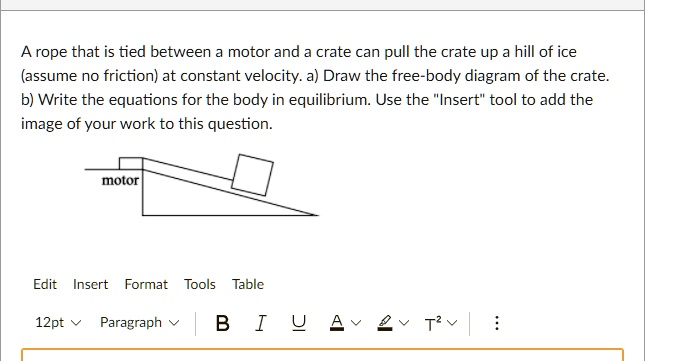
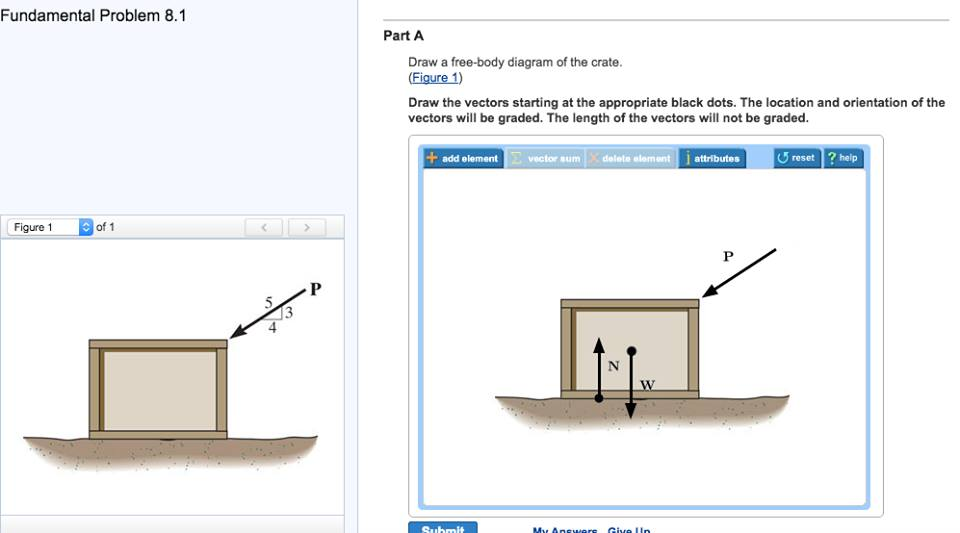
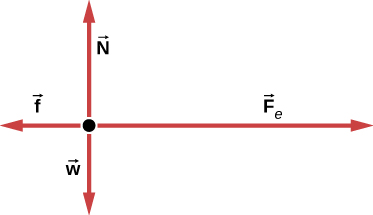
38 draw a free-body diagram of the crate a.
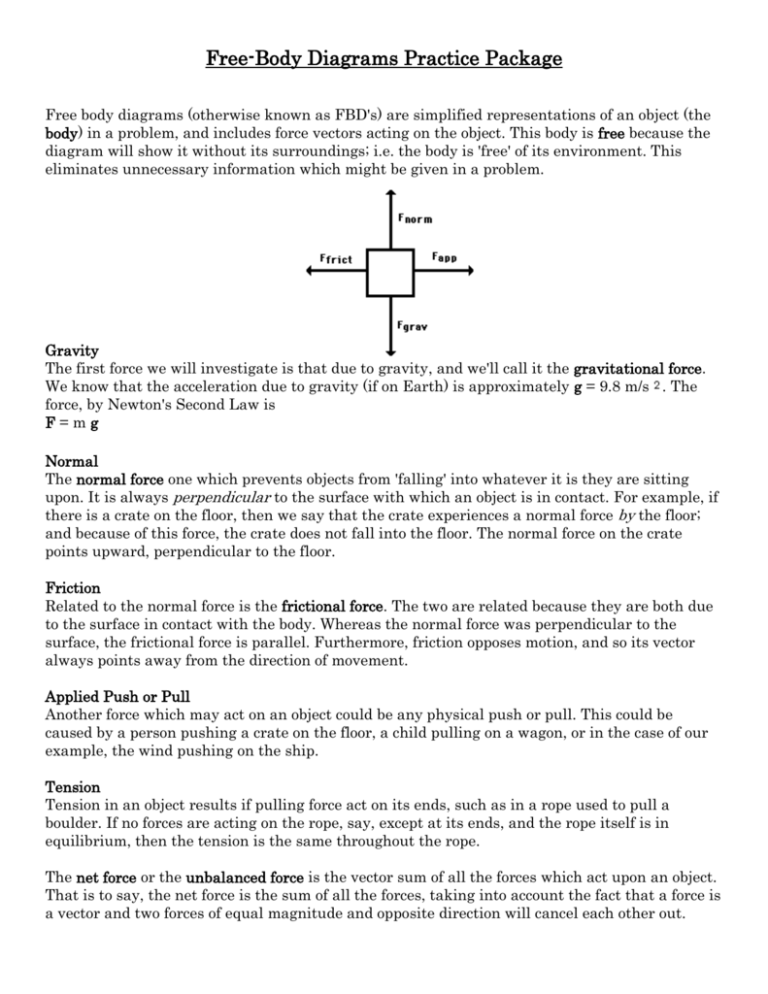
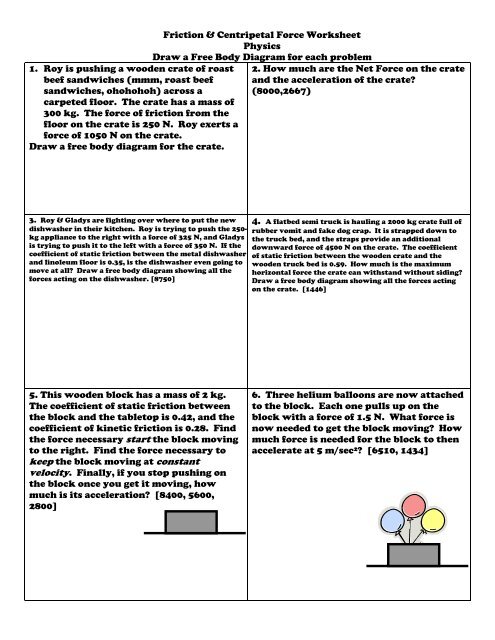
Draw a free-body diagram for the load and compare the magnitudes and directions of the all forces. 36. A crate is accelerated at a constant rate along a rough horizontal floor. Draw a free-body diagram for the crate and compare all the forces exerted on the crate. 37. A hockey puck slides on a rough horizontal surface. A free-body diagram can be drawn very simply, with squares and arrows, or you can make it much more complex. The only requirement is that you or someone else looking at it should be able to understand what the diagram is telling. A free-body diagram (FBD) is a representation of a certain object showing all of the external forces that acts on it.
Free editor to create online diagrams. Use our diagram editor to make Flowcharts, UML diagrams, ER diagrams, Network Diagrams, Mockups, floorplans and many more. Open and save your projects and export to Image or PDF.

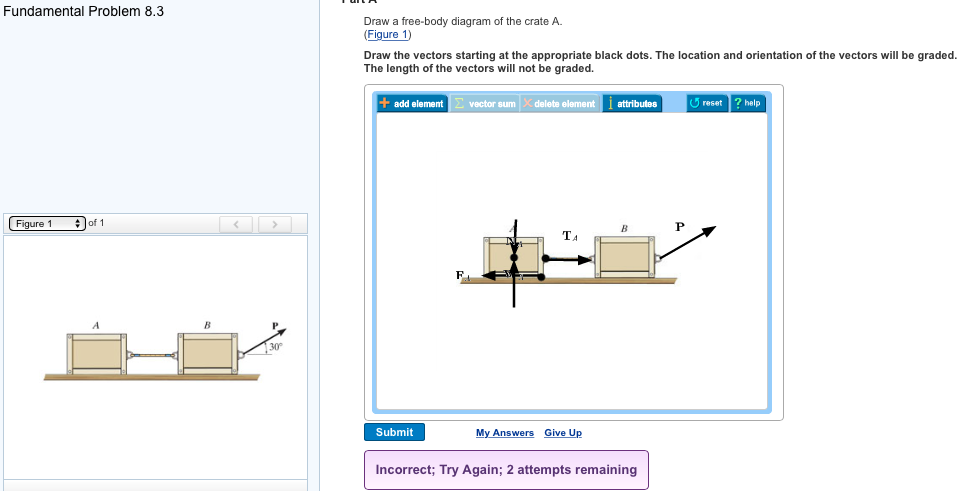
Draw a free-body diagram of the crate a.
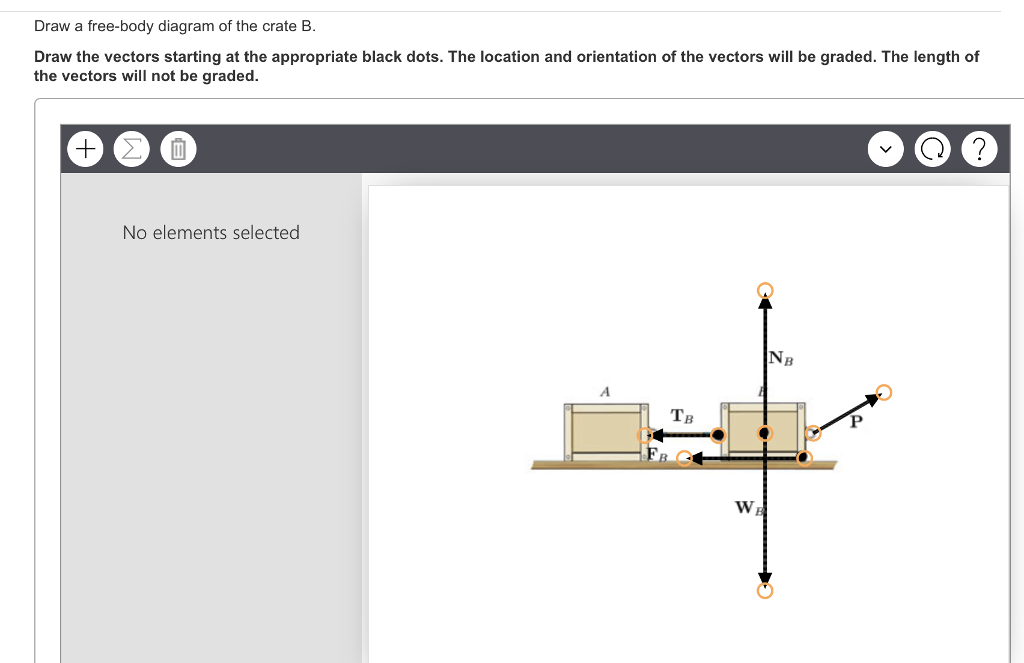
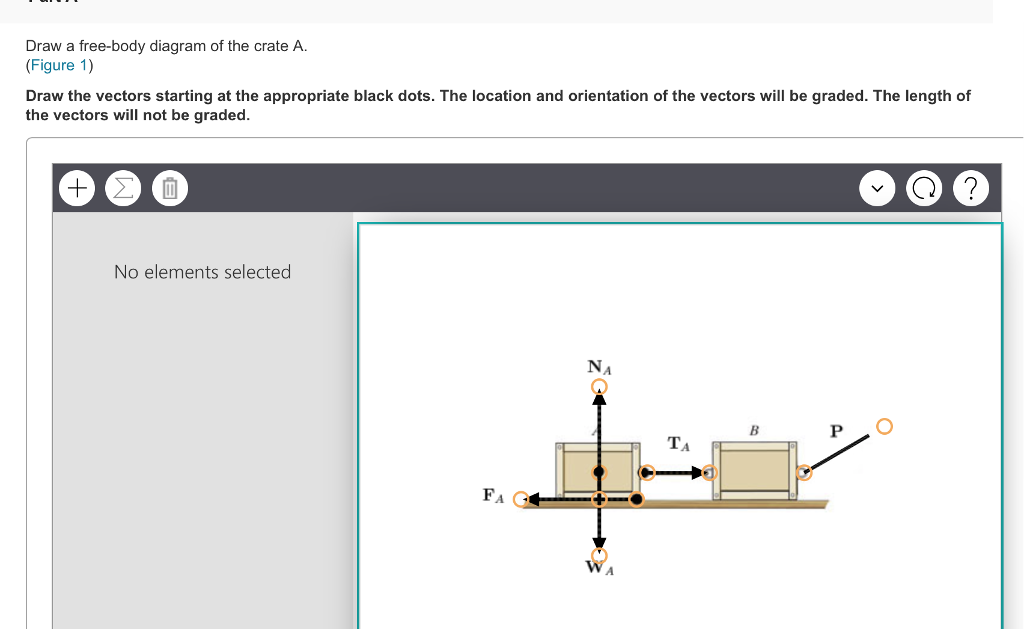
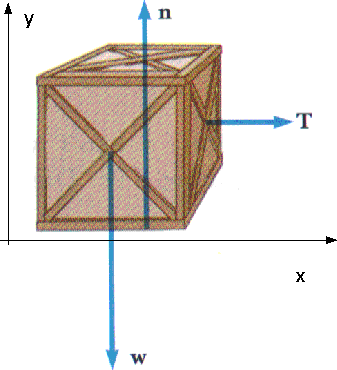
Draw a free-body diagram of the crate and draw the vectors starting at the appropriate black dots. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. Draw the free-body diagram of the crate when the truck ca n have from a speed of 7 0 . km/h with constant decel eration if the crate is not to slip forward. 2. A bar of length l and negligible mass connects the car t of mass M and the parti cle of. mass m. Transcribed image text: Draw a free-body diagram of the crate that has a center of gravity at G. Draw the vectors starting at the appropriate black dots.
Draw a free-body diagram of the crate a.. Examples of drawing free-body diagrams. To better understand how to draw free-body diagrams using the 3 steps, let's go through several examples. Example 1. A box is pushed up an incline with friction which makes an angle of 20 ° with the horizontal. Let's draw the free-body diagram of the box. The first step is to sketch what is happening: Transcribed image text: Draw a free-body diagram of the crate A. Draw the vectors starting at the appropriate black dots. The location and orientation of ... Draw a free-body diagram of the crate that has a center of gravity at G. (Figure 1). Draw the vectors starting at the appropriate black dots. The location and ... Draw a free-body diagram of the crate in the diagram below. Use the dot as the particle representing the crate and make sure to draw your vectors so that they have the correct orientation and their magnitudes, in newtons, are consistent with the conditions of the problem. Draw the vectors starting at the black dot.
Free-Body Diagrams and Newtonian Physics 1. Draw a sketch of the situation. 2. Draw a free-body diagram for the object of interest, showing all the forces acting on the object. Also, include any unknown forces that you must solve for. Do not show any forces that chosen object exerts on other objects. Instead draw free-body diagrams for Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. Draw a free-body diagram of the crate A. (Figure 1). Draw the vectors starting at the appropriate black dots. The location and orientation of the vectors will ... To draw a free-body diagram, we draw the object of interest, draw all forces acting on that object, and resolve all force vectors into x – and y -components. We must draw a separate free-body diagram for each object in the problem.
Transcribed image text: Draw a free-body diagram of the crate A. (Figure 1) Draw the vectors starting at the appropriate black dots. Transcribed image text: Draw a free-body diagram of the crate that has a center of gravity at G. Draw the vectors starting at the appropriate black dots. Draw the free-body diagram of the crate when the truck ca n have from a speed of 7 0 . km/h with constant decel eration if the crate is not to slip forward. 2. A bar of length l and negligible mass connects the car t of mass M and the parti cle of. mass m. Draw a free-body diagram of the crate and draw the vectors starting at the appropriate black dots. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded.



















0 Response to "38 draw a free-body diagram of the crate a."
Post a Comment