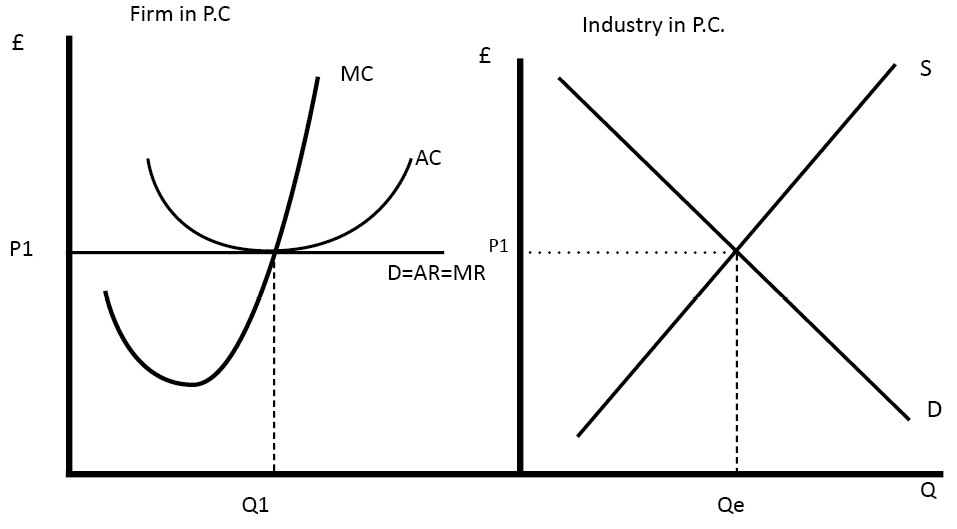
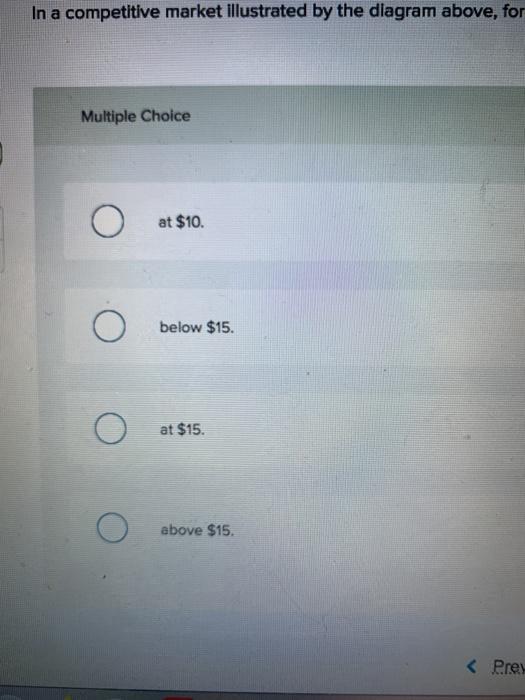
40 in a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above
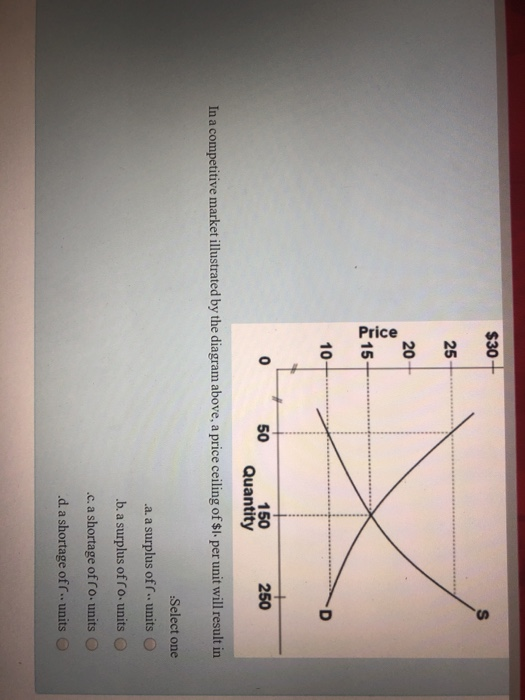
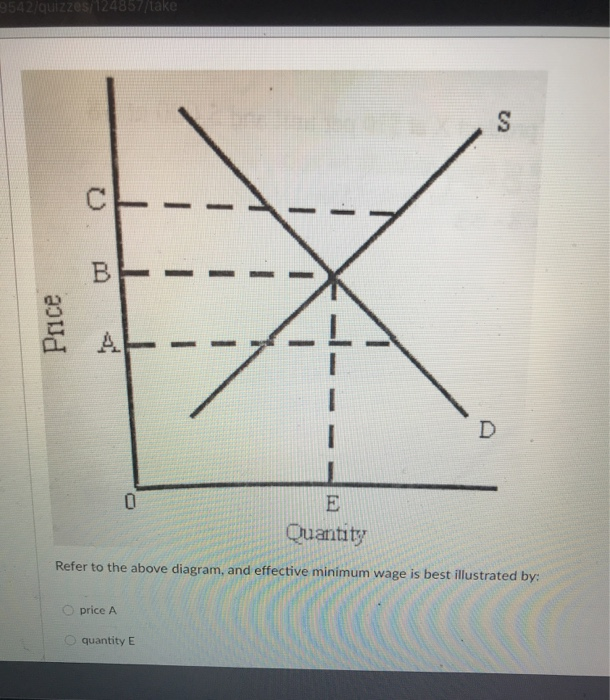
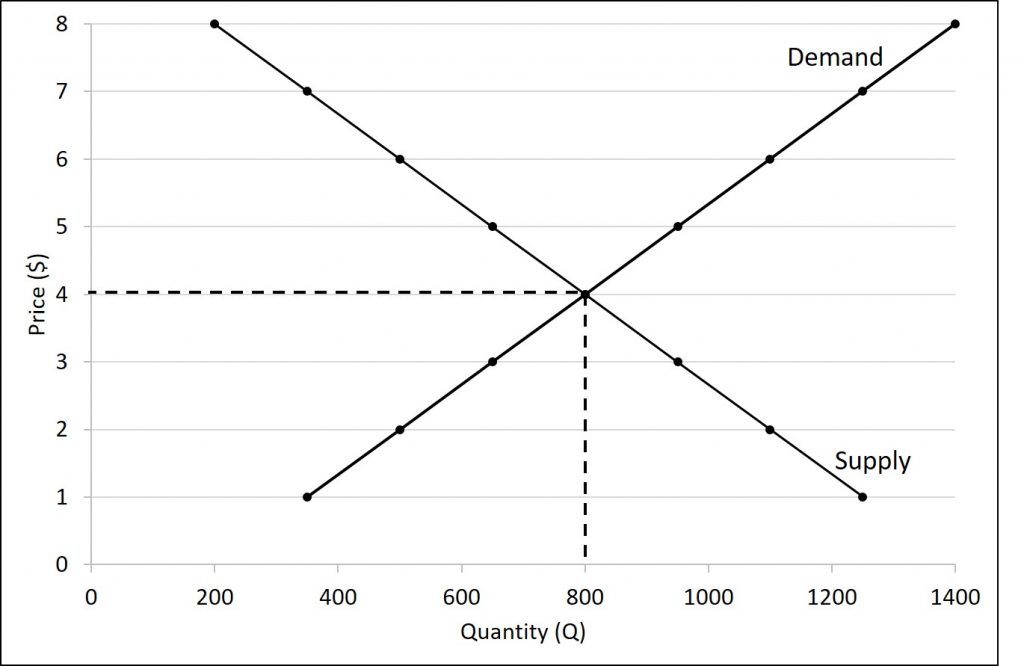
Diagram of Monopoly - Economics Help In a competitive market, the price would be lower and more consumers would benefit Productive inefficiency. A monopoly is productively inefficient because it is not the lowest point on the AC curve. X - Inefficiency. It is argued that a monopoly has less incentive to cut costs because it doesn't face competition from other firms. In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above ... In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above, a price ceiling of $10 per unit will result in A) a shortage of 200 units. B) a surplus of 200 units. C) a surplus of 250 units. D) a shortage of 250 units.
In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above a ... In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above, a price ceiling of $25 per unit will result in: A) The market stays at equilibrium price of $15 B) A surplus of 200 units C) A shortage of 200 units D) A shortage of 150 units Answer: A Topic: Application: Government-Set Prices Difficulty: 3 Hard Learning Objective: 03-05 Bloom's: Level 2 Understand AACSB: Reflective Thinking Refer To: 03-139 [QUESTION] 142.
In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above
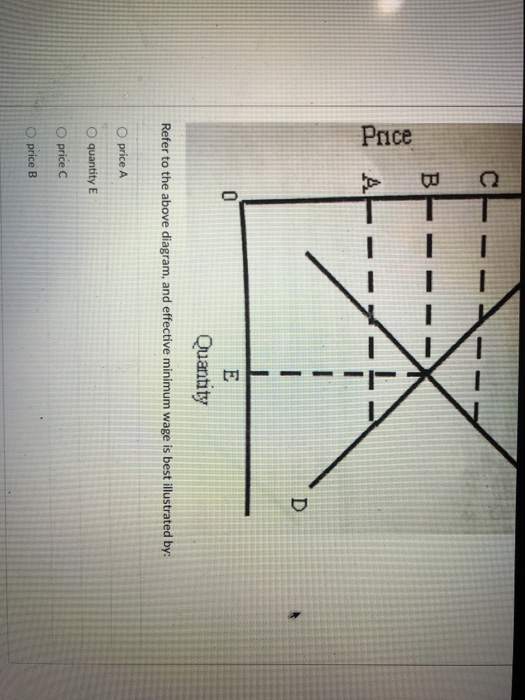
In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above a ... In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above, a price ceiling of $25 per unit will result in: A. The market staying at an equilibrium price of $15 B. A surplus of 200 units C. A shortage of 200 units D. A shortage of 150 units 3-58 Chapter 03 - Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium (+ Appendix) 142. South-Western: Increase in the Minimum Wage Because the cost of hiring an extra worker (the marginal factor cost) exceeds the wage rate, a monopsony firm will hire fewer workers than would be hired in a perfectly competitive labor market. This is illustrated in the diagram below. Price Taker - Learn More About Price Takers vs. Price Makers The example above illustrates that in a perfectly competitive market where the price is set by supply and demand, a single company cannot influence market prices and must accept the prevailing price set by the market. Price Taker vs. Price Maker A price maker is the opposite of a price taker:
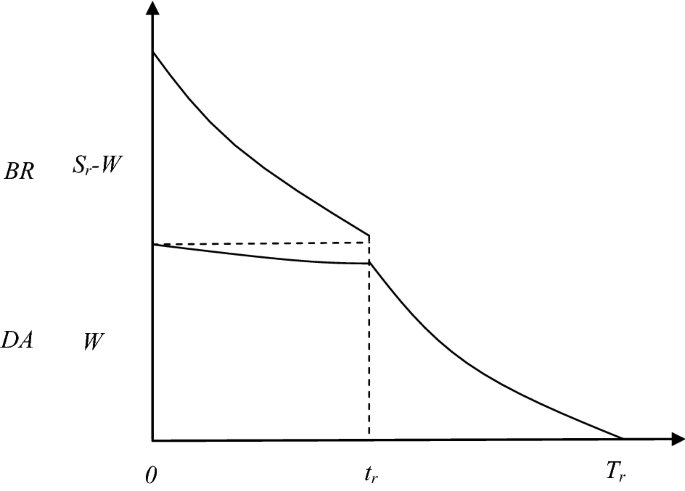
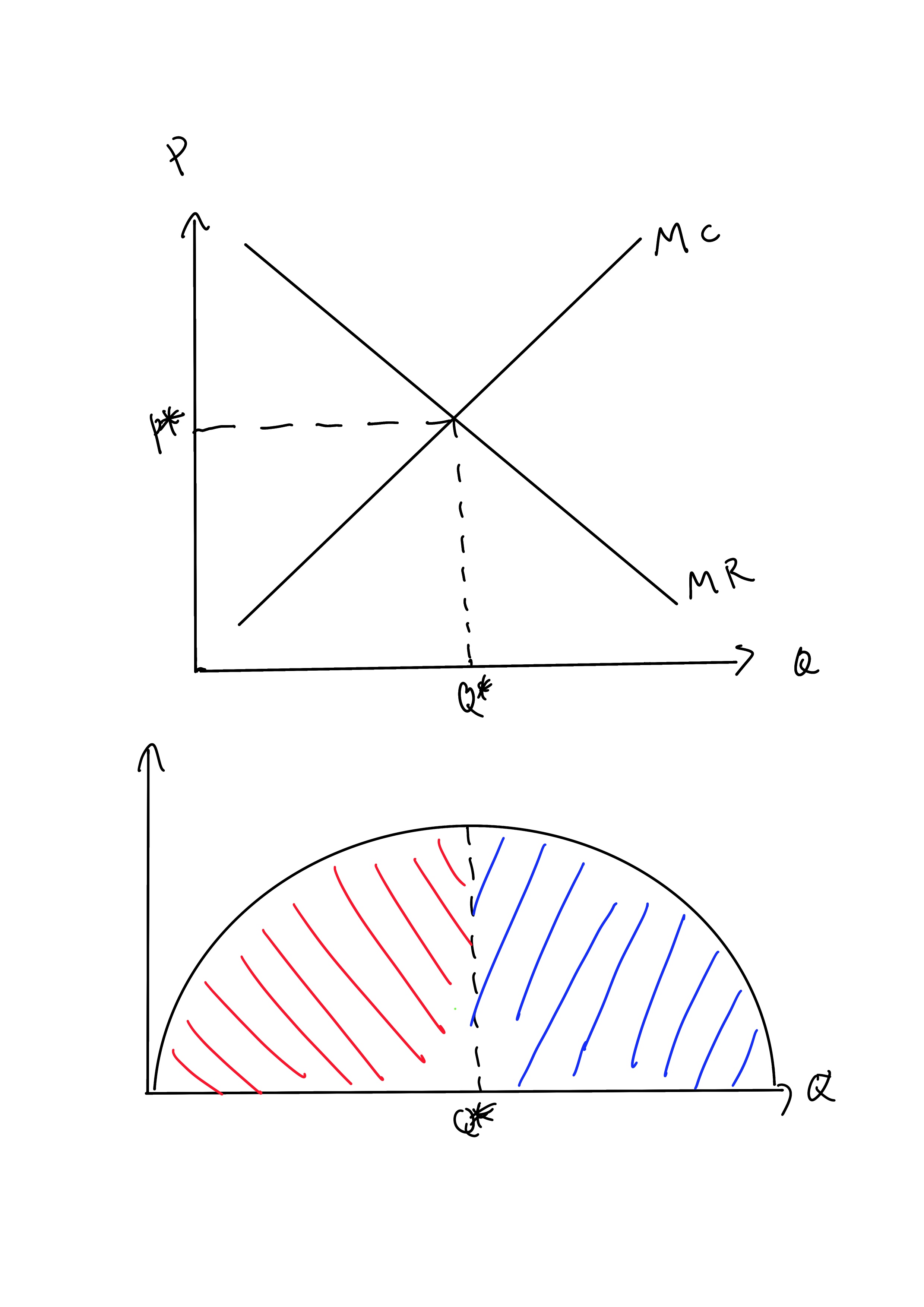
In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above. Profit maximization worked example (video) - Khan Academy Assume corn is produced in a perfectly competitive market. Draw correctly labeled side-by-side graphs for the corn market and a representative corn farmer. On your graphs show each of the following: The equilibrium price and quantity in the corn market, labeled P sub M and Q sub M, respectively. In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram below ... In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram below, a price floor of $25 per unit will result in: asked Aug 9, 2018 in Economics by rmcneill19. A. A shortage of 200 units B. A surplus of 200 units C. A surplus of 250 units D. A shortage of 250 units. principles-of-economics Price Determination under Perfect Competition (With Diagram) In the above diagram, the old price was PM for quantity OM and it rises to P'M' when OM" is demanded and produced. In the same manner, it can be easily shown that a decrease in demand for coal will reduce the price much more. This is so because reduced production will be obtained at a lower cost when the law of diminishing returns operates. Profit Maximization - Quickonomics As mentioned above, we can visualize the principle of profit maximization in a simple diagram (see below). The x-axis represents output quantity (Q), while the y-axis stands for costs and revenue respectively (C and R). Illustration 1: Profit Maximization. The Marginal revenue curve (MR) is a horizontal line at the level of the market price (p*).
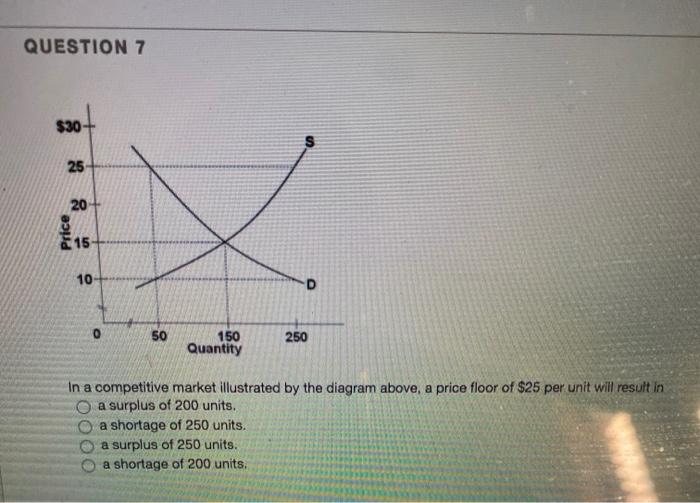
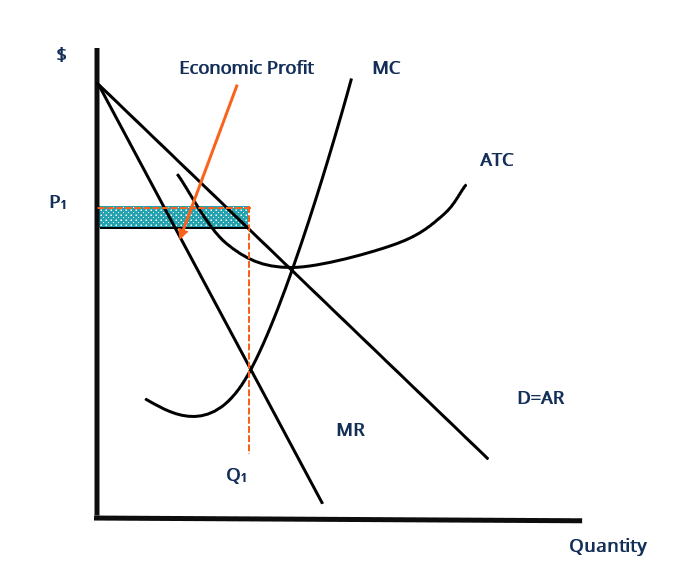
Solved > 131.If a price ceiling is set:1321645 ... | ScholarOn In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above, for a price floor to be effective and alter the market situation, it must be set: A. At $15 B. Below $15 C. Above $15 D. At $10 138. In a market with supply and demand curves as shown above, a price ceiling of $2.50 will result in: A. A surplus of 10 units B. Price Determination under Monopolistic Competition - MA ... In the above diagram, the short run average cost is MT and short run average revenue is MP. Since the AR curve is above the AC curve, therefore, the profit is shown as PT. PT is the supernormal profit per unit of output. Total supernormal profit will be measured by multiplying the supernormal profit to the total output, i.e. PT × OM or PTT'P' as shown in figure (a). In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above ... In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above, a price ceiling of $25 per unit will result in A) the market staying at an equilibrium price of $15. B) a surplus of 200 units. C) a shortage of 200 units. D) a shortage of 150 units. Solved Question 18 1 pts 83 10+ 0 50 150 Quantity In a ... Economics questions and answers. Question 18 1 pts 83 10+ 0 50 150 Quantity In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above, a price floor of $25 per unit will result in a shortage of 200 units. a shortage of 250 units, a surplus of 200 units. a surplus of 250 units.
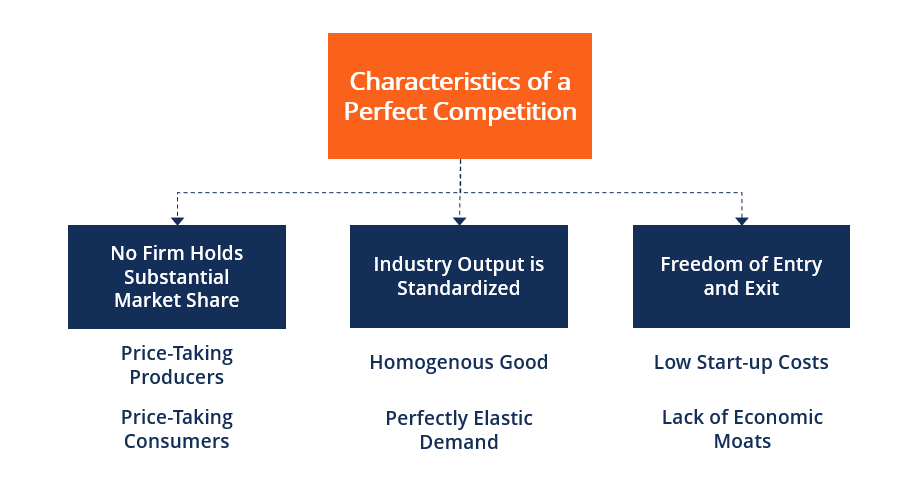
quiz 3 Flashcards | Quizlet In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above, for a price floor to be effective and alter the market situation, it must be set: Above $15. In a market with supply and demand curves as shown above, a price ceiling of $2.50 will result in: No shortage or surplus. 8 Major Causes of Market Failure (Explained With Diagram) This is illustrated in Figure 18.2 where PMC is the private marginal cost curve or supply curve of firms. The demand curve D intersects the PMC curve at point E and determines the competitive market price OP and output OQ. Perfect Competition | Boundless Economics A perfectly competitive market is characterized by many buyers and sellers, undifferentiated products, no transaction costs, no barriers to entry and exit, and perfect information about the price of a good. The total revenue for a firm in a perfectly competitive market is the product of price and quantity (TR = P * Q). Monopoly in a Perfectly Competitive Market (With Diagram) In a competitive market, there is a relationship between price and the quantity supplied. That relationship is the supply curve which tells us how much will be produced at every price. A monopolist has no supply curve. There is no one-to-one relationship between price and the quantity supplied.
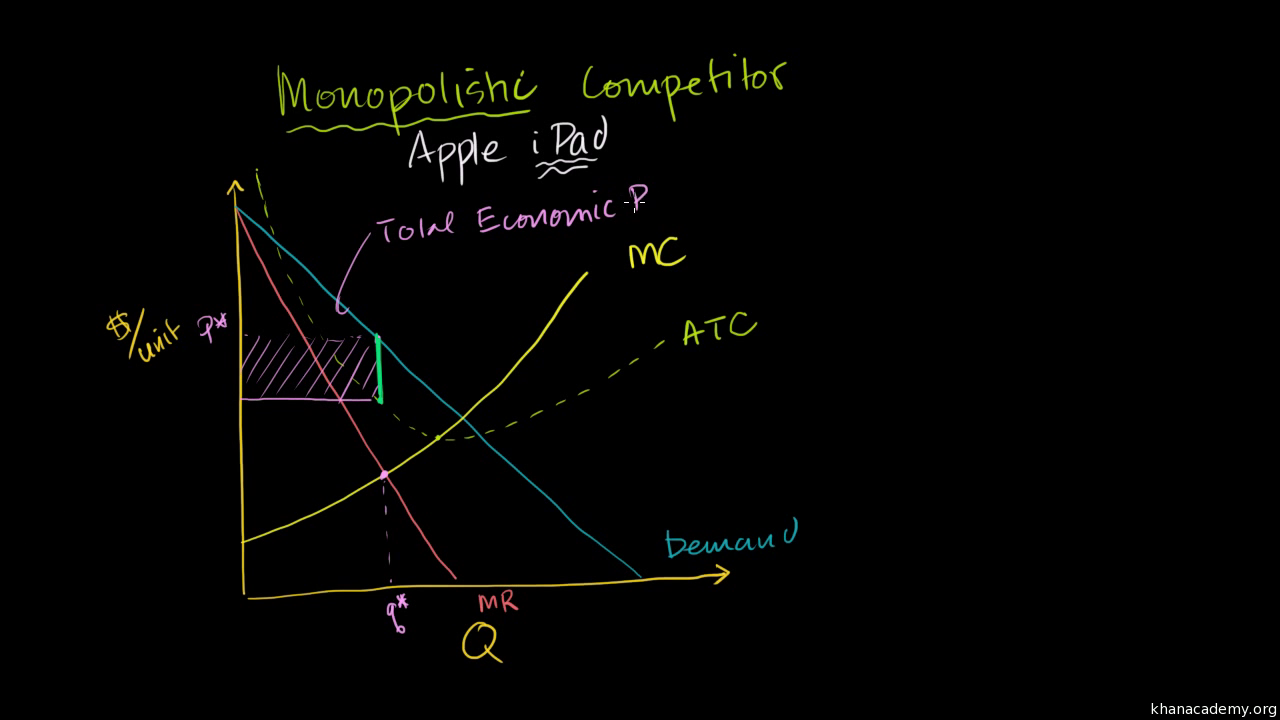
10.1 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Economics In a perfectly competitive market, each firm produces at a quantity where price is set equal to marginal cost, both in the short run and in the long run. This outcome is why perfect competition displays allocative efficiency: the social benefits of additional production, as measured by the marginal benefit, which is the same as the price, equal ...
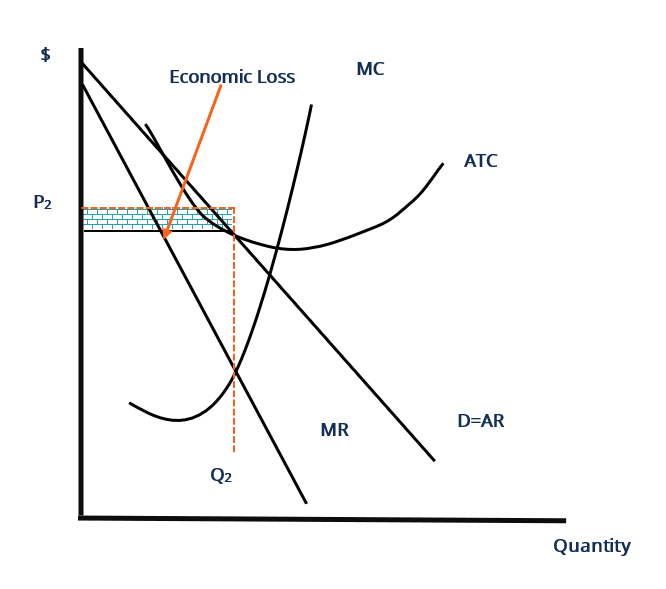
Deadweight Loss - Examples, How to Calculate Deadweight Loss In a perfectly competitive market, which comprises. In imperfect markets, companies restrict supply Law of Supply The law of supply is a basic principle in economics that asserts that, assuming all else being constant, an increase in the price of goods to increase prices above their average total cost. Higher prices restrict consumers from ...
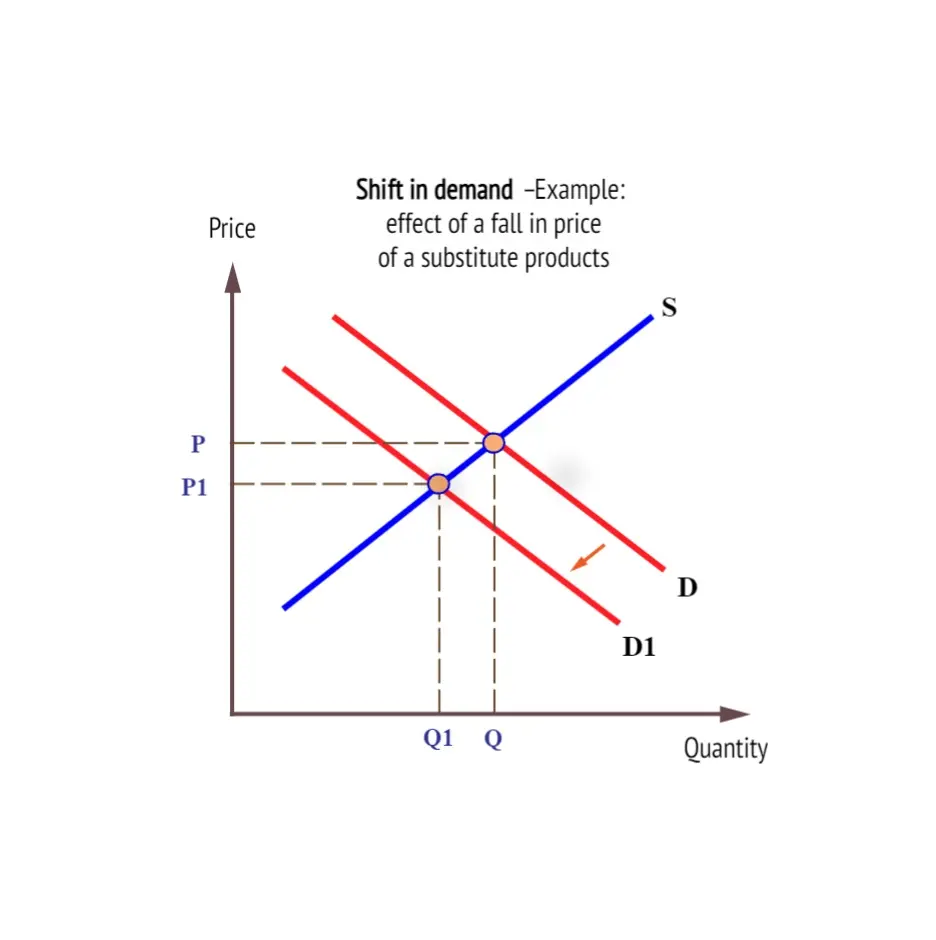
PDF Student: - Mount Saint Mary College Refer to the above diagram, which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for product X. Given D0, if the supply curve moved from S0to S1, then:€ € A.€supply has increased and equilibrium quantity has decreased. B.€supply has increased and price has risen to 0G. C.€there has been an increase in the quantity supplied.
5.2 Indirectly Correcting Externalities - Principles of ... The following TWO questions refer to the diagram below, which illustrates the supply and demand curves for a perfectly competitive market. Assume that each unit of output results in a marginal external cost of $5. 3. In the absence of government intervention, what will the deadweight loss equal? a) $0. b) $30. c) $60.
Solved In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram ... See the answer In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above, a price floor of $25 per unit will result in Multiple Choice a surplus of 200 units. a shortage of 200 units. a shortage of 250 units. a surplus of 250 units. Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 88% (16 ratings)
In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram below ... In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram below, for a price floor to be effective and alter the market situation, it must be set: asked Aug 9, 2018 in Economics by Kindred A.
3.1 Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium in Markets for Goods ... This above-equilibrium price is illustrated by the dashed horizontal line at the price of $1.80 in Figure 3. At this higher price, the quantity demanded drops from 600 to 500. This decline in quantity reflects how consumers react to the higher price by finding ways to use less gasoline.
The Equilibrium Wage | S-cool, the revision website The point where MRP = MFC on the labour diagram is above the supply curve from which the wage is obtained. The two sentences are the same except for the bits in italics. The implication of all this is that the monopsonist pays a lower wage (W1 < W2) and employs fewer workers (L1 < L2) than if the industry had a perfectly competitive labour market.
econ ch 3 Flashcards - Quizlet In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above, a price ceiling of $25 per unit will result in: The market stays at equilibrium price of $15 The ___________ is the only price where quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied.
Competitive Markets - Revision World Dynamics of Competition and Competitive Market Processes. In addition to efficiency there are a number of benefits that in the short and long run can lead to a number of benefits. In perfectly competitive markets firms need to keep their costs to a minimum this results in reduced wastage of resources. Competition in the domestic market ...
What postulate is illustrated by the diagram above ... What postulate is illustrated by the diagram above? - 8919699
Price Taker - Learn More About Price Takers vs. Price Makers The example above illustrates that in a perfectly competitive market where the price is set by supply and demand, a single company cannot influence market prices and must accept the prevailing price set by the market. Price Taker vs. Price Maker A price maker is the opposite of a price taker:
South-Western: Increase in the Minimum Wage Because the cost of hiring an extra worker (the marginal factor cost) exceeds the wage rate, a monopsony firm will hire fewer workers than would be hired in a perfectly competitive labor market. This is illustrated in the diagram below.
In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above a ... In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above, a price ceiling of $25 per unit will result in: A. The market staying at an equilibrium price of $15 B. A surplus of 200 units C. A shortage of 200 units D. A shortage of 150 units 3-58 Chapter 03 - Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium (+ Appendix) 142.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Supply_and_demand_curves-5c5dd1bb46e0fb0001849d18.png)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Neg-Ext-Prod-2-56a27da73df78cf77276a5be.png)








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/fashion-and-consumerism-concept-smart-man-with-beard-choosing-clothes-in-clothing-store-at-shopping-center--looking-for-new-shirts-design-that-hanging-on-the-rail-961651632-5c49f0e946e0fb00014a9d85.jpg)



0 Response to "40 in a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above"
Post a Comment