40 b2 molecular orbital diagram
Our videos prepare you to succeed in your college classes. Let us help you simplify your studying. If you are having trouble with Chemistry, Organic, Physics, Calculus, or Statistics, we got your back! Our videos will help you understand concepts, solve your homework, and do great on your exams. This video shows the end of the Be2 molecule MO diagram and explains pi orbitals, paramagnetism, and the MO diagrams for B2.
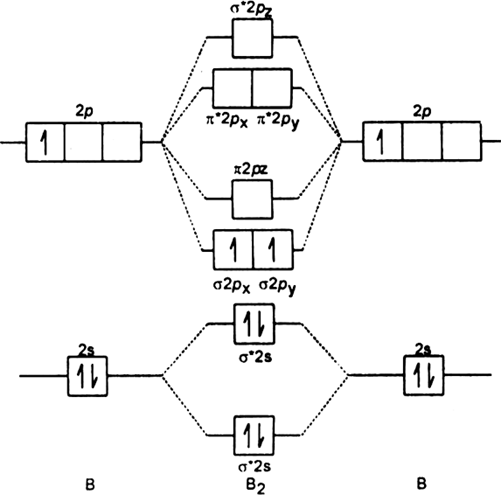
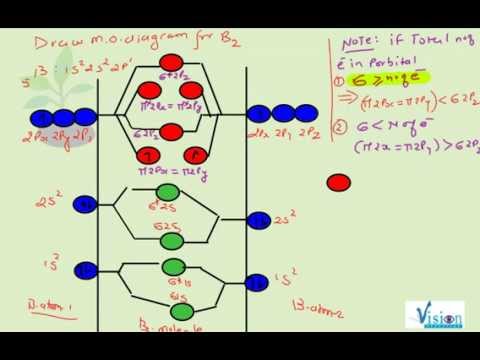
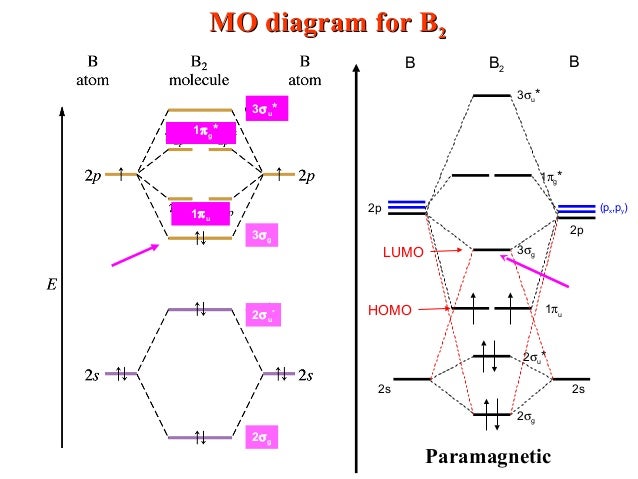
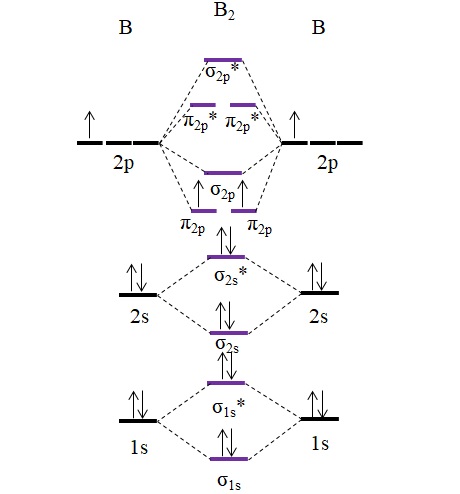
B2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. Magnetic properties: Since each 2px and 2py MO contains unpaired electron, therefore B2 molecule is paramagnetic. The compound does not exist but that doesn't mean its MO diagram And From the MOT concept Be2 doesn't exists as its Border is 0 and in.CAcT Home Molecular ...
B2 molecular orbital diagram
Answer (1 of 7): UNDERSTANDABLE VERSION- See boy... If you are in class 11th then don't look for stuff like this. It hasn't been explained for a good reason. I will explain it to you in very crude terms but not its role in MOT as you wont be able to understand and I am saying this from experience... B2 molecular orbital diagram. This also causes a large jump in energy in the 2p σ orbital. For example when two hydrogen atoms bond a σ1s bonding molecular orbital is formed as well as a σ1s antibonding molecular orbital. Valence bond model vs. The molecular orbital diagram for an o 2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both ... + and Be2.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. 1. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following ...
B2 molecular orbital diagram. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following species Be2+, Be2, and Be Indicate theirnumbers of unpaired electron and mention their magnetic diagramweb.netate their bond orders, and state which species is moststable% (1). Molecular orbitals of Li 2, Be 2, to F 2 The molecular orbital theory (MO) has been introduced ... From the periodic table as we have already discussed the Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules of 1st two periods starting from Hydrogen to Neon. ... Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers. Answer to Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. N22+ B22+ B B2 CeV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the 3s orbital of sulfur interact only weakly; this is shown in the diagram by a slight stabilization of the lowest energy ...
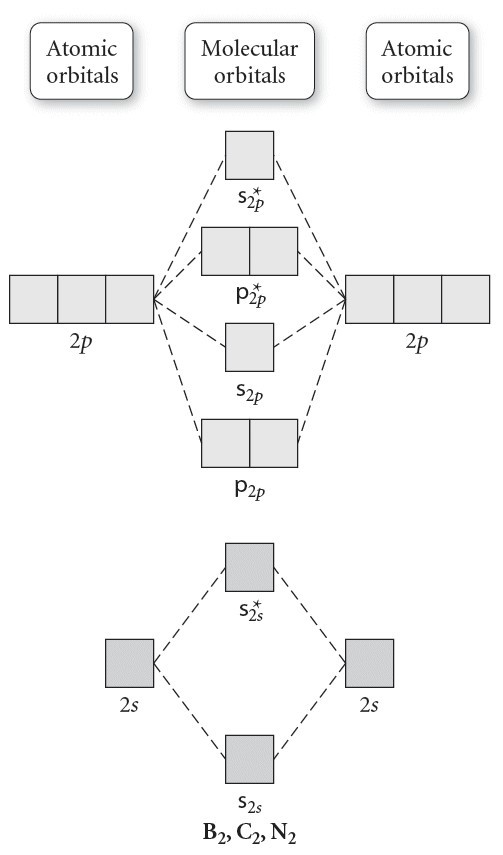
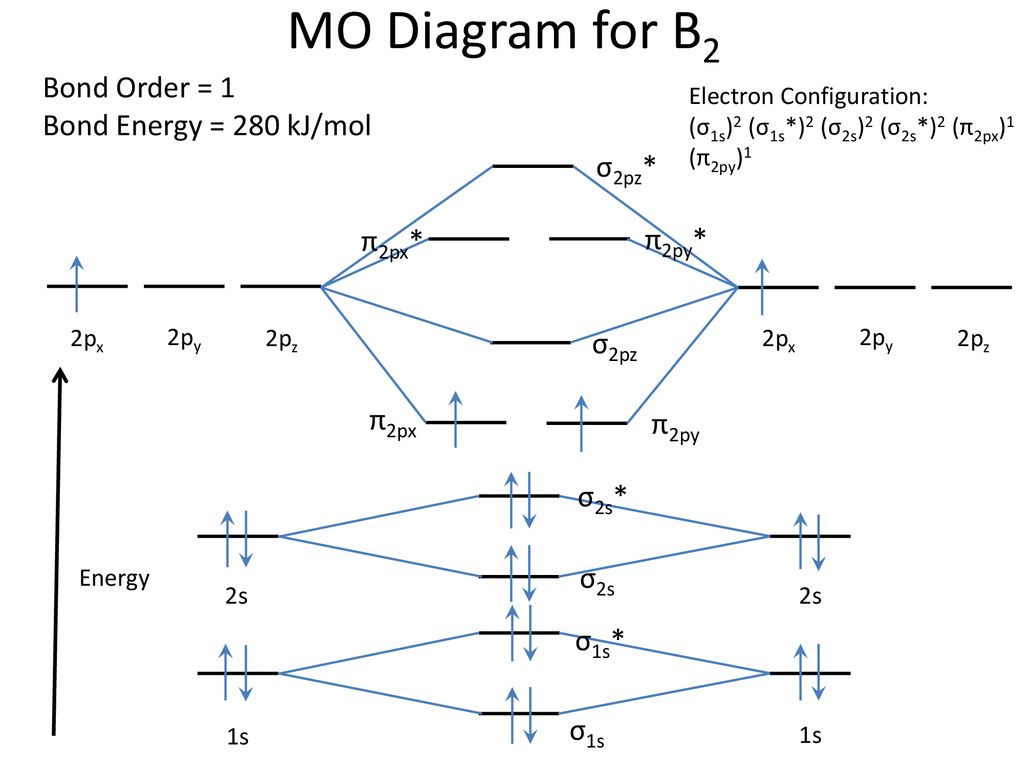
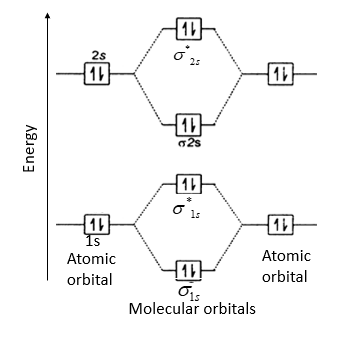
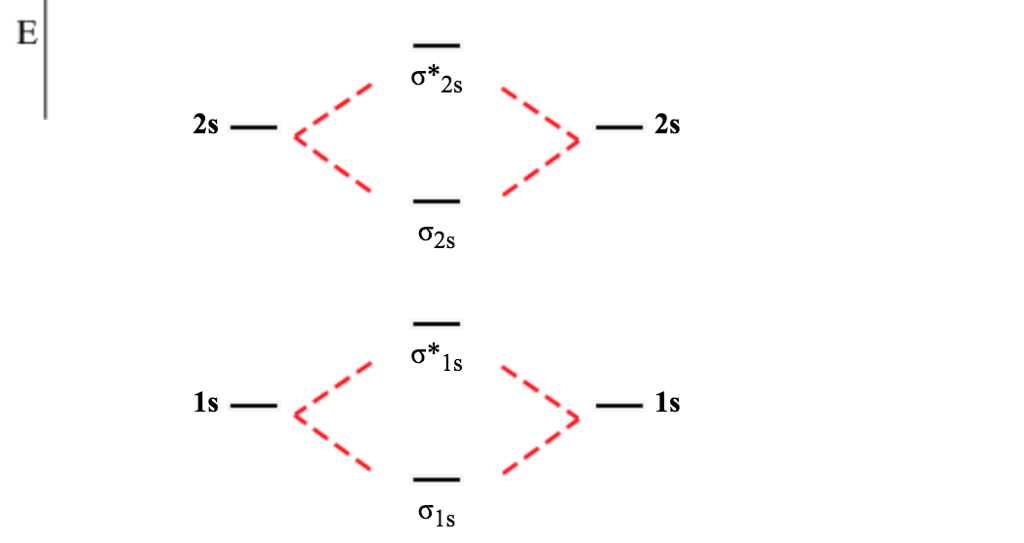
Molecular orbital diagram of b2. The next two would fill the 1 sigma e antibonding orbital. I can draw be2 but not this. B 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. The electronic configuration of b atom z 5 is. It is diamagnetic due to the absence of any unpaired electron. Introduction: In chemistry molecular orbital (MO) theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule.In this theory, each molecule has a set of molecular orbitals. Objectives: Practice energy diagrams for molecular orbital theory. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
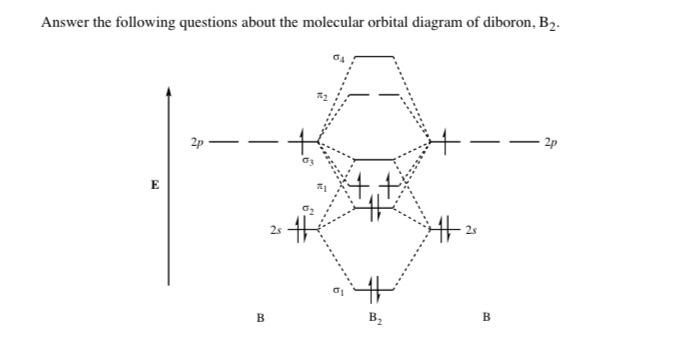
Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic B2 Place the following in order of decreasing X-A-X bond angle, where A represents the central atom and X represents the outer atoms in each molecule. A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals method in particular. However the bond order of b2 124 2 1. This means there are 5 valence electrons. As discussed in class the MO diagram for B 2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in the equivalent bond strength of one bond. As discussed in class it is not a bond. This example was covered in class to show the rare exception that this single bond is a bond. Before we get there it is worth while knowing a generic valence molecular orbital diagram where no s-p mixing occurs. This one pretty much applies to all main group elements heavier than nitrogen. The core orbitals, in case of lithium to neon these are the 1s orbitals, sodium to argon these are 1s, 2s, and 2p orbitals, are not included, as they ...
B2 Lewis Structure 35 Images Use The M O Theory Explain Why Be2 Molecule Does Not 5 7a Pi Answered Two Posssible Lewis Structures For The Bartleby
The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2.This video shows the end of the Be2 molecule MO ...
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2+ (this is not B-B. it has an electron missing, so its B-B cation!) The number of unpaired electrons in the B2+ molecule is 2 (two) 1 (one) 3 (three) zero ; Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2+ (this is not B-B. it has an electron missing, so its B-B cation!) The number of unpaired ...
2. The bond order of a homonuclear diatomic molecule can be decreased by. removing electrons from a bonding MO or adding electrons to an antibonding MO. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A) N2^2+. B) B2^2+. C) B2^2-. D) C2^2-. E) B2.

Chapter 10 Bonding And Molecular Structure Orbital Hybridization And Molecular Orbitals Dr S M Condren Ppt Video Online Download
Molecular orbital diagram for b2. By drawing molecular orbital diagrams for b2 c2 n2 o2 and f2 predict which of these homonuclear diatomic molecules are magnetic. The molecular orbital diagram for an o 2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals.
Use The Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram To Show That N 2 Would Be Expected To Have A Triple Bond F 2 A Single Bond And Ne 2 No Bond
Molecular orbitals the region an electron is most likely to be found in a molecule. I drew a diagram of b2 in which i filled both bonding and anti bonding orbitals of 2s sigma and 2s sigma. Draw molecular diagram of h2 b2 and n2. A number of valence electrons of each boron atom 3in the formation of b2 molecule three valence electrons of each ...
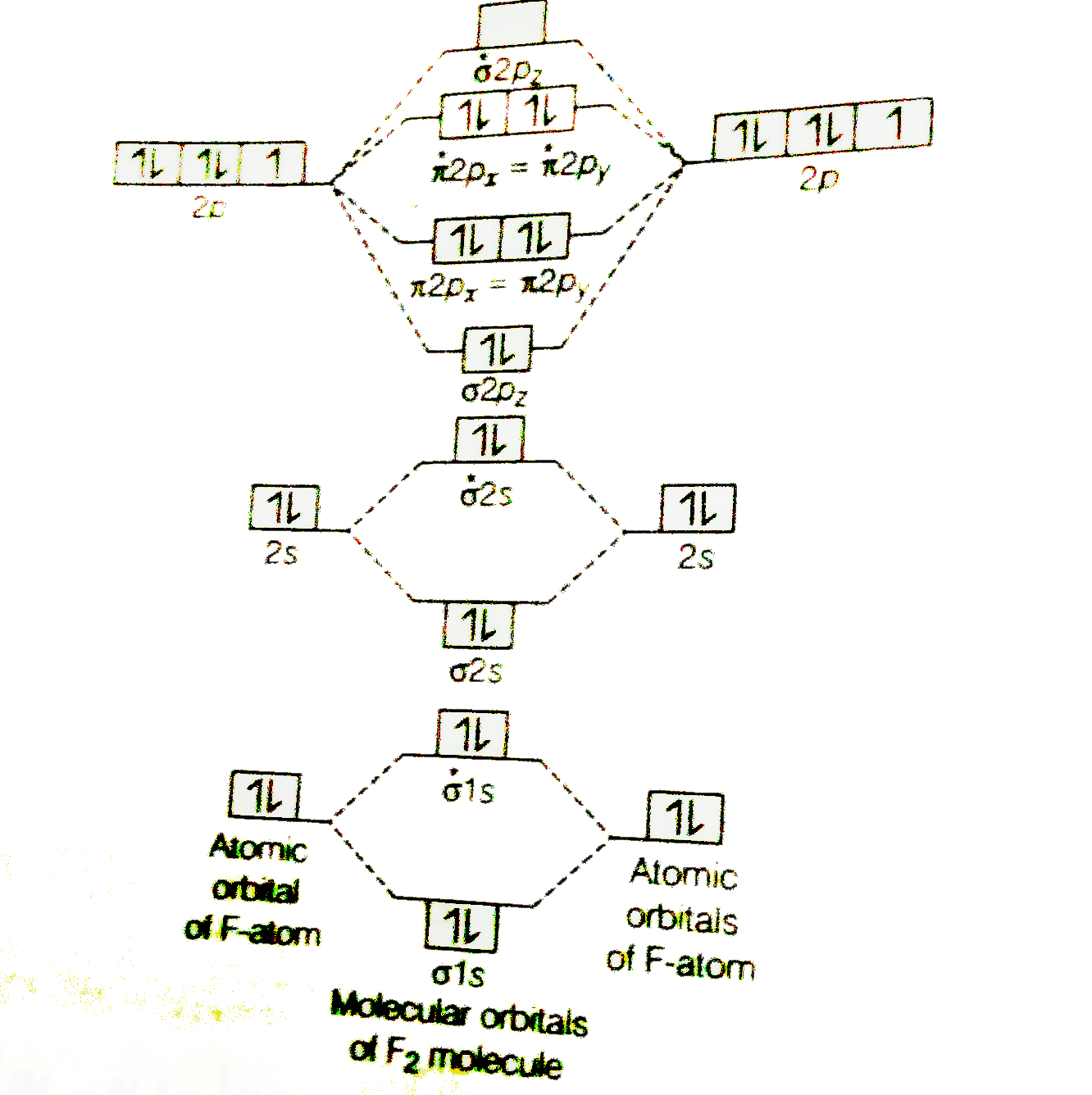
Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For I Be2 Ii B2 And Predict Bond Order And Magnetic Properties From Chemistry Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Class 11 Haryana Board English Medium
According to molecular orbital theory, the atomic orbitals having comparable energy overlap and result in the formation of the same number of molecular orbitals. The molecular orbitals having the same sign combine and give bonding molecular orbitals. We have to draw the molecular orbital diagram for ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule.
Molecular orbital diagram of b2. Fill in the mo diagram that corresponds to each of the molecules given. Therefore this diagram explains the observed paramagnetism of b2. The two electrons from the b 2p orbitals now occupy separate degenerate π2p molecular orbitals and thus have parallel spins. The result is a slight change in the relative ...
2) Use molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2^2-B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A) B2^2+ B) B2^2-C) N2^2+ D) C2^2-E) B2

Scielo Brasil A Brief Introduction To Molecular Orbital Theory Of Simple Polyatomic Molecules For Undergraduate Chemistry Students A Brief Introduction To Molecular Orbital Theory Of Simple Polyatomic Molecules For Undergraduate
Pembuatan Senyawa kompleks asetial asetanoat. Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals. The 2s orbitals will overlap to form 2sσ and 2sσ ...
Answer (1 of 4): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons).
By drawing molecular orbital diagrams for b2 c2 n2 o2 and f2 predict which of these homonuclear diatomic molecules are magnetic. A number of valence electrons of each boron atom 3in the formation of b2 molecule three valence electrons of each boron atom ie. I drew a diagram of b2 in which i filled both bonding and anti bonding orbitals of 2s ...

Part A By Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams For B2 C2 N2 O2 And F2 Predict Which Of These Brainly Com
Electron in Si (removed from) (3)p orbital / electron (removed) from higher energy orbital or sub-shell / electron in silicon is more shielded Predict the element in Period 3 that has the highest second ionisation energy.Give a reason for your answer.
B2 Molecular orbital Diagram. molecular orbital theory b2 this video shows the end of the be2 molecule mo diagram and explains pi orbitals paramagnetism and the mo diagrams for b2 molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules chem in chemistry molecular orbital mo theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms but ...
B2 molecular orbital diagram. Since bond order is zero be 2 molecule does not exist. This was on a quiz and i somehow got the bond order and the lumo indicated wrong. I also calculated the bond order of this molecule to be 32. B 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms.
Molecular simulation of double layer expansion mechanism during low- salinity waterflooding, M Mehana and M Fahes and QJ Kang and H Viswanathan, JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR LIQUIDS, 318, 114079 (2020). (DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114079) abstract
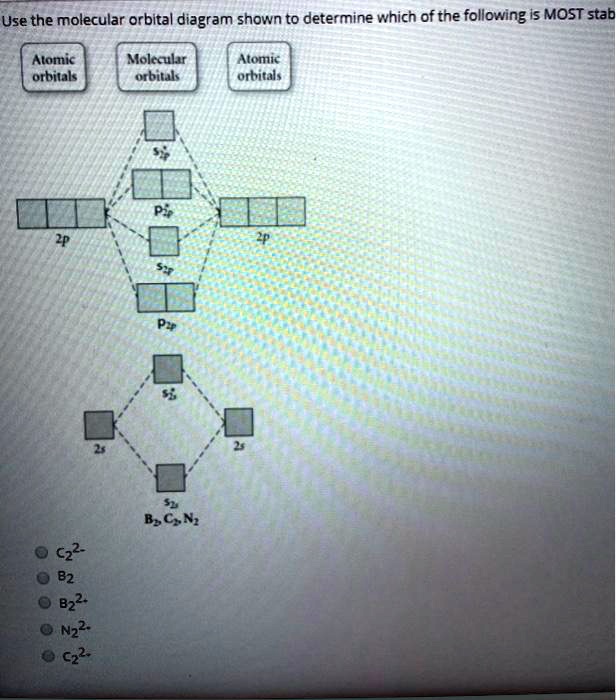
Solved Use The Molecular Orbital Diagram Shown To Determine Which Of The Following Is Most Stab Alomic Orbitals Molaular Orbiuak Alomic Orbital B C N B2 Nz2
(i) Be2 molecule: The electronic configuration of Be(Z = 4) is: 4 Be 1s 2 2s 1 Be 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both beryllium atoms. Number of valence electrons in Be atom = 2 Thus in the formation of Be 2 molecule, two outer electrons of each Be atom i.e. 4 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies.
+ and Be2.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. 1. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following ...
B2 molecular orbital diagram. This also causes a large jump in energy in the 2p σ orbital. For example when two hydrogen atoms bond a σ1s bonding molecular orbital is formed as well as a σ1s antibonding molecular orbital. Valence bond model vs. The molecular orbital diagram for an o 2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both ...
Answer (1 of 7): UNDERSTANDABLE VERSION- See boy... If you are in class 11th then don't look for stuff like this. It hasn't been explained for a good reason. I will explain it to you in very crude terms but not its role in MOT as you wont be able to understand and I am saying this from experience...
In The Mot Diagram Of B2 How Is Pi Orbital Created Before Sigma Doesn T That Violate Normal Formation Quora
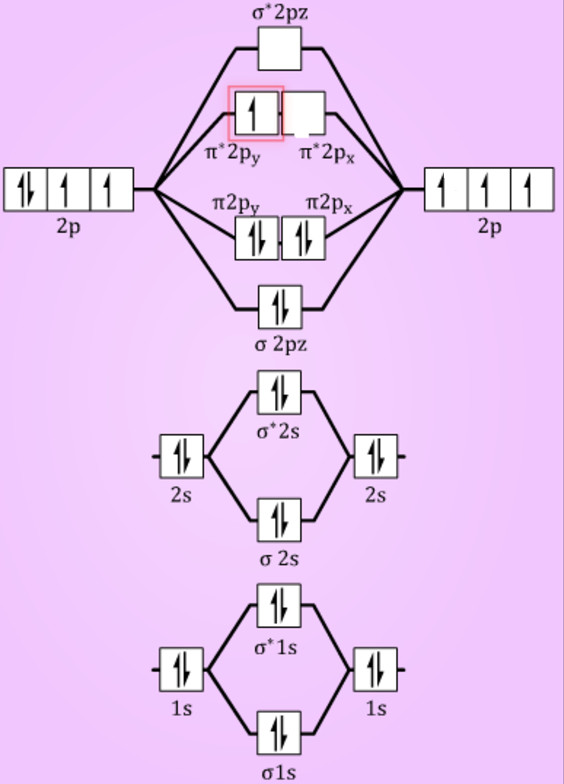
Energy Level Diagram For Molecular Orbitals Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Chemistry Class 11

5 What Is The Bond Order In O2 6 Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For B2 The Number Of Unpaired Electrons In The B2 Molecule Is 7 Which One Of The Following











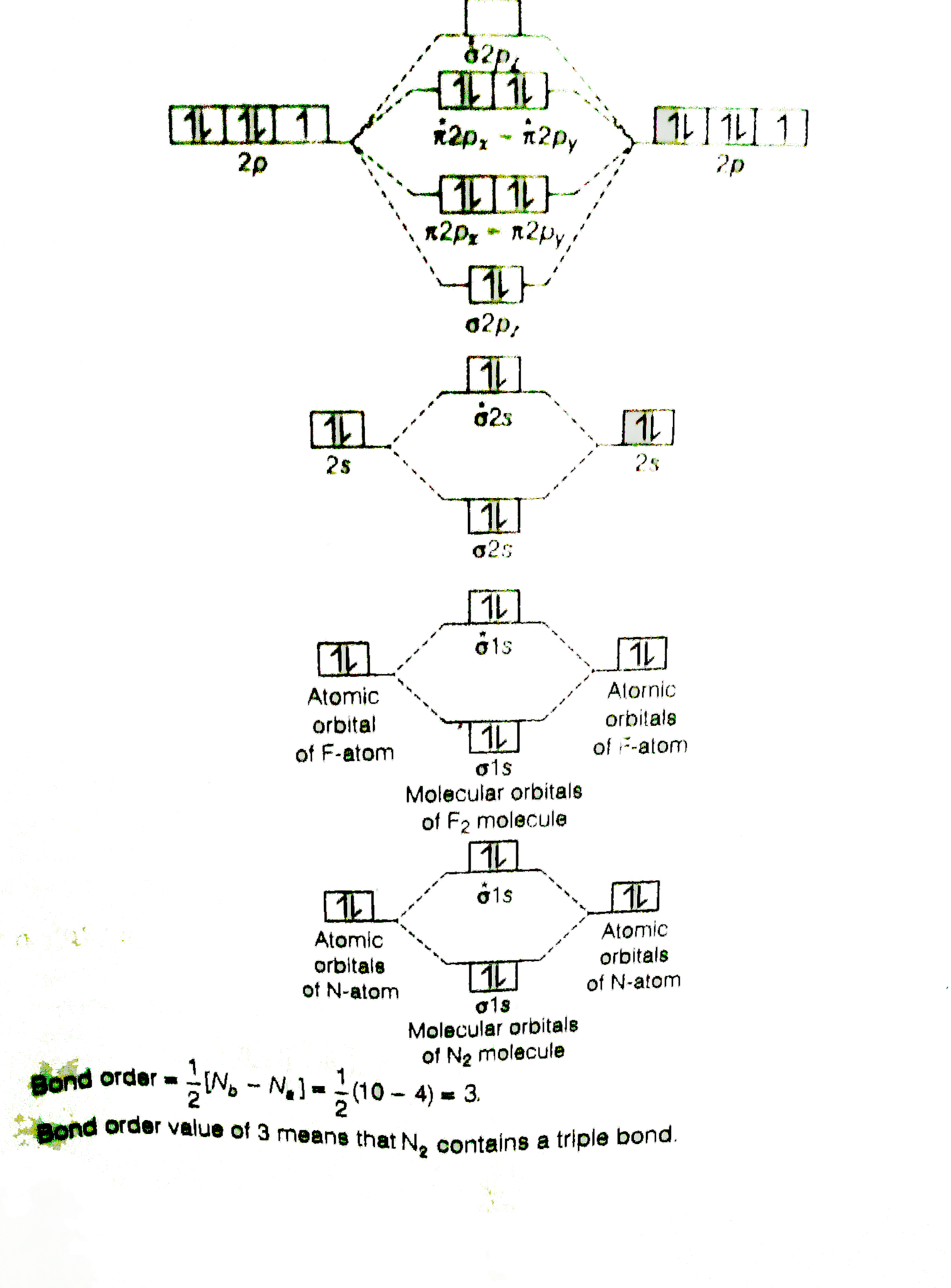

0 Response to "40 b2 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment