40 cellular respiration electron transport chain diagram
› bitesize › guidesElectron transport chain - Cellular respiration - Higher ... The electron transport chain is the last stage of the respiration pathway and is the stage that produces the most ATP molecules. The electron transport chain is a collection of proteins found on ... Cellular Respiration Diagram | Quizlet Cellular Respiration. The catabolic pathways of aerobic and anaerobic respiration, which break down organic molecules and use an electron transport chain for the production of ATP. Chemiosmosis. An energy-coupling mechanism that uses energy stored in the form of a hydrogen ion gradient across a membrane to drive cellular work, such as the ...
Electron Transport Chain Diagram - 17 images - chapter 9 ... Here are a number of highest rated Electron Transport Chain Diagram pictures upon internet. We identified it from trustworthy source. Its submitted by management in the best field. We acknowledge this nice of Electron Transport Chain Diagram graphic could possibly be the most trending subject subsequent to we ration it in google lead or facebook.

Cellular respiration electron transport chain diagram
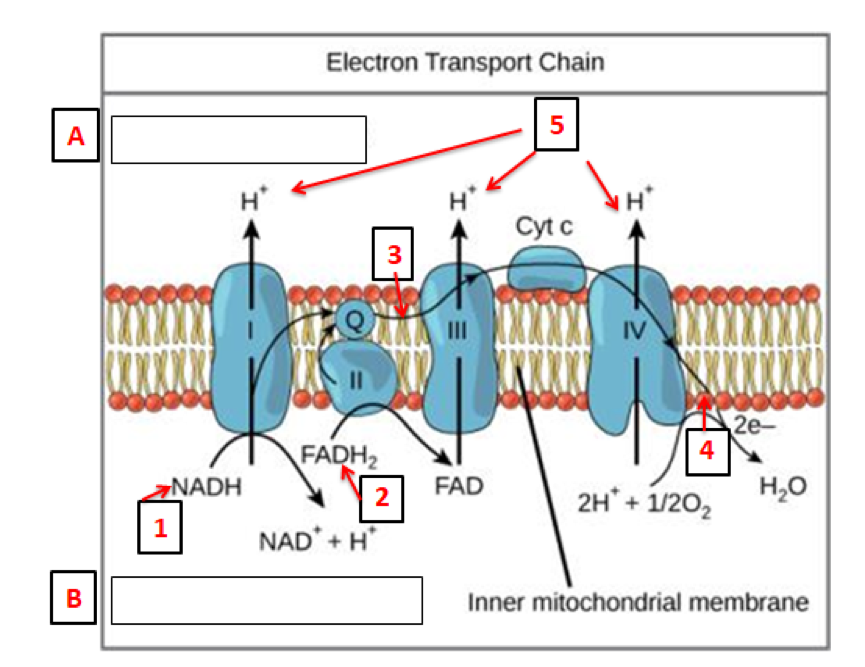
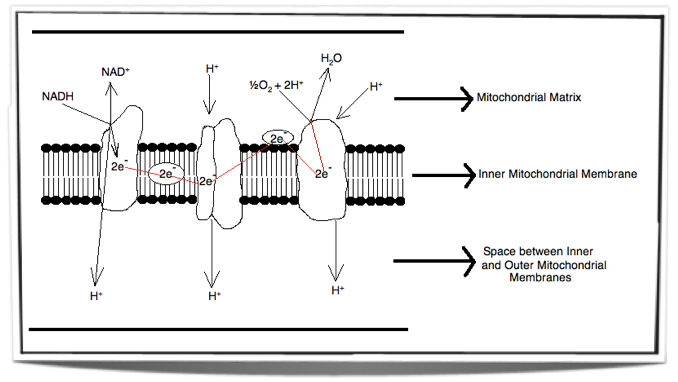
› cell_respirationCellular Respiration - Exploring Nature More About Cellular Respiration So now we know that cellular respiration is a three stage process that converts glucose and oxygen to ATP and releases carbon dioxide and water. What are the 3 phases that do this? 1) Glycolysis 2) Krebs Cycle 3) The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) This is a very simple overview of these 3 stages: Glycolysis (Stage 1) PDF 2.5 D: Cellular Respiration Quiz PROCTOR VERSION The electron transport chain is a part of cellular respiration. The diagram below shows the movement of ions in the electron transport chain within a mitochondrion. € € Which statement best describes the movement of ions shown in the diagram? (A) The electron transport chain is used to move hydrogen ions to the inner membrane space, Cellular Respiration Diagram | Quizlet Cellular respiration that uses glycolysis and fermentation when no oxygen is present, producing about 2 ATP per molecule of glucose Inner mitochondrial membrane The location of electron transport chains and ATP synthase, folded many times to increase surface area
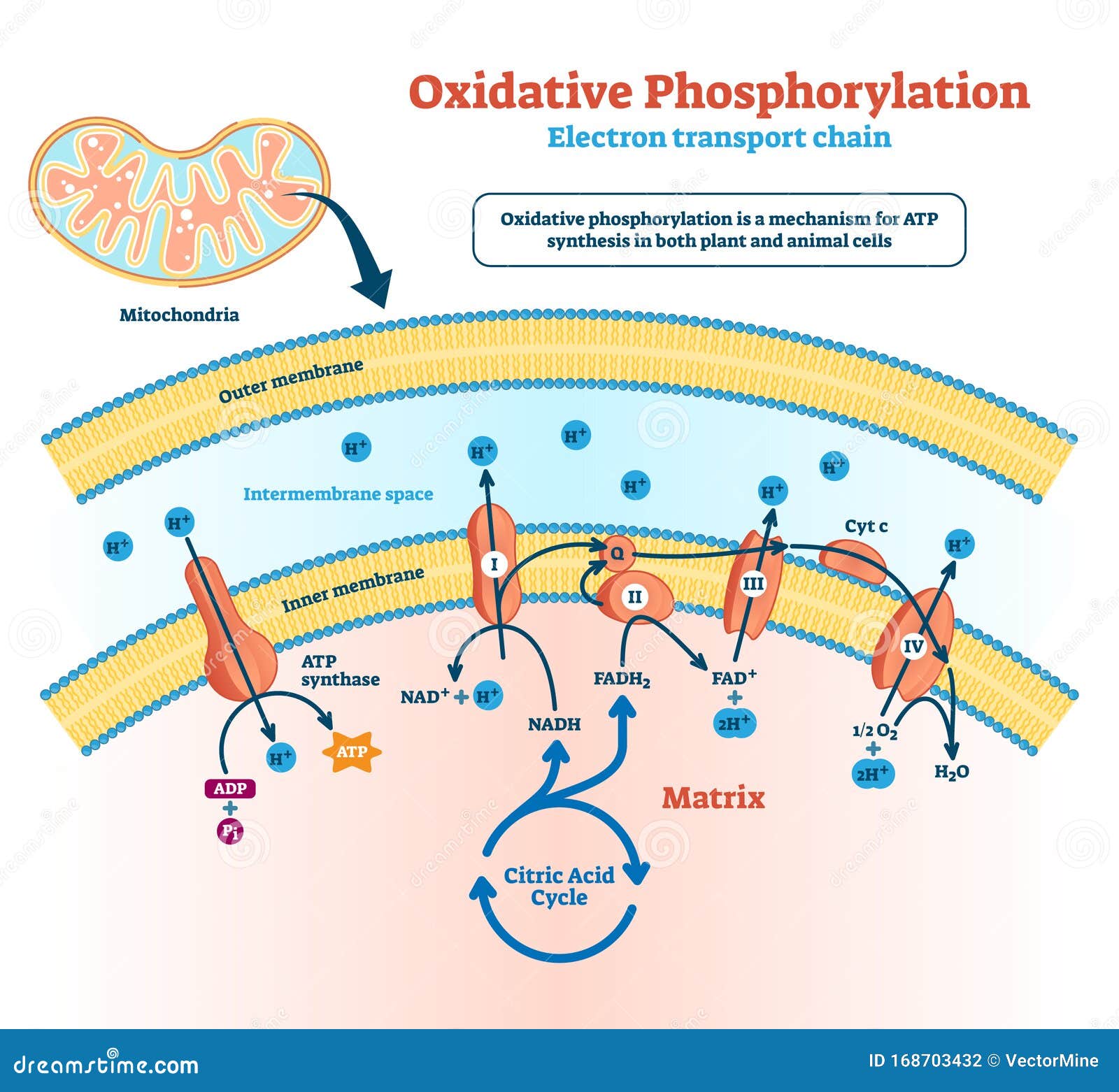
Cellular respiration electron transport chain diagram. Oxidative phosphorylation | Biology (article) | Khan Academy Oxidative phosphorylation is made up of two closely connected components: the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis. In the electron transport chain, electrons are passed from one molecule to another, and energy released in these electron transfers is used to form an electrochemical gradient. In chemiosmosis, the energy stored in the ... Electron Transport Chain of Cellular Respiration - Page 2 It is easiest to understand how electron transport works by dividing this process into three main events: In the electron transport chain, these electron carriers are oxidized, transferring their electrons to the carrier molecules embedded in the ETC membrane. In aerobic respiration, these electrons are passed from one carrier molecule to ... 10 Difference Between Cellular Respiration And ... Cellular respiration on the other hand, uses glucose molecules and oxygen to produce ATP molecules and carbon dioxide as the by-product. Electron Transport Chain. In photosynthesis, the electron transport chain occurs at the beginning of the process, however, in cellular respiration, the electron transport chain occurs at the end of the process. Cellular Respiration Simple Diagram - Weavingaweb Cellular respiration diagram biologywise after successful pletion of the krebs cycle begins the electron transport chain as you can see in the diagram this stage is where energy is released in bulk in the process of cellular respiration it requires direct use of oxygen molecules this is also known as the oxidative phosphorylation process cellular.
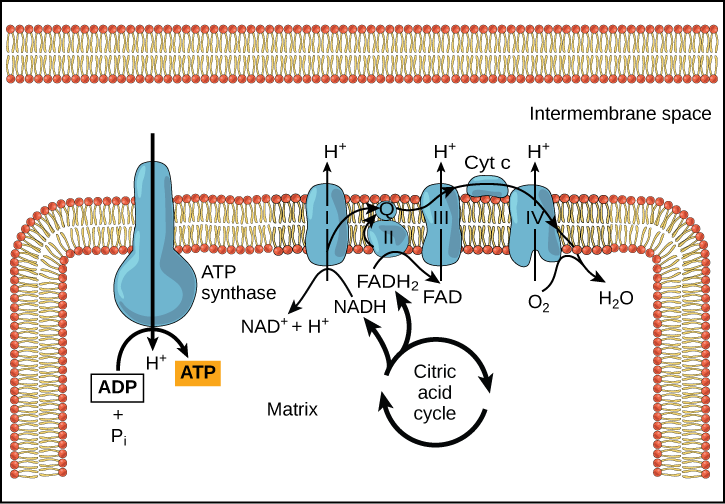
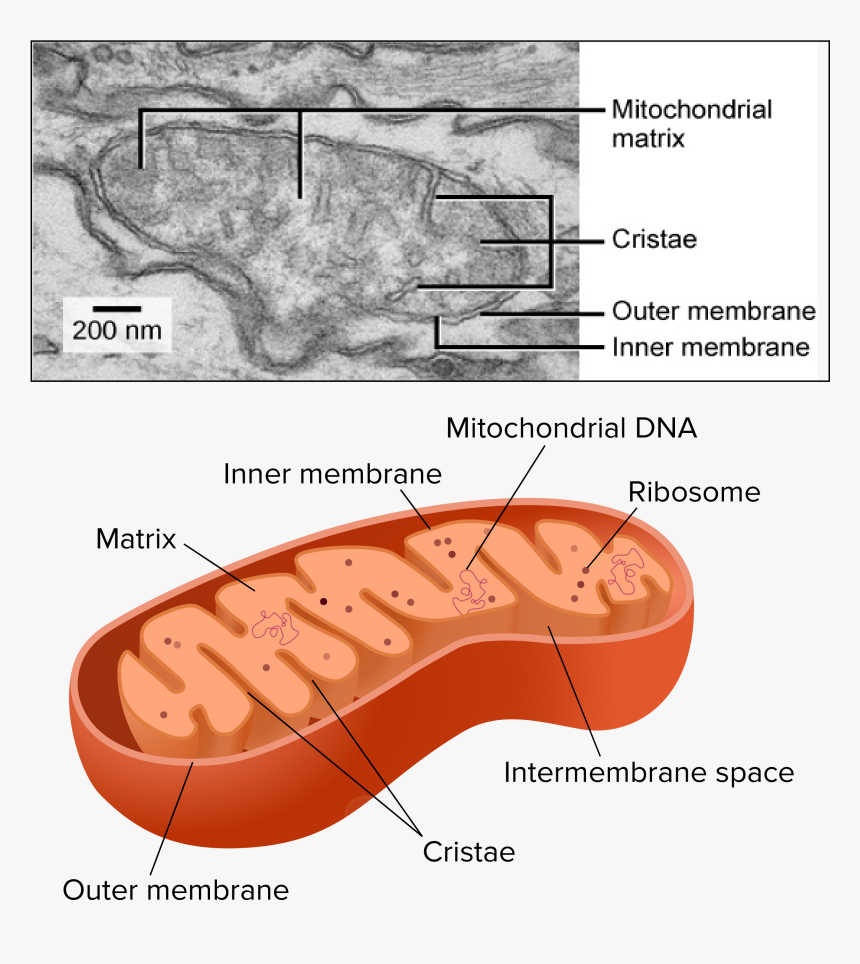
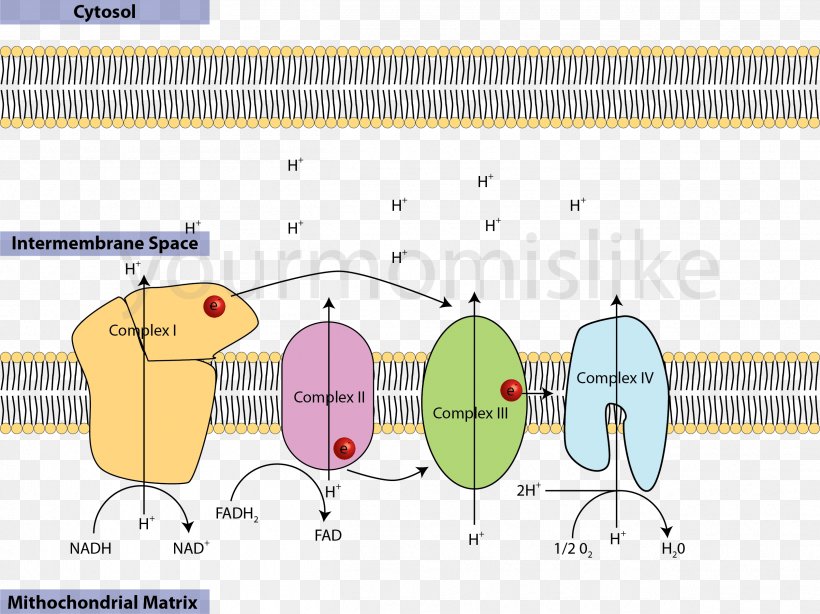
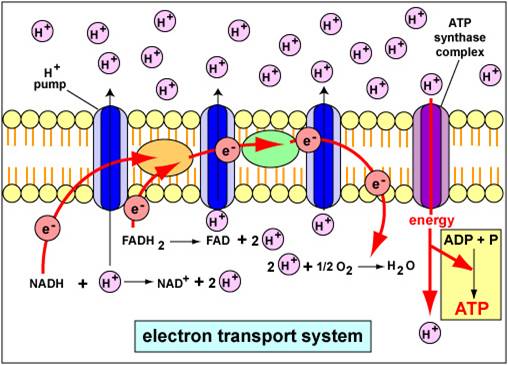
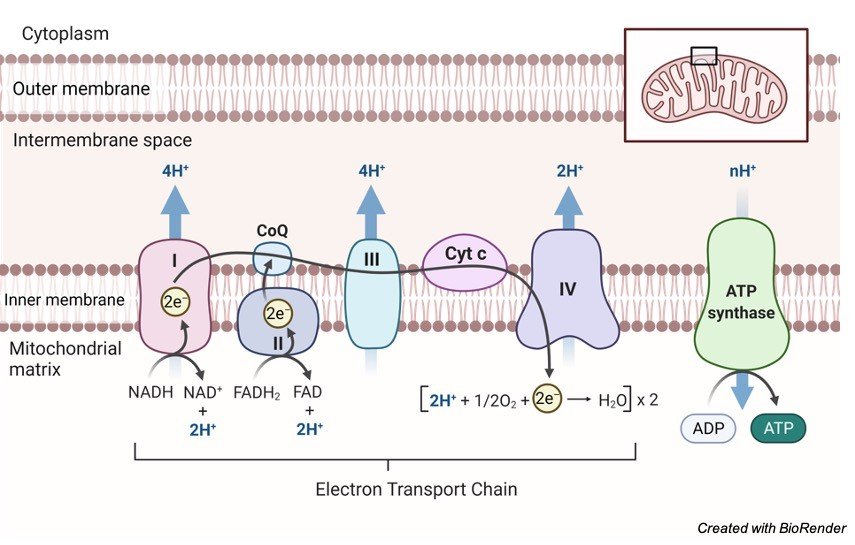
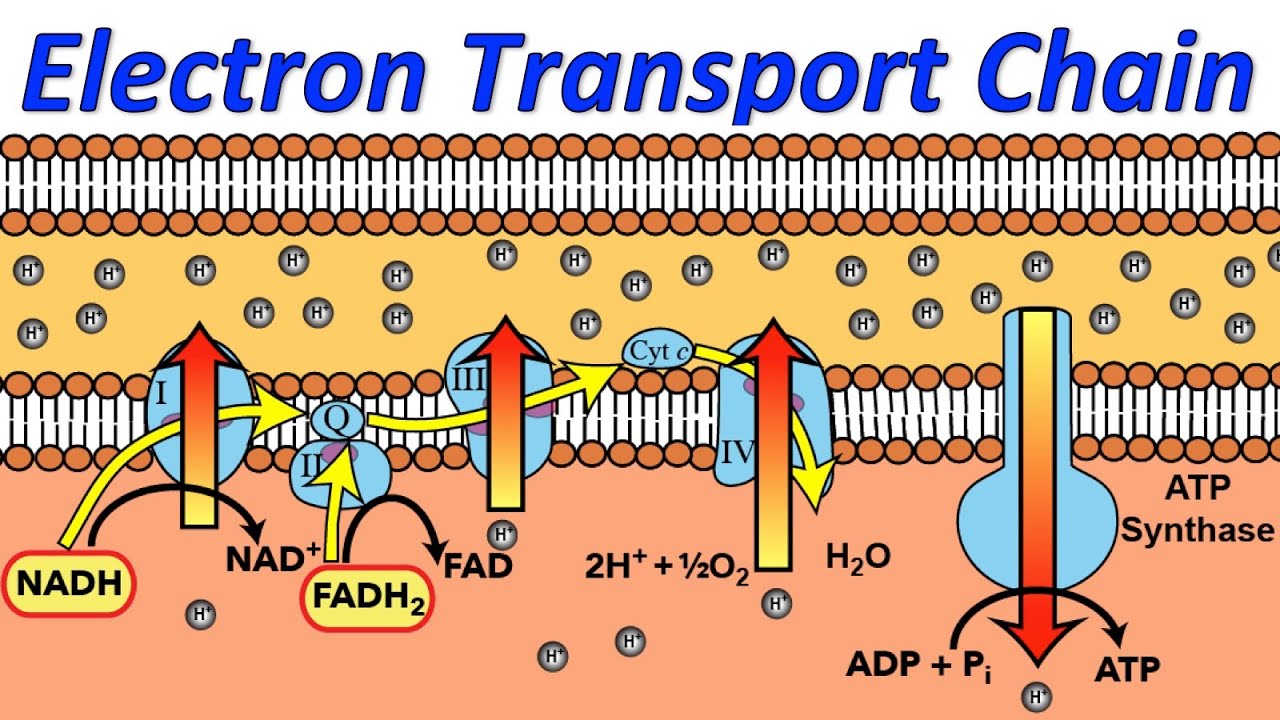
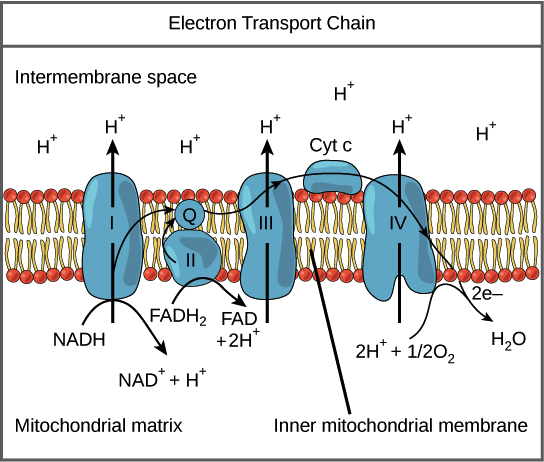
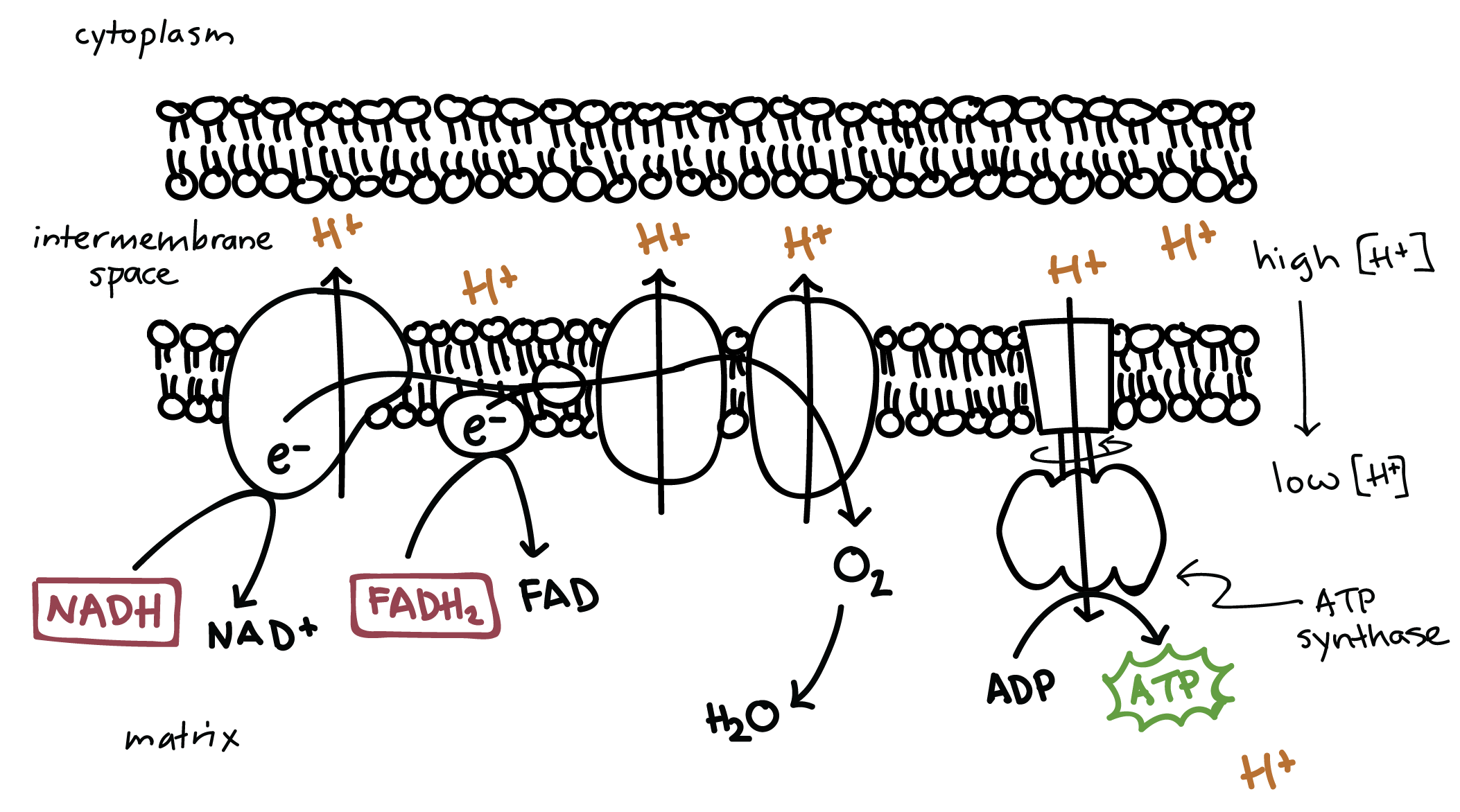
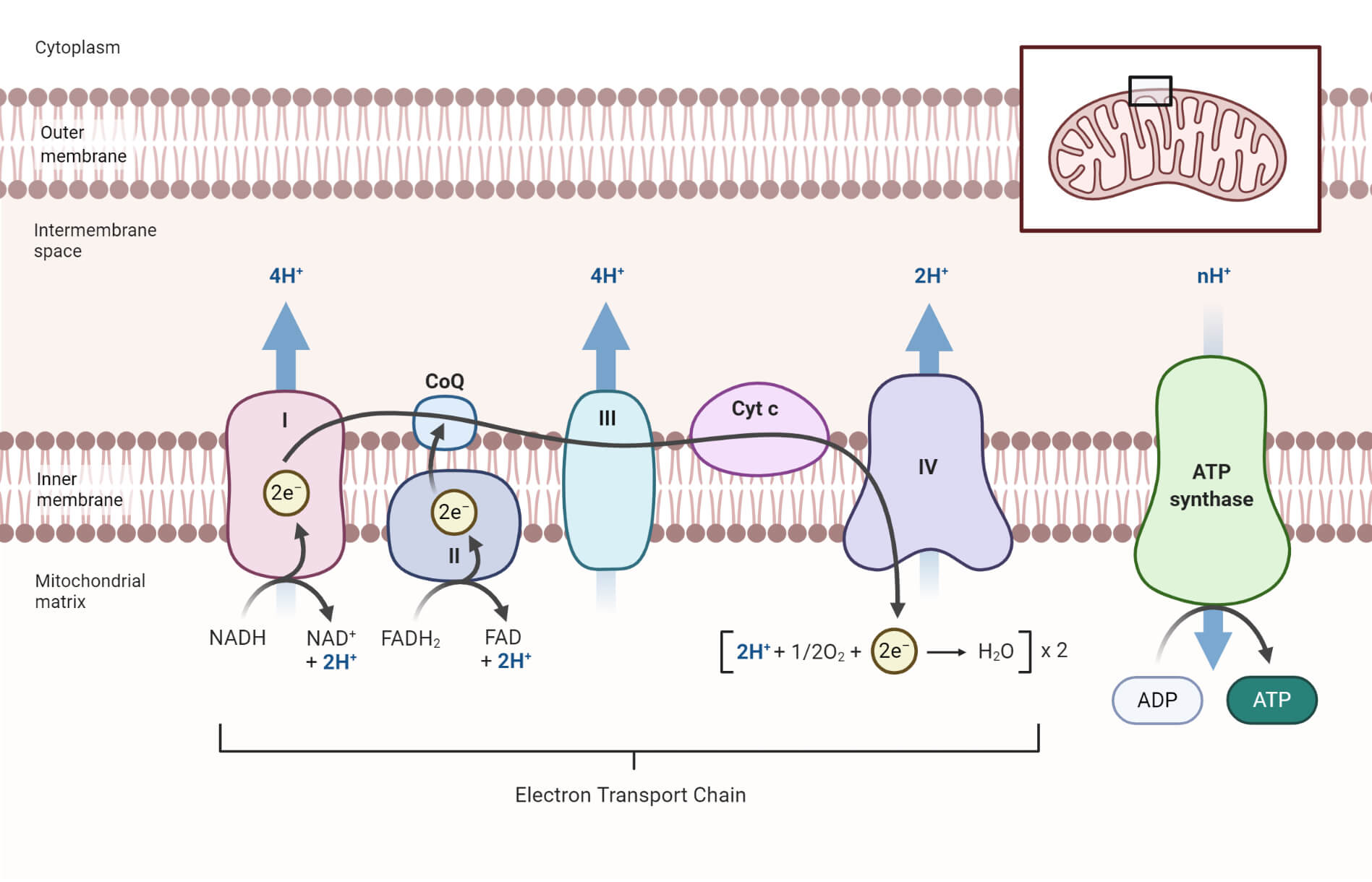
courses.lumenlearning.com › wm-biology1 › chapterElectron Transport Chain | Biology for Majors I There are four complexes composed of proteins, labeled I through IV in Figure 1, and the aggregation of these four complexes, together with associated mobile, accessory electron carriers, is called the electron transport chain. The electron transport chain is present in multiple copies in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes and the plasma membrane of prokaryotes. Note, however, that the electron transport chain of prokaryotes may not require oxygen as some live in anaerobic ... Cellular Respiration.pdf - 1 Cellular respiration = the ... ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN The excited hydrogens are passed along from one member of the chain to the next. They lose energy as they go. That energy is used to make a lot of ATP's. Bucket of excited hydrogens Oxygen tank Oxygen + hydrogen = water A coenzyme that picks up excited H's In this cartoon, the truck represents a coenzyme called NAD (remember, a coenzyme is a chemical that helps ... PDF Chapter 9 Study Guide - Mrs. Luzier's Science Classroom - Home Electron Transport Chain The electron transport chain uses the high-energy electrons produced by the Krebs cycle to move hydrogen ions from one side of the inner membrane to the other. Label the diagram with the following terms: electron, hydrogen ion, and inner membrane. Intermembrane space 2 H20 FADH2 2 NADH FAD 2 NAD* 4 H+ 02 Matrix › metabolism › electronElectron Transport Chain of Cellular Respiration 2. conversion of acetyl-CoA, 3. Kreb’s cycle & 4. electron transport. Electron transport is the most complex and productive pathway of cellular respiration. During aerobic respiration, the ETC produces 34 of the 38 ATP molecules obtained from every molecule of glucose.
Cellular Respiration Diagram - Labelled diagram Drag and drop the pins to their correct place on the image.. In Cytoplasm, In Mitochondria, Glucose, ATP, Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport Chain, Glycolysis. BIO 151-Cellular Respiration 7. Describe the role of NAD+ and the electron transport chain during respiration. 8. Describe the cellular regions where glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain occur. 10. Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. 11. › lifesciences › StevenChapter 6: CELLULAR RESPIRATION Electron Transport High energy electrons (e-) from NADH, FADH 2 transferred to e-transport chain (ETC) Energy released through e-transport used to create H+ gradient (necessary to make ATP) • ETC is a series of proteins in the inner mitochondrial membrane through which e-are passed • H+ pumped across inner mitochondrial membrane out of the matrix into the intermembrane space Electron Transport Chain Steps Explained with Diagram ... Electron Transport Chain Steps Explained with Diagram. The electron transport chain is an essential metabolic pathway that produces energy by carrying out a series of redox reactions. This BiologyWise article provides a simple explanation of this pathway.
biologywise.com › cellular-respiration-diagramCellular Respiration Diagram - Biology Wise Electron Chain Transport. After successful completion of the Krebs cycle, begins the electron transport chain as you can see in the diagram. This stage is where energy is released in bulk in the process of cellular respiration. It requires direct use of oxygen molecules. This is also known as the oxidative phosphorylation process. Electrons are passed from the organic acids of Krebs cycle to the electron acceptor as shown in the diagram above.
Cellular Respiration Equation, Types, Stages, Products ... Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, "biological machines" also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as ATP).Basically, ATP serves as the main energy currency of the cell.
Solved Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration A. MATCH THE ... Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration A. MATCH THE LETTER IN THE DIAGRAM WITH THE LABEL: (You can use them MORE THAN ONCE or NOT AT ALL) B Place where glycolysis happens. E D Place where enzymes for the Electron Transport Chain are located. Place that fills with H+ ions as electrons move down the Electron transport chain.
The Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation ... The Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation (Interactive Tutorial) 1. Introduction. In the previous tutorials in this series about cellular respiration, we've seen how glycolysis, the link reaction, and the Krebs cycle oxidize food so that the mobile electron carriers NAD + and FAD can be reduced to NADH and FADH 2, respectively.
DOC CELLULAR RESPIRATION - Monroe Township School District The Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Chain. MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle the answer or answers that best complete the statement or answer the question. (THERE MAY BE MORE THAN ONE RIGHT ANSWER.) Which of the following shows the correct sequence during cellular respiration? A. Electron transport chain → glycolysis → Krebs cycle
IB Biology Notes - 8.1 Cell respiration The Electron Transport Chain. Inside the inner membrane of the mitochondria there is a chain of electron carriers. This chain is called the electron transport chain. Electrons from the oxidative reactions in the earlier stages of cell respiration pass along the chain. NADH donates two electrons to the first carrier in the chain.
Steps of cellular respiration | Biology (article) | Khan ... Steps of cellular respiration. Overview of the steps of cellular respiration. Glycolysis. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). ATP and NADH are made. These reactions take place in the cytosol. Pyruvate oxidation. Pyruvate travels into the mitochondrial matrix and is converted to a two-carbon molecule bound to ...
Cellular Respiration Cycle Diagram - Diy Color Burst Cellular respiration diagram biologywise after successful pletion of the krebs cycle begins the electron transport chain as you can see in the diagram this stage is where energy is released in bulk in the process of cellular respiration it requires direct use of oxygen molecules this is also known as the oxidative phosphorylation process cellular.
Cellular Respiration, the details, Part 1 (HS Interactive ... The electron transport chain uses this electron energy to create ATP. Here's another analogy that might help. If cellular respiration were a game of football and energetic electrons were the ball, then the end zone would be the inner membrane of the mitochondria (where the electron transport chain is found).
› books › NBK526105Biochemistry, Electron Transport Chain - StatPearls - NCBI ... The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation. It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis. In the former, the electrons come from breaking down organic molecules, and energy is released.
Cellular Respiration Diagram Mitochondria - Idalias Salon Cellular respiration diagram biologywise after successful pletion of the krebs cycle begins the electron transport chain as you can see in the diagram this stage is where energy is released in bulk in the process of cellular respiration it requires direct use of oxygen molecules this is also known as the oxidative phosphorylation process cellular.
Cellular Respiration Diagram | Quizlet Cellular respiration that uses glycolysis and fermentation when no oxygen is present, producing about 2 ATP per molecule of glucose Inner mitochondrial membrane The location of electron transport chains and ATP synthase, folded many times to increase surface area
PDF 2.5 D: Cellular Respiration Quiz PROCTOR VERSION The electron transport chain is a part of cellular respiration. The diagram below shows the movement of ions in the electron transport chain within a mitochondrion. € € Which statement best describes the movement of ions shown in the diagram? (A) The electron transport chain is used to move hydrogen ions to the inner membrane space,
› cell_respirationCellular Respiration - Exploring Nature More About Cellular Respiration So now we know that cellular respiration is a three stage process that converts glucose and oxygen to ATP and releases carbon dioxide and water. What are the 3 phases that do this? 1) Glycolysis 2) Krebs Cycle 3) The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) This is a very simple overview of these 3 stages: Glycolysis (Stage 1)








/electron-transport-chain-58e3be435f9b58ef7ed96112.jpg)















0 Response to "40 cellular respiration electron transport chain diagram"
Post a Comment