38 life cycle of a virus diagram
Chapter 5: Vector-Borne Diseases | Climate and Health ... The seasonal occurrence of Lyme disease cases is related, partially, to the timing of a blood meal (host-seeking activity) of ticks and the three-stage life cycle (larvae, nymph, and adult) of ticks. 66 Increasing temperatures and the accompanying changes in seasonal patterns are expected to result in earlier seasonal tick activity and an expansion in tick habitat range, increasing the risk … Human papillomavirus: gene expression, regulation and ... The key events in the virus replication cycle are indicated to the right hand side of the diagram of the epithelium. B. A schematic diagram of the gene expression program of the virus within the infected epithelium. Shading on the arrows represents the quantity of expression of each protein subset during the virus replication cycle.
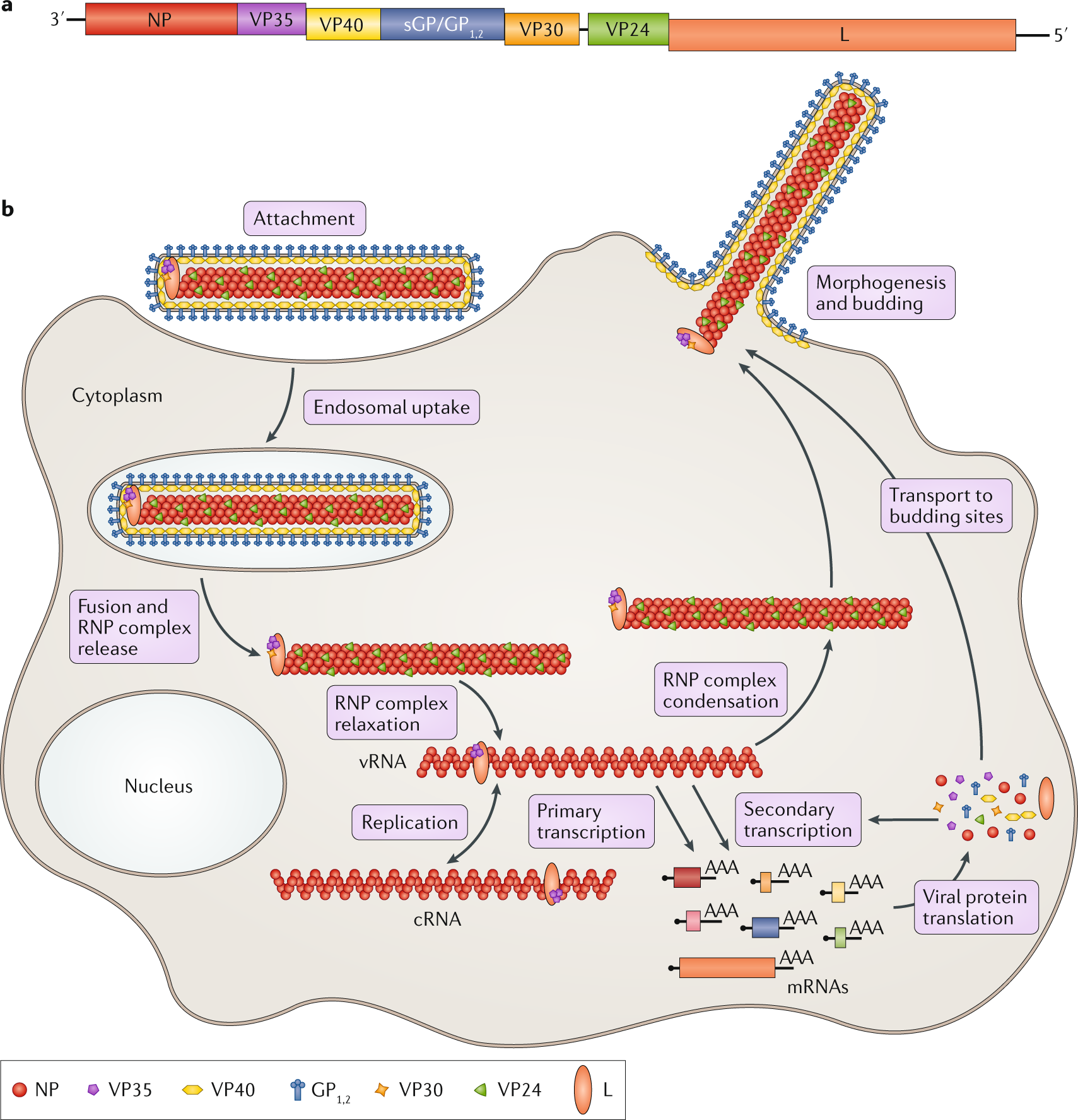
Ebola Virus Life Cycle: Definition & Stages | Study.com Life Cycle. The life cycle of the Ebola virus begins with the extracellular virion, or enveloped virus outside of a cell or host.Once it finds a host, the virus has to make its way inside. This ...

Life cycle of a virus diagram
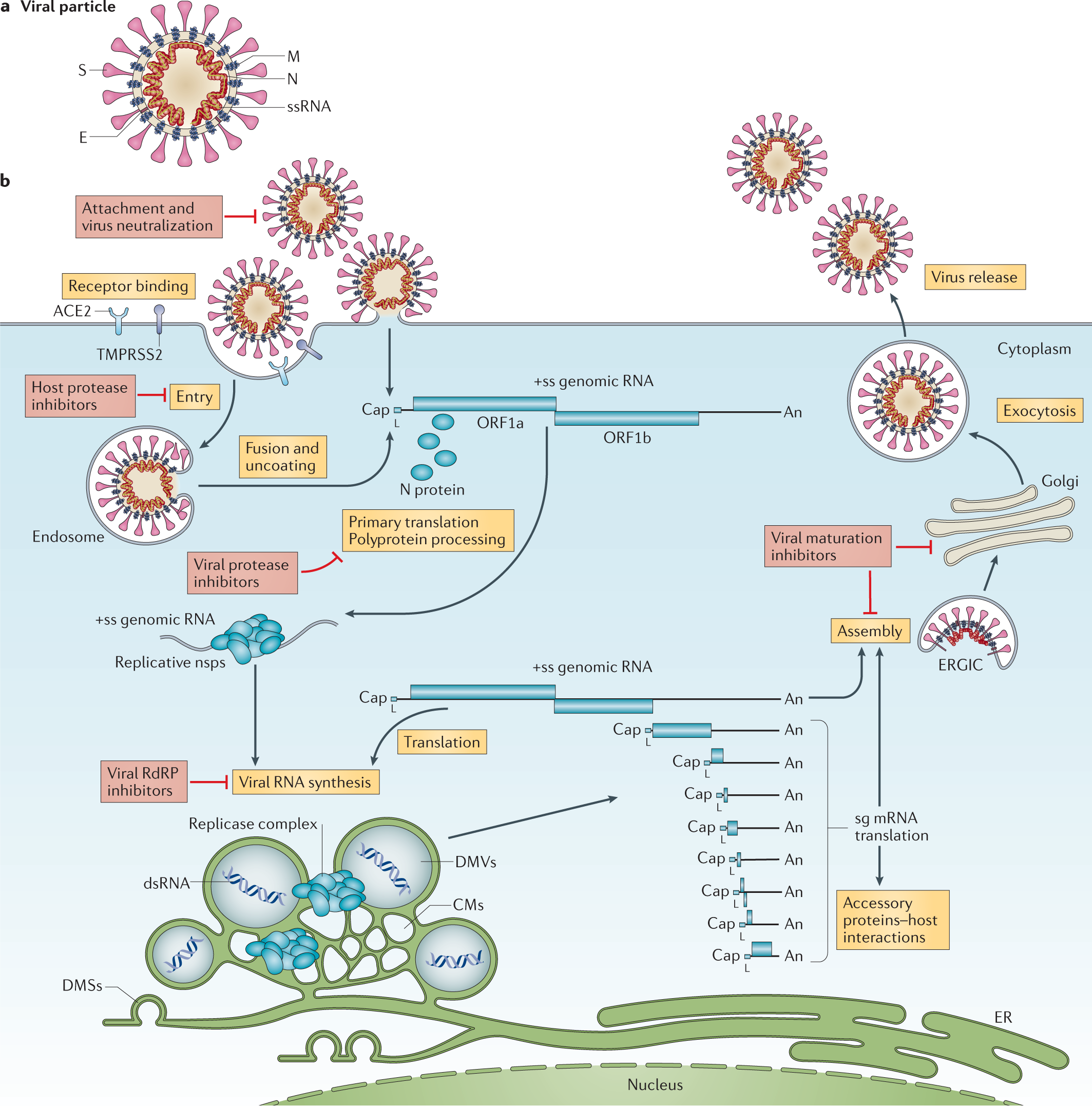
SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle: Stages and Inhibition Targets Stages of the SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle: 1. Virus Entry 2. Translation of Viral Replication Machinery 3. Replication 4. Translation of Viral Structure Proteins 5. Virion Assembly 6. Release of Virus SARS-CoV-2 Replication Cycle SARS-Cov-2 Replication Cycle and Inhibitors. Possible targets for inhibitors are marked in red and numbered in roman numerals. The Viral Life Cycle | Microbiology - Lumen Learning The life cycle begins with the penetration of the virus into the host cell. Next, the virus is uncoated within the cytoplasm of the cell when the capsid is removed. Depending on the type of nucleic acid, cellular components are used to replicate the viral genome and synthesize viral proteins for assembly of new virions. What is Bacteriophage: Structure and Life Cycle Life Cycle of Bacteriophage. There are two different life cycles that a bacteriophage exhibits: Lytic Cycle; Lysogenic Cycle; Lytic Cycle (Virulent Cycle) In this cycle, a bacteriophage enters bacteria and kills them. It then releases a progeny virus. The cycle goes through the below-mentioned steps:
Life cycle of a virus diagram. Plasmodium Life Cycle – Stages, Diagram and Important FAQs Through this diagram representing the entire life cycle of the Plasmodium, we can easily understand how this parasite completes its life using two organisms. In the figure above we can easily distinguish the life cycle of Plasmodium in a human and life cycle of Plasmodium in a mosquito. Life Cycle of Human . The human life cycle begins as a single cell barely visible to … Prognostic Value of “Cycle Threshold” in Confirmed COVID ... Bar diagram showing the mean cycle threshold of nonsurvivors and survivors. Forty-nine (25.5%) patients required ICU admission and 143 (74.4%) patients were managed in general wards. The mean CT of patients who required ICU admission was 24.1 (SD, 4.65) and the mean CT of patients who did not require ICU admission was 26.1 (SD, 4.47) Fig. 2). The p-value was … Baculoviridae - Wikipedia Diagram of a NPV lifecycle. The baculovirus lifecycle involves two distinct forms of virus. Occlusion-derived virus (ODV) is present in a protein matrix (polyhedrin or granulin) and is responsible for the primary infection of the host. while the budded virus (BV) is released from the infected host cells later during the secondary infection. Baculoviruses have very species … The Viral Life Cycle – Microbiology The life cycle begins with the penetration of the virus into the host cell. Next, the virus is uncoated within the cytoplasm of the cell when the capsid is removed. Depending on the type of nucleic acid, cellular components are used to replicate the viral genome and synthesize viral proteins for assembly of new virions.
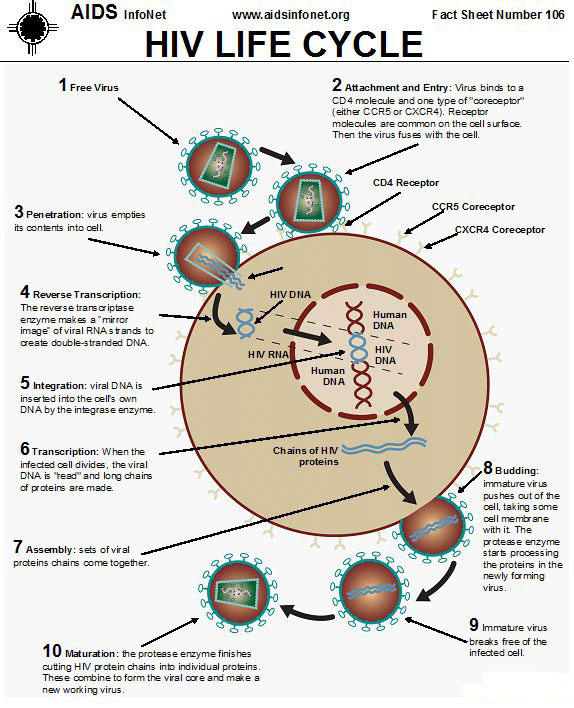
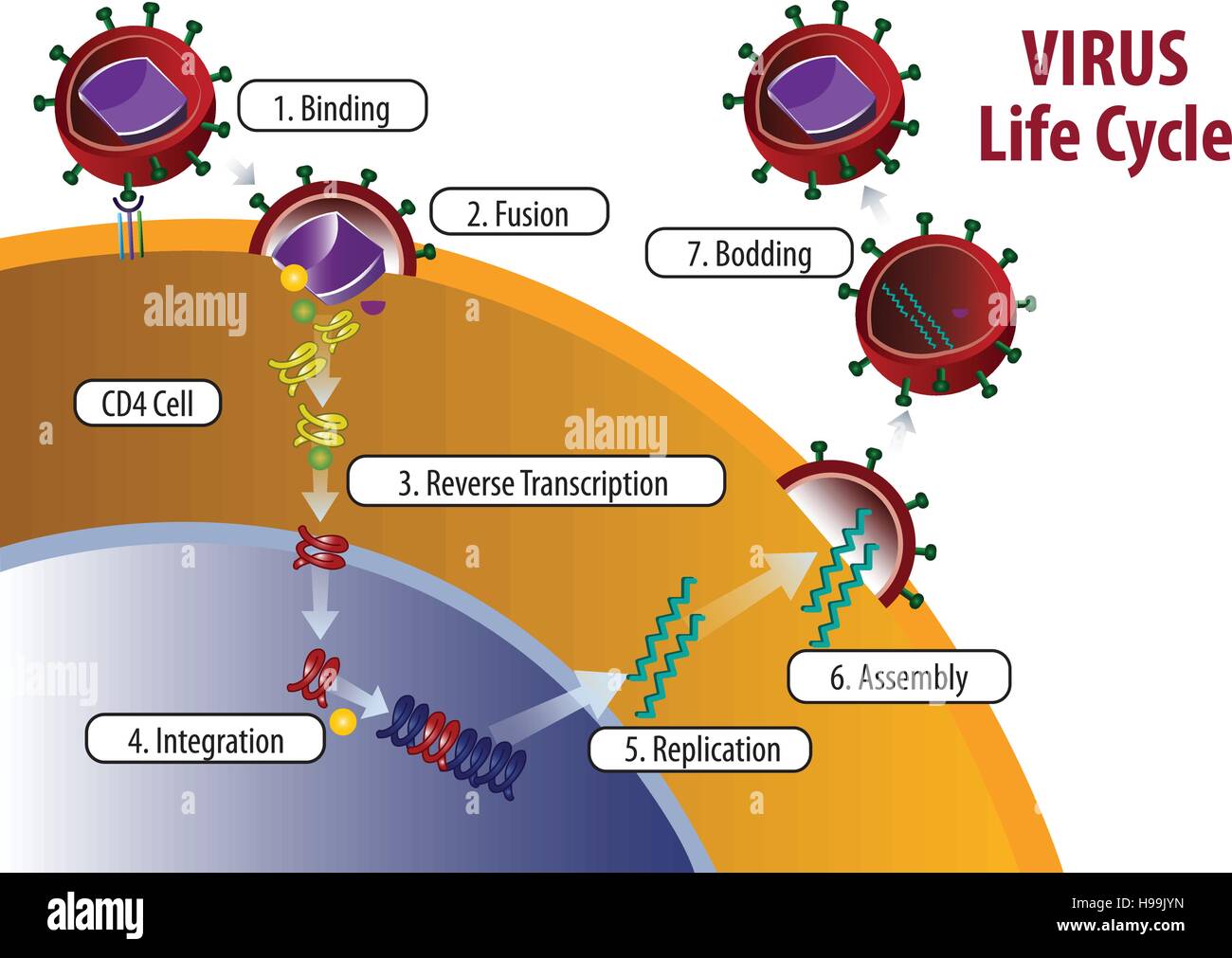
Rabies Virus | Structure, Function, & Life Cycle | Study.com Learn about the structure and life cycle of the rabies virus. Discover how rabies affects humans and the ways to treat and prevent this lethal disease. Updated: 02/17/2022 Life Cycle - Marburg Investigation Life Cycle. Figure 3: 3D structure of the Riemann-Pick C1 protein. For the Marburg Virus to infect the host's cell an essential element is needed. For Marburg and Ebola that element is the Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) membrane protein (1). This protein mediates infection by binding to the viral envelope glycoprotein. Life cycle of a poliovirus | Media Library | Integration ... Life cycle of a poliovirus. Conceptual diagram illustrating the life cycle of a poliovirus. diagram poliovirus life cycle enteroviruses asymptomatic infection illness vaccine excretion blood cell bloodstream nerve cell virus. Author (s) Kate Bentsen. Author Company. Integration and Application Network. The 7 stages of the HIV life cycle explained - IAS The 7 stages of the HIV life cycle explained. #1 Binding. This is the very first stage of the HIV Lifecycle. The HIV virus attacks the CD4 cell and attaches Itself to the cell on its surface. It does this by first attaching to the CD4 cell's receptor than the CCR5 or the CXCR4 coreceptor. #2 Fusion.
Retrovirus Life Cycle - Stanford University The retroviral life cycle begins in the nucleus of an infected cell. At this stage of the life cycle the retroviral genome is a DNA element integrated into and covalently attached to the DNA of the host cell.The genome of the virus is of approximately 8-12 kilobases of DNA (depending upon the retroviral species). HIV: Structure, Life Cycle, and Pathogenecity Human Immunodeficiency Virus: Structure, Life Cycle, and Pathogenecity . Jonathan Hughes . Viruses are the smallest infectious agents of animal and plant tissues. They range in size from 20 to 300 nm (lnm = one billionth ofa meter). To cause a disease, viruses Virus Life Cycle Worksheet Diagram Answers : Targethiv Org Virus Life Cycle Worksheet Diagram Answers : Targethiv Org -. You can see real examples of viral lifecycles in the . Like the lytic cycle, in the lysogenic cycle the virus attaches to. Understand how replication cycles of lytic and lysogenic viruses differ among. Each time the host's cells go through replication, the virus's dna . The HIV Life Cycle | NIH The seven stages of the HIV life cycle are: 1) binding, 2) fusion, 3) reverse transcription, 4) integration, 5) replication, 6) assembly, and 7) budding. To understand each stage in the HIV life cycle, it helps to first imagine what HIV looks like. Now, follow each stage in the HIV life cycle as HIV attacks a CD4 cell and uses the machinery of ...
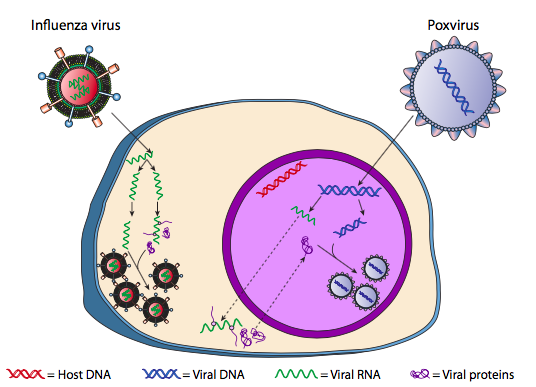
Influenza A: Understanding the Viral Life Cycle Influenza A virus belongs to the family of Orthomyxoviridae. It is an enveloped virus with a negative sense RNA segmented genome that encodes for 11 viral genes. This virus has evolved a number of mechanisms that enable it to invade host cells and subvert the host cell machinery for its own purpose, that is, for the sole production of more virus.
Bacteriophage - Structure And Life Cycle Of Bacteriophage In the Lytic Cycle, a bacteriophage infects a bacteria and kills it to release progeny virus. This cycle takes place in the following steps: Adsorption. The bacteriophage attaches itself on the surface of bacteria. This process is known as adsorption. The tips of the tail fibres attach to specific receptors on the surface of the bacterial cell.
PDF The HIV Life Cycle - University of Nevada, Reno School of ... The HIV Life Cycle Binding and Fusion: HIV begins its life cycle when it binds to a CD4 receptor and one of two co-receptors on the surface of a CD4 + T- lymphocyte. The virus then fuses with the host cell. After fusion, the virus releases RNA, its genetic material, into the host cell. Reverse Transcription: An HIV enzyme called reverse ...
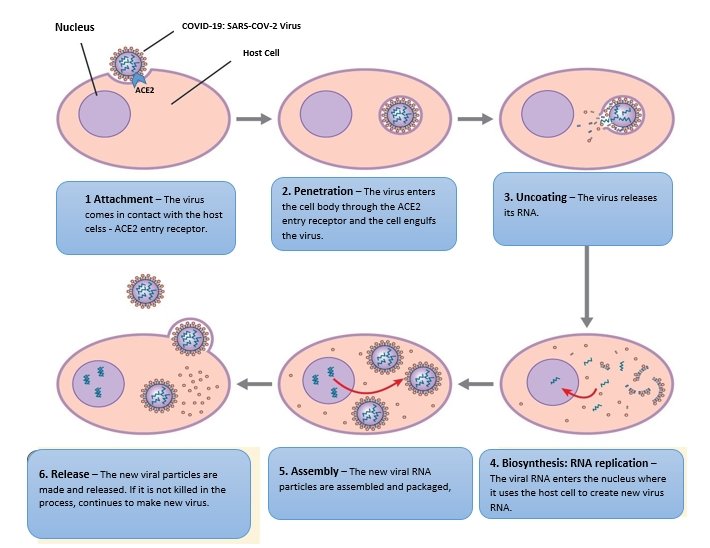
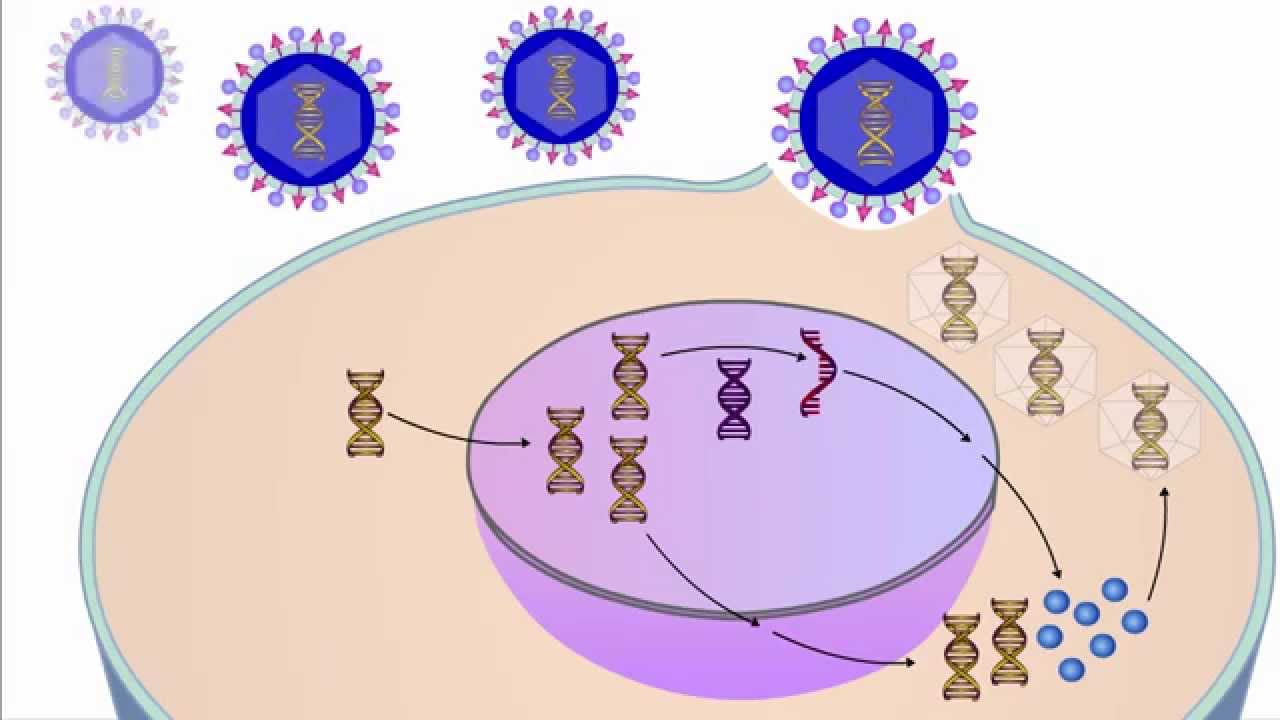
Label the Life Cycle of the Virus - Google Docs Label the Life Cycle of the Virus. 1. Label the diagram using the descriptions: Host cell makes copies of virus parts ( Biosynthesis) Virus attaches to host cell (Attachment) Virus is released from host cell (Release) Virus is assembled (Assembly) DNA from virus enters host cell (Penetration) 2.
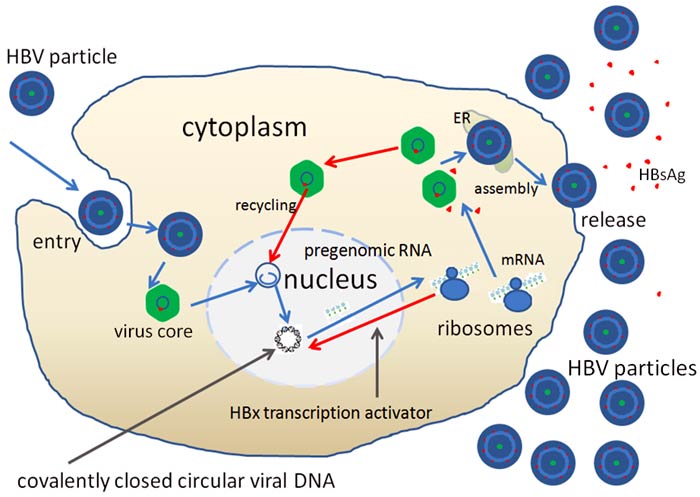
Hepatitis B virus biology and life cycle Hepatitis B virus (HBV) specifically infects hepatocytes and causes severe liver diseases. The HBV life cycle is unique in that the genomic DNA (relaxed-circular partially double-stranded DNA: rcDNA) is converted to a molecular template DNA (covalently closed circular DNA: cccDNA) to amplify a viral RNA intermediate, which is then reverse-transcribed back to viral DNA.
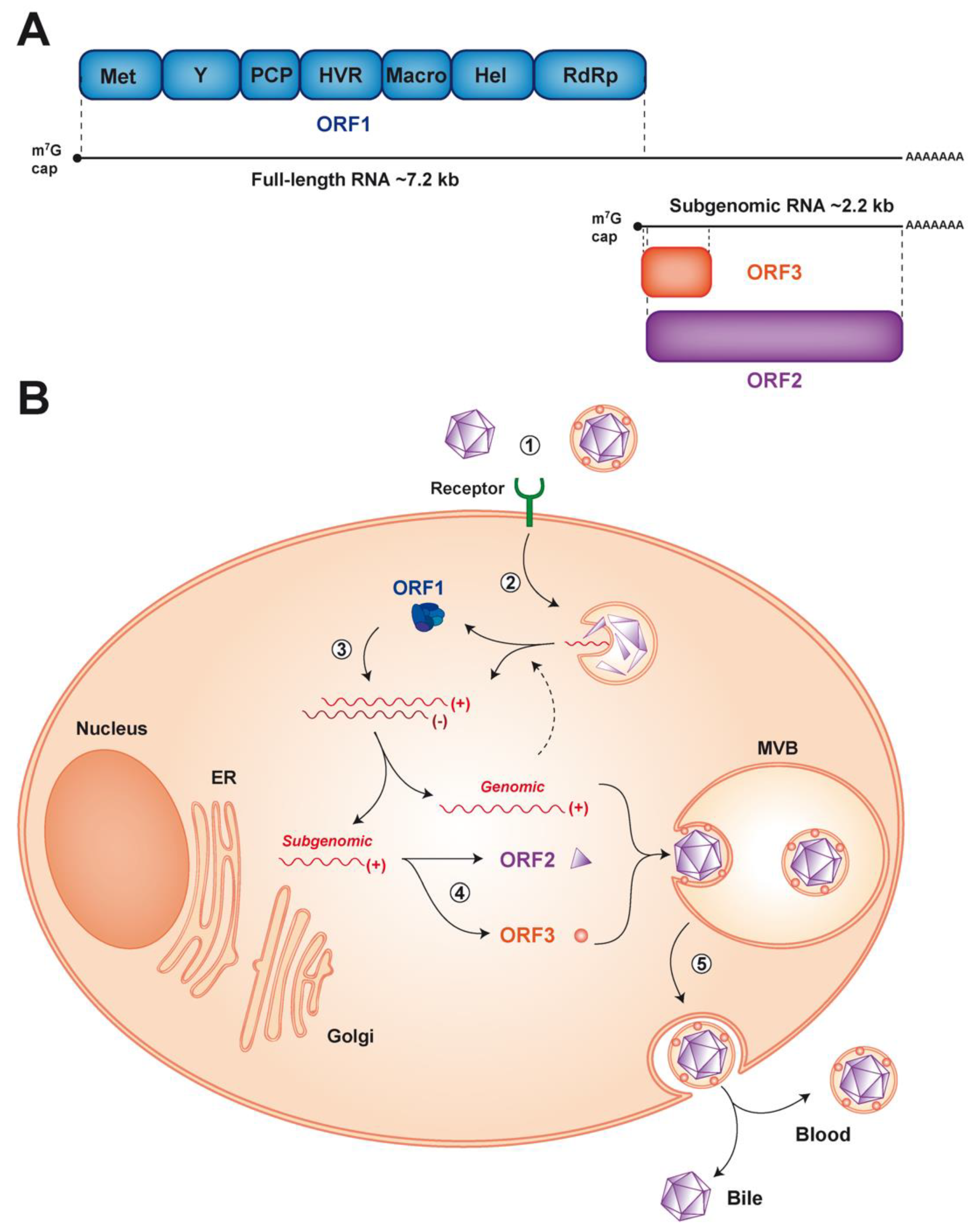
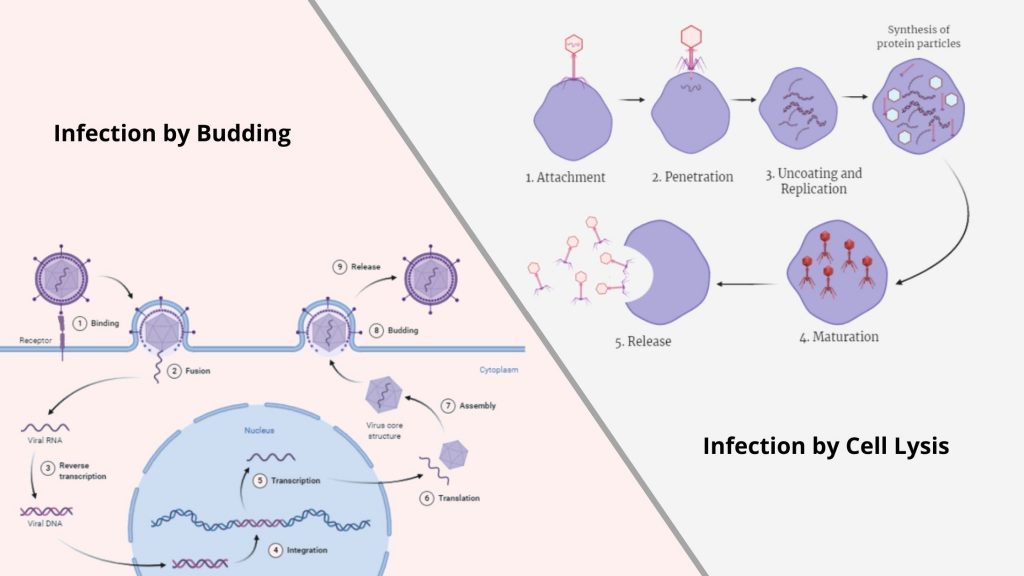
Virus Life Cycle The life cycle of virus. The virus life cycle could be divided into six steps: attachment, penetration, uncoating, gene expression and replication, assembly, and release. The viral capsid (blue) and genome (brown) are schematically drawn for the purpose of explanation. The nucleus is omitted for clarity. 3.2. Viral Entry
Life Cycle of a Virus - Science with Amy Apr 14, 2020 · The life cycle of HIV virus. Some infections are for life. HIV virus is one such example. A person infected with HIV can experience no symptoms for years as the virus remain dormant. The virus is sophisticated in avoiding detection from our immune cells and interfere with the body’s immune function.
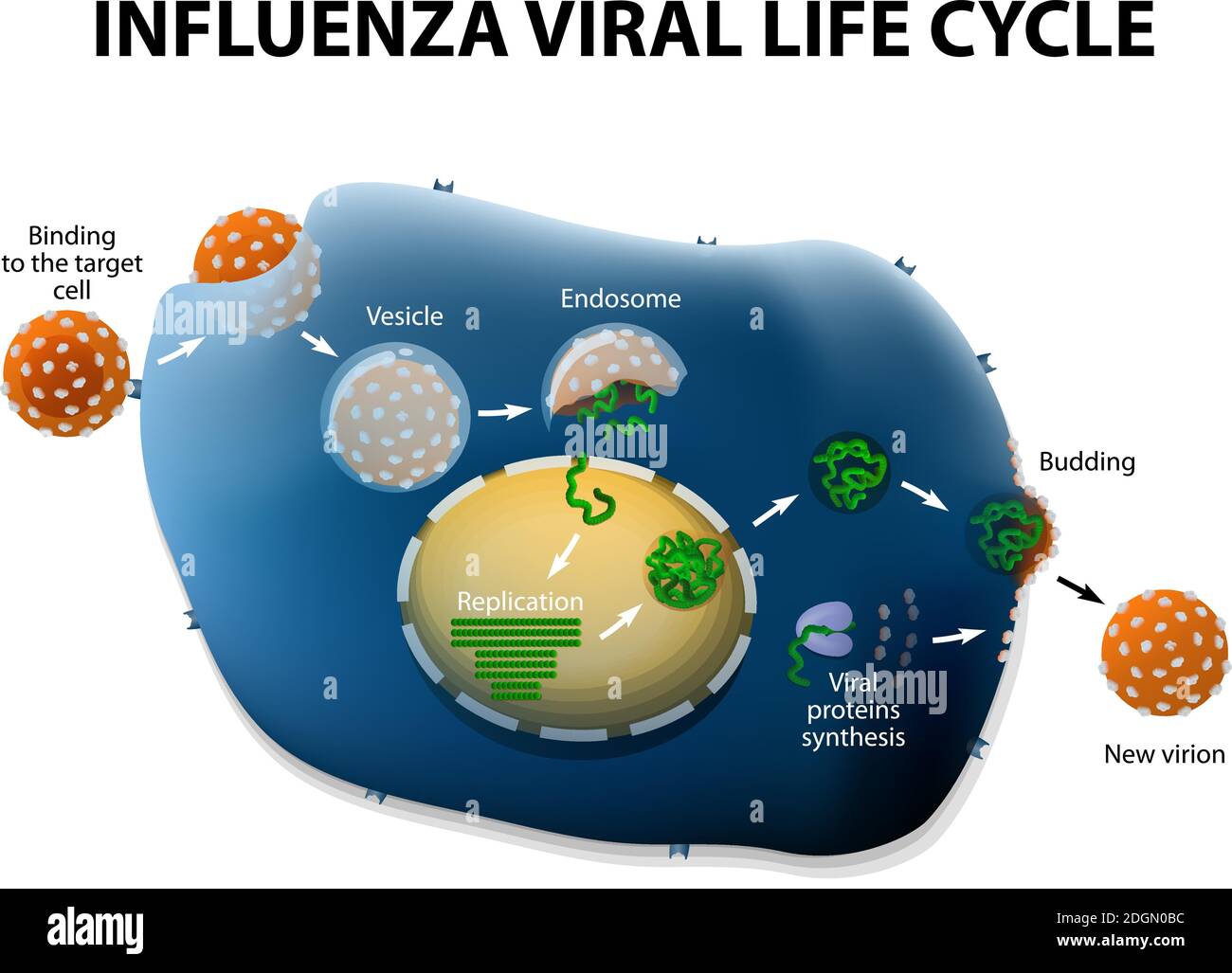
2 Life Cycle of Influenza Virus | Download Scientific Diagram Download scientific diagram | 2 Life Cycle of Influenza Virus from publication: STUDY ON EPITOPE MAPPING OF HEMAGGLUTININ PROTEIN IN H5N1 INFLUENZA VIRUS | Influenza viruses circulating in animals ...
Influenza virus- Structure, Types, Life Cycle - Virology ... Influenza virus- Structure, Types, Life Cycle. Influenza commonly called a flue is a highly contagious viral infection of the respiratory tract mainly infects humans and animals. Influenza virus belongs to the family: Orthomyxoviridae. The annual attack rate of influenza virus is 5-10% in adults and 20-30% in children.
Angiosperms vs Gymnosperms - Difference and Comparison ... Since gymnosperms and angiosperms are both vascular plants, they have a sporophyte-dominant life-cycle. Tissue formation in angiosperms exceeds the amount and complexity found in gymnosperms. Angiosperms have a triploid vascular tissue, flat leaves in numerous shapes and hardwood stems. Because of the innumerable varieties of the fruit and/or flower-bearing plants, …
6.2 The Viral Life Cycle - Microbiology | OpenStax The life cycle begins with the penetration of the virus into the host cell. Next, the virus is uncoated within the cytoplasm of the cell when the capsid is removed. Depending on the type of nucleic acid, cellular components are used to replicate the viral genome and synthesize viral proteins for assembly of new virions.
Eukaryotic Cells - Definition, Parts, Examples, and Structure Browse more Topics under Cell The Unit Of Life. Introduction to Cell and Cell Theory; Prokaryotic Cell ; Cell Wall. Description: The cell wall is a non-living, rigid structure outside the plasma membrane in plant cells and fungi. It is absent in Eukaryotic cells of animals. Structure and composition: It is made of different components in different Eukaryotes: Cellulose, …
Virus - Wikipedia A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck …
The Life Cycle of Rous Sarcoma Virus diagram drawing (1 ... RE: Calisphere: Request high-resolution copy of item for The Life Cycle of Rous Sarcoma Virus diagram drawing (1) Message Check to send a copy of this message to your email.
Virus Life Cycle: Introduction, Life Cycle, FAQs Viruses encode proteins that hinder the host genome, aid in viral replication and have a major role in the life cycle of viruses. 4) Assembly Capsomers are the outer covering of proteins that protect the genetic information of a virus.
Calvin Cycle: Definition, Function, Steps & Products ... 2019-10-04 · Calvin Cycle Definition. The Calvin cycle is the cycle of chemical reactions performed by plants to “fix” carbon from CO 2 into three-carbon sugars.. Later, plants and animals can turn these three-carbon compounds into amino acids, nucleotides, and more complex sugars such as starches.. This process of “carbon fixation” is how most new organic matter is created.
Viral life cycle - Wikipedia Viruses are only able to replicate themselves by commandeering the reproductive apparatus of cells and making them reproduce the virus's genetic structure and particles instead. How viruses do this depends mainly on the type of nucleic acid DNA or RNA they contain, which is either one or the other but never both. Viruses cannot function or reproduce outside a cell, and are totally dependent on ...
Virus Structure | Forms of Viruses | Virus Structure Types ... A virus is an infectious non-living particle that cannot survive on its own. The life cycle of the virus is a series of steps that enable the virus to infect a host and replicate itself. Explore virus structure, structure of virus, viral structure types, and functions of virus structure.
The Hantavirus Lifecycle and Structure | Hanta Virus The lifecycle begins when the Hantavirus attaches to a cell using one of two proteins, called G1 and G2. G1 and G2 work by binding to a cellular receptor, which allows the virus into the cell through endocytosis. Endocytosis is a process in which the cellular membrane caves inward, drawing everything nearby into the cell, and then pinching off ...
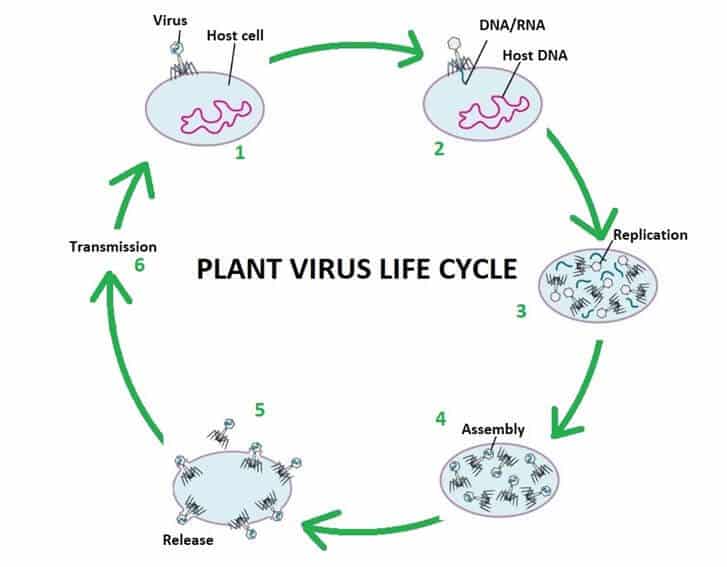
Life cycle of a virus - Communicable disease - Edexcel ... Life cycle of a virus. The life cycle of a virus. is the same as other pathogens. They can often survive outside a host. for long periods of time. When they do infect a suitable host cell or cells ...
What is Bacteriophage: Structure and Life Cycle Life Cycle of Bacteriophage. There are two different life cycles that a bacteriophage exhibits: Lytic Cycle; Lysogenic Cycle; Lytic Cycle (Virulent Cycle) In this cycle, a bacteriophage enters bacteria and kills them. It then releases a progeny virus. The cycle goes through the below-mentioned steps:
The Viral Life Cycle | Microbiology - Lumen Learning The life cycle begins with the penetration of the virus into the host cell. Next, the virus is uncoated within the cytoplasm of the cell when the capsid is removed. Depending on the type of nucleic acid, cellular components are used to replicate the viral genome and synthesize viral proteins for assembly of new virions.
SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle: Stages and Inhibition Targets Stages of the SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle: 1. Virus Entry 2. Translation of Viral Replication Machinery 3. Replication 4. Translation of Viral Structure Proteins 5. Virion Assembly 6. Release of Virus SARS-CoV-2 Replication Cycle SARS-Cov-2 Replication Cycle and Inhibitors. Possible targets for inhibitors are marked in red and numbered in roman numerals.
























0 Response to "38 life cycle of a virus diagram"
Post a Comment