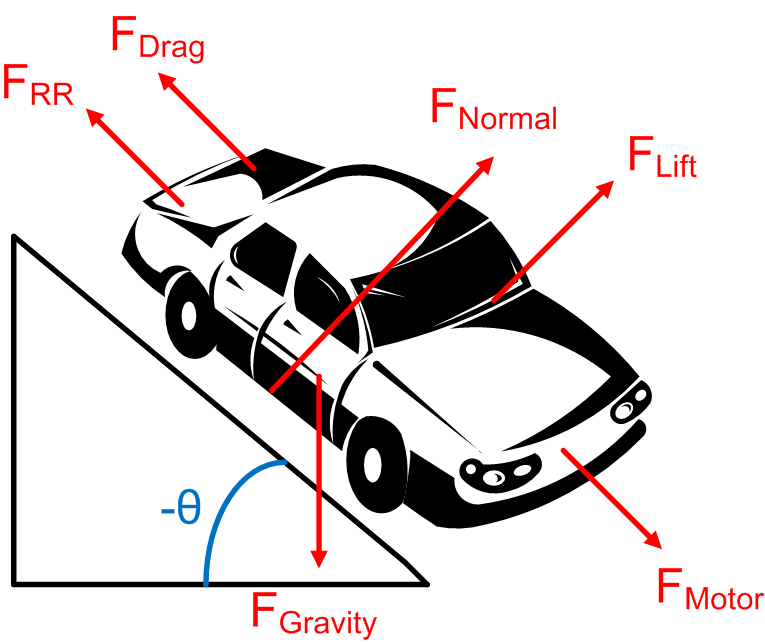
Point mass model. The simplest model of a car is to treat the entire vehicle as a point mass. On a free body diagram we have vertical force balance for a stationary car. When the car accelerates, there is a horizontal forward force on the car, and a corresponding backwards horizontal force on the ground.As the car picks up speed, air resistance produces a backwards force.
A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. The external environment (other objects, the floor on which the object sits, etc.), as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects, are omitted in a free-body diagram. Below you can see an example of a free-body diagram:
On top of a hill. The only forces acting on the rider are the upward normal force n exerted by the car and the downward force of gravity w, the rider's weight.These add together, as vectors, to provide the net force F net which is the centripetal force F c, directed toward the center of the circle. The normal force may also be called the rider's "apparent weight" for this is the force of the ...
Friction Demo: Driven wheels vs. Trailing wheels Horse pulling a cart The horse The Earth Force on a car Free Body Force Diagrams and Newton's Third Law Types of Forces 1. Gravitational or Weight 2. Electrostatic 3. Electromagnetic 4. Nuclear - strong and weak 5. Push or pull - Contact 6. Elastic or Strain 7.
A free-body diagram for the car is shown at left. Both the normal force, N (blue components) and the friction force, f (red components) have been resolved into horizontal and vertical components. Notice that the friction force acts up the incline, to keep the car from sliding toward the center of the turn.
FREE-BODY DIAGRAM. Pretend the dot at right is your mousetrap car. Draw and corectly label the four force vectors acting on the mouse cart. 2. Record the following in the data table below: Distance covered by mousetrap car x (in m) Time, t (in sec), to cover the distance Mass, m, of mousetrap car (in kg) Length (in m) of mouestrap spring arm
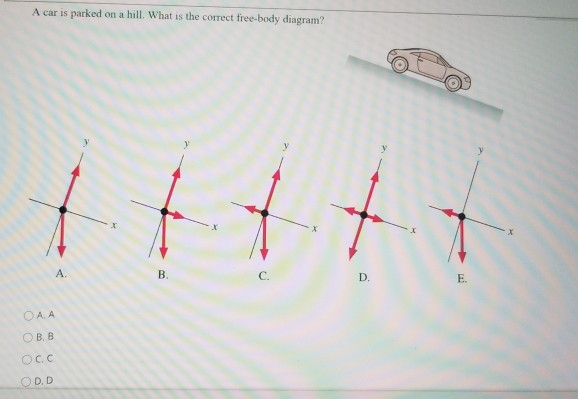

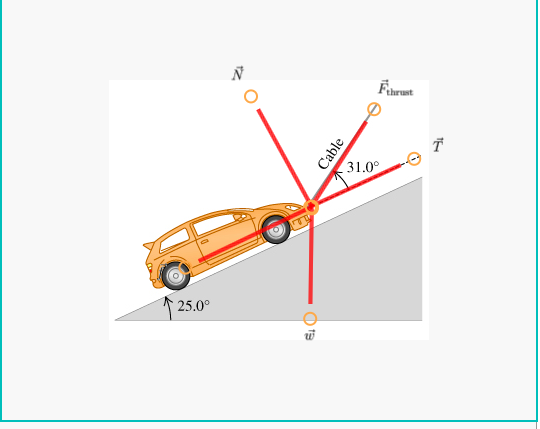




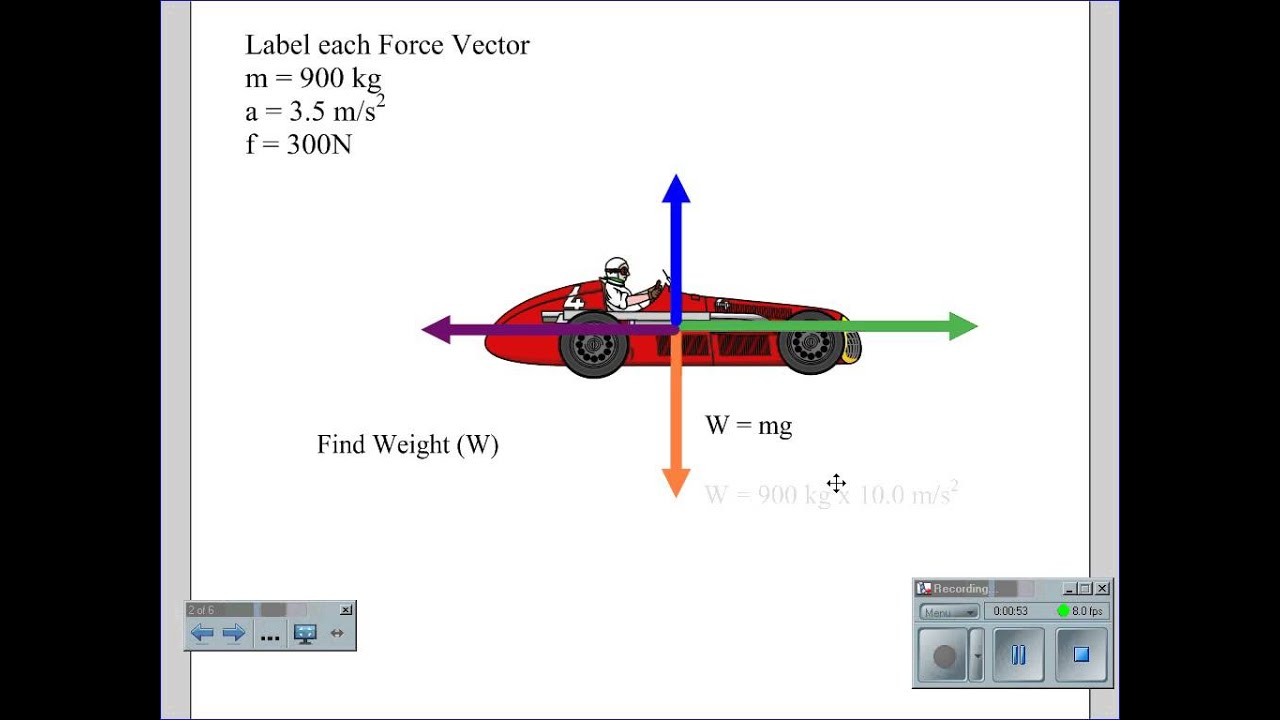


















0 Response to "35 car free body diagram"
Post a Comment