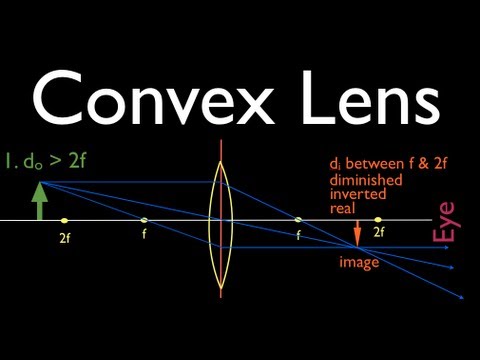
41 ray diagram for convex lenses
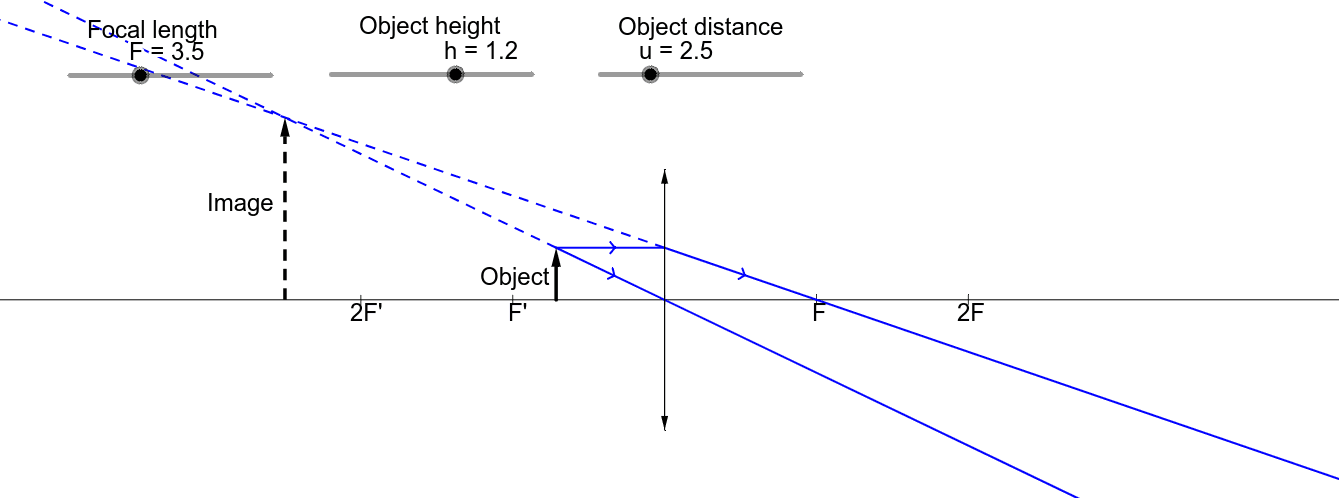
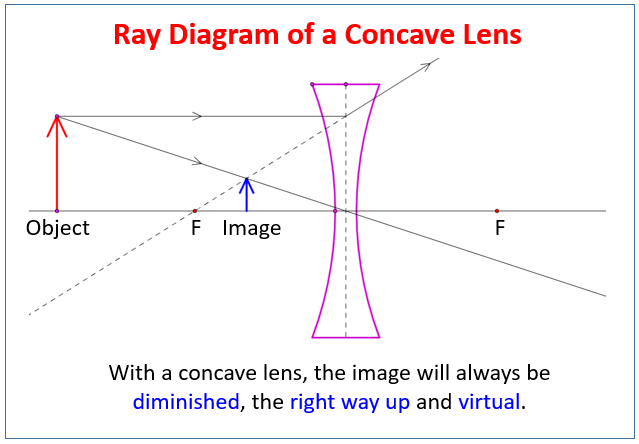
Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. You can also illustrate the magnification of a lens and the difference between real and virtual images. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. A light ray that enters the lens is an incident ray. Ray 1 is parallel to the axis and refracts as if from F. Ray 2 heads towards F' before refracting parallel to the axis. Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens. image is always virtual, upright and reduced O F I F' Ray diagram for diverging lens
Convex Lenses and Ray Diagrams. A series of free GCSE/IGCSE Physics Notes and Lessons. The following diagrams show the ray diagrams for convex lens: for objects at different distances from the lens. Convex Lenses.
Ray diagram for convex lenses
A light ray traveling through a convex lens experiences refraction when it enters the lens through the front surface and again when it leaves the lens through the back surface. In this diagram here, we have drawn a particularly wide convex lens, which we can use to help us see the effects of the refraction more clearly. Ray diagrams for convex lenses. Typically this requires determining where the image of the upper and lower extreme of the object is located and then tracing the entire image. Image formation by convex lens ray diagrams. Im doing my best to draw this convex lens just like that. Ray diagrams the lens equation and the mirror equation. Arial Calibri Default Design Lenses What phenomenon is evident in lenses? Basic Types of Lenses Convex Lens Concave Lens Type of Image Convex Lens Ray Diagram for Convex Lens Rules for Ray Diagrams for Convex Lens PowerPoint Presentation Summary for Convex Lens Sign Convention Magnification Lens Equation Concave Lens Summary for Concave Lens ...
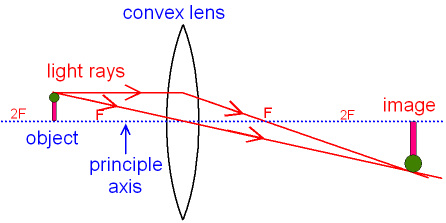
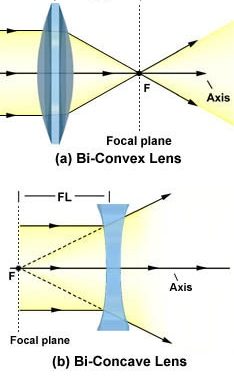
Ray diagram for convex lenses. A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge. They come together at a point called the principal focus. In a ray diagram, a ... Shows how to draw ray diagrams to locate the image formed by a convex lens. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscienc... Convex Lens Ray Diagrams For lenses, the following three rays are typically used in ray diagrams. Keep in mind that an inflnite number of rays actually form the image. Ray # 1 For a lens, the flrst ray starts from the top of the object and extends parallel to the optical axis to the center of the lens. This ray, for a converging (convex) lens, Ray diagrams for convex lenses are based on the principle that convex lenses converge light rays passing through them. The following points are to be kept in mind while drawing ray diagrams for convex lens:-A ray of light passing through the optical center of a convex lens passes through the lens undeviated. A ray of light parallel to the principal axis, on passing through the lens, gets ...
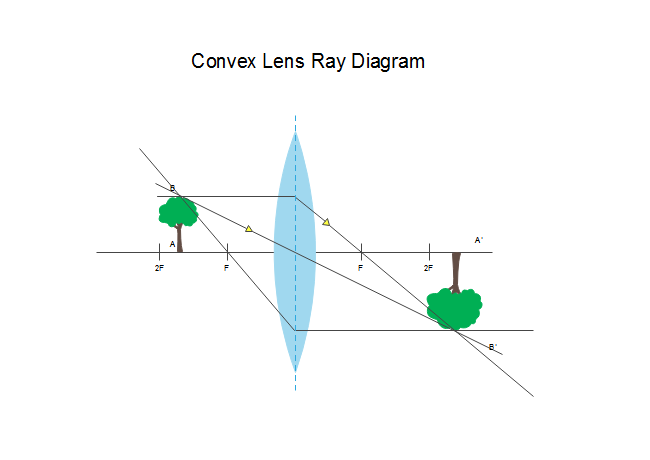
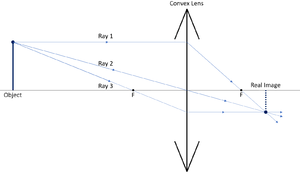
The method of drawing ray diagrams for double convex lens is described below. The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the 2F point of a double convex lens. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Hi, in this quick video with animation of a Convex Lens , one can get a good feel for the lens itself, what it looks like, and how to draw Ray Diagrams from ... Ray tracing diagram for convex lens. "A lens is an optical device which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element. A compound lens is an array of simple lenses (elements) with a common axis; the use of multiple elements allows more optical aberrations to be corrected than ... Here in this post, you will get Ray Diagrams for Images formed by convex & concave lenses as a Quick Reference. Image formation by lenses is an interesting topic of the Light chapter. Here along with the ray diagram, you will get the related details like Object position, image position, and nature of the image.
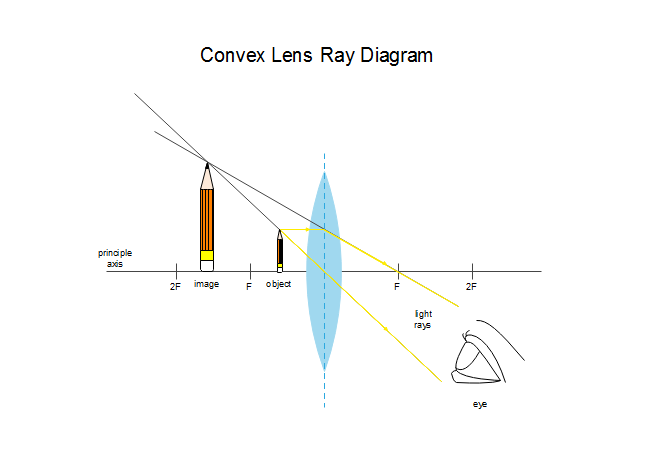
Q2: How many foci does a convex lens have? Q3: Each of the following diagrams shows a ray entering a thin convex lens. The point marked P is the focal point of the lens. Before the ray enters the lens, it is parallel to the optical axis and it passes through the center of the lens. Which diagram correctly shows the path of the ray after it has ... Convex Mirror Image. A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The cartesian sign convention is used here.. Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back-projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror. A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram. Ray Diagrams for Convex Lenses. Now that we understand these basic rules governing lenses we can create what are called ray diagrams in order to predict the position, orientation, and size of the image generated by the lens. 1. Draw two incident rays traveling towards the lens from the top of the object. Draw one ray so that it passes exactly ...
Ray diagram for an object placed between 2F and F from a convex lens In a film or data projector, this image is formed on a screen. Film must be loaded into the projector upside down so the ...
Rule 3 - Ray passing through Optical Center will emerge without deviation. For a both convex and concave lens, we see that ray passing through Optical center emerges without deviation. Next: Convex Lens - Ray diagram→. Facebook Whatsapp.
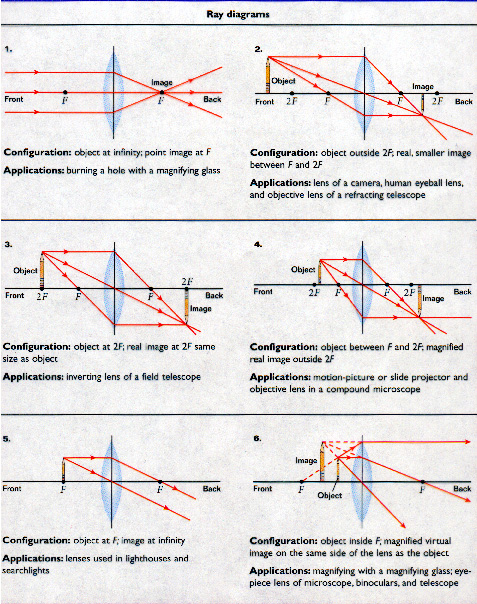
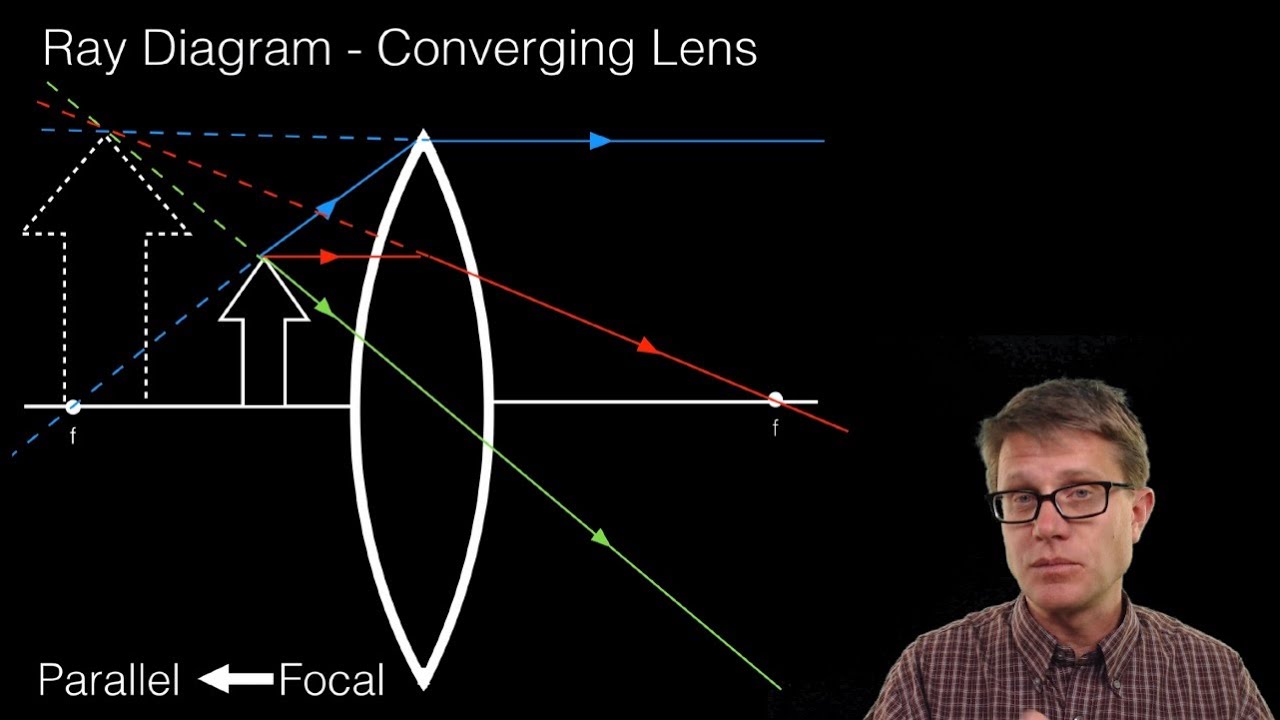
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are:
When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object.
The convex lens ray diagrams give people an idea about the position of the image and the object. The students can also have ideas about the nature of the lens. They can also know how the light rays experience a change in path due to a convex lens's presence there.
Image formation by convex lens ray diagrams. Image formation in a convex lens can be explained with the help of three principal rays shown in the figure. The ray parallel to the principal axis passes through the focal point after refraction by the lens. The ray passing through optical centre passes straight through the lens and remains undeviated.
13+ Convex Lens Ray Diagram. This set of 3 rays is a standard way of simplifying the. Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a converging lens will refract through the lens and travel. To draw these ray diagrams, we will have to recall the three rules of refraction for a double convex lens: Wikipedia] the example ray ...
Convex concave ray diagrams. 1. J.M. Gabrielse Ray Diagrams. 2. J.M. Gabrielse Spherical Mirrors (concave & convex) 3. J.M. Gabrielse Concave & Convex (just a part of a sphere) C: the centre of curvature (centre point of the sphere) F: the focus (focus) of the mirror (halfway between C and the mirror) • C • F Principal Axis Curved Surface. 4.
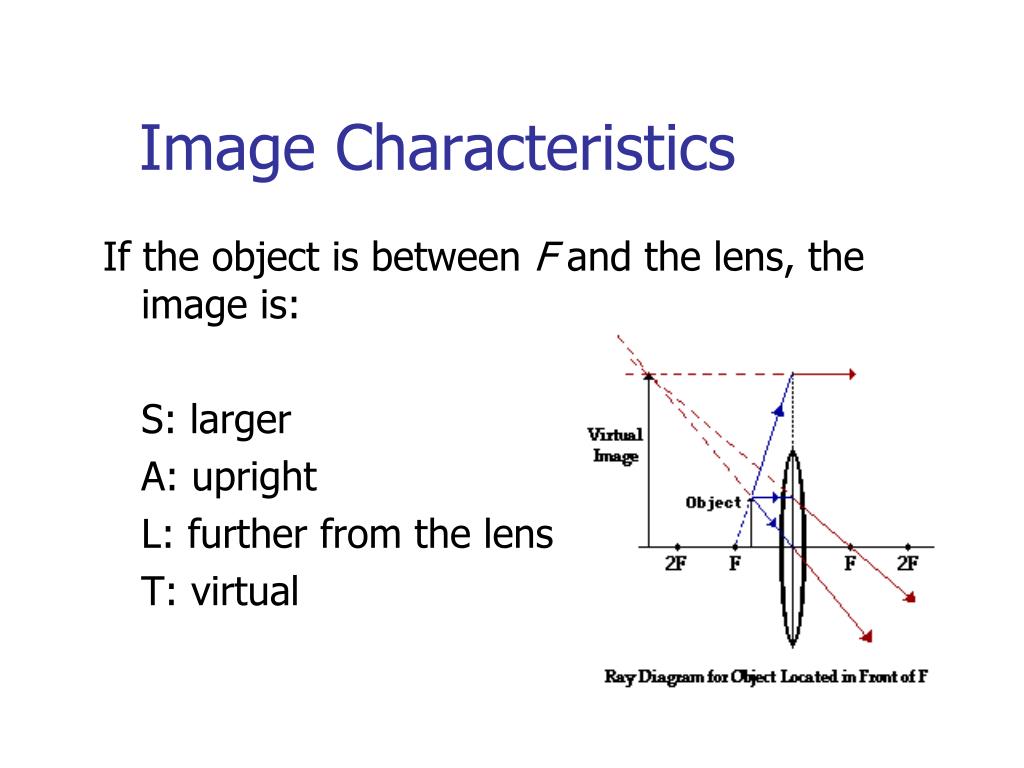
A ray from the top of the object proceeding parallel to the centerline perpendicular to the lens, passing through the principal focal point beyond the lens. What is a lens ray diagram? A convex lens is drawn as a vertical line with outward facing arrows to indicate the shape of the lens in a ray diagram, and the focal length is the distance ...
10 practice problems drawing the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses, 5 problems for each. Students will draw ray diagrams to determine where the image will be observed from an object at varying distances in front of concave and convex lenses. Then state if the image is real or virtual,
The example "Ray tracing diagram for convex lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Ray tracing diagram. Used Solutions.
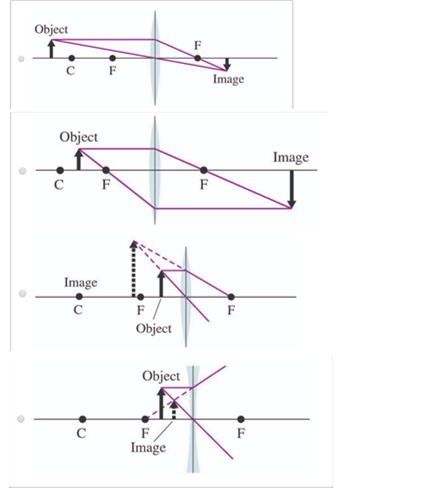
For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes through t
Arial Calibri Default Design Lenses What phenomenon is evident in lenses? Basic Types of Lenses Convex Lens Concave Lens Type of Image Convex Lens Ray Diagram for Convex Lens Rules for Ray Diagrams for Convex Lens PowerPoint Presentation Summary for Convex Lens Sign Convention Magnification Lens Equation Concave Lens Summary for Concave Lens ...
Ray diagrams for convex lenses. Typically this requires determining where the image of the upper and lower extreme of the object is located and then tracing the entire image. Image formation by convex lens ray diagrams. Im doing my best to draw this convex lens just like that. Ray diagrams the lens equation and the mirror equation.
A light ray traveling through a convex lens experiences refraction when it enters the lens through the front surface and again when it leaves the lens through the back surface. In this diagram here, we have drawn a particularly wide convex lens, which we can use to help us see the effects of the refraction more clearly.










---teachoo.png)





0 Response to "41 ray diagram for convex lenses"
Post a Comment