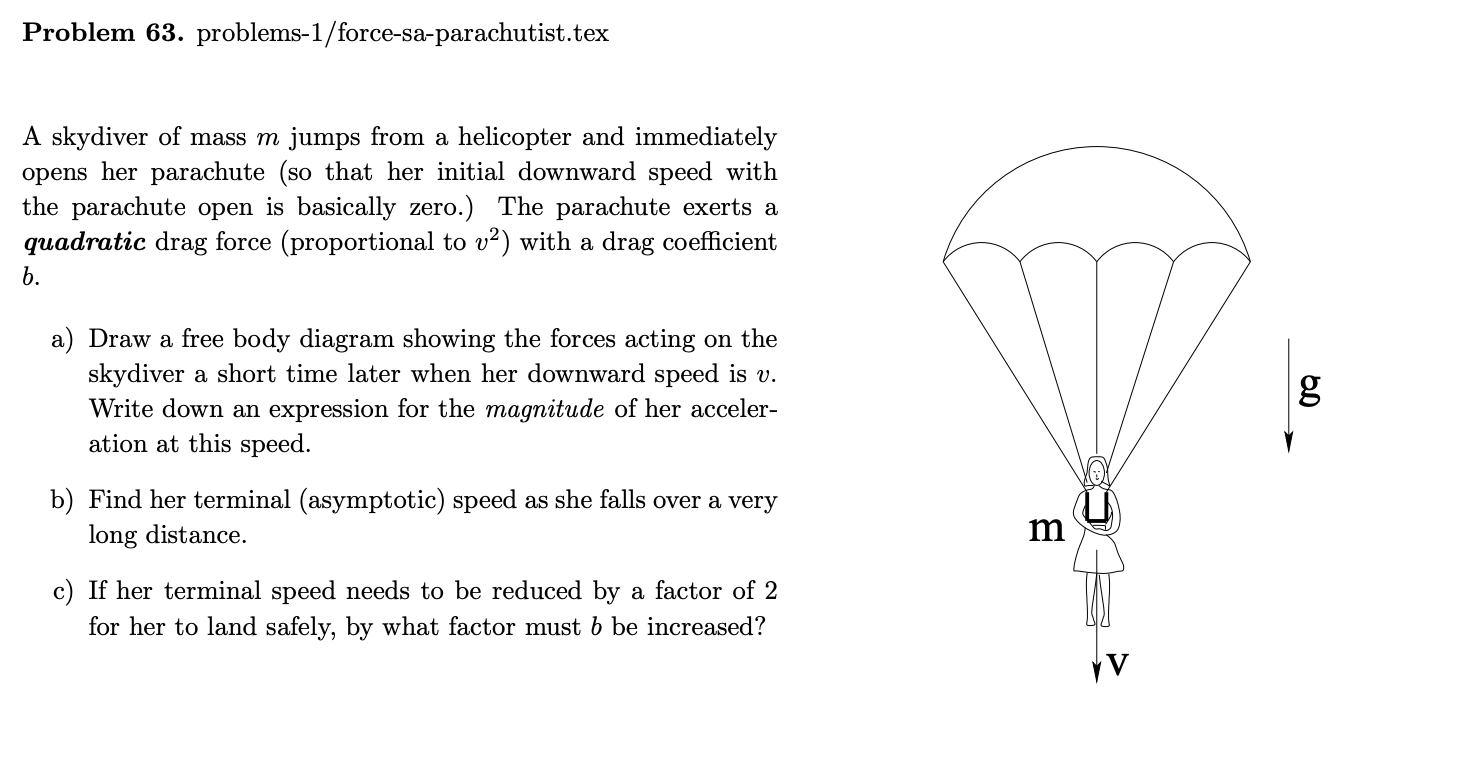
41 draw a free-body diagram of the system skydiver-parachute.
Free Body Diagram Showing Man Running Stock Vector Royalty Free Draw a free body diagram use the fact that upthrust weight of water displaced. Draw a free body diagram of the system skydiver parachute. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. Each force arrow in the diagram is labeled to indicate the exact type of force. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: 4. A skydiver is descending at a constant velocity. Considering the air resistance, the free body diagram for this situation would like the following: Free Body Diagram Solved Problem. Example: Draw a free body diagram of three blocks placed one over the other as shown in the figure. Solution:
Free-Body Diagrams. a physical model that represents the forces acting on a system. ... Before a skydiver opens her parachute, she might be falling at a velocity higher than the terminal velocity that she ... If you draw a free-body diagram for any point on the rope, there will be two tension forces acting in opposite directions. Fnet = Fup ...
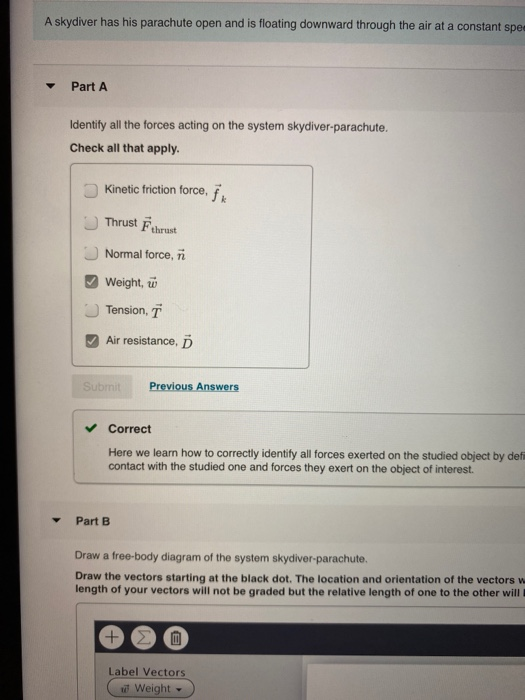
Draw a free-body diagram of the system skydiver-parachute.
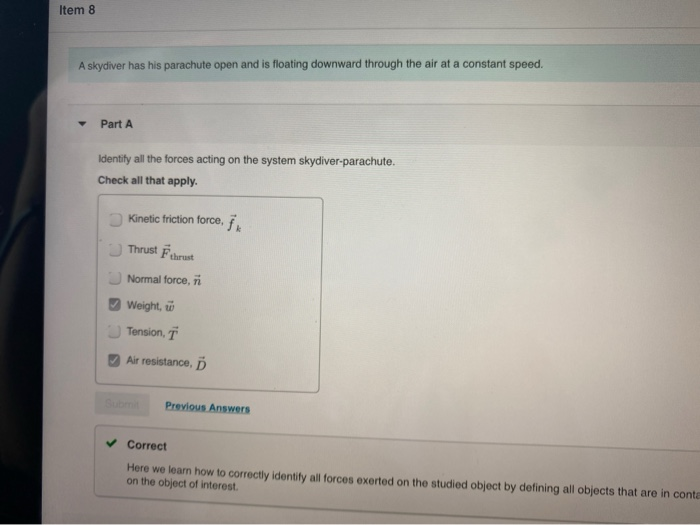
This problem has been solved! See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. 1) A skydiver has his parachute open and is floating downward through the air at a constant speed. Identify all the forces acting on the system skydiver-parachute. Check all that apply. A skydiver is falling straight down, along the negative y direction. During a later part of the fall, after the parachute has opened, her speed decreases from 48 to 26 m/s in 11s. Which of the following is correct? ... draw a Free Body Diagram (FBD) for the car. How many forces are acting on the car? 3 Fn = Normal Force W = Weight, the force of ... chute has opened, the skydiver descends with constant speed. a. In the space provided below, draw separate free-body diagrams for the system consisting of the skydiver and parachute: i. immediately after the diver has jumped out of the plane, and ii. shortly after the skydiver (with parachute open) begins to move with constant speed.
Draw a free-body diagram of the system skydiver-parachute.. An open parachute provides an upward drag force of 855 N to a 56 kg skydiver. Draw a free body diagram showing all the forces acting on the skydiver. Determine the weight of the skydiver. Determine the magnitude and direction of the net force on the skydiver. Determine the magnitude and direction of the skydiver's acceleration. To draw a free body diagram, start by sketching a simple representation of the body you want to make the diagram of, like a square to represent a box. Next, draw arrows on the shape that show the forces acting on the object. For example, draw a downward arrow to signify the weight of the object, since gravity pulls the object down. The free-body diagram for block. m. along with Newton's second law gives . T w Ma. −= m my. With . a. My = - g. and . w. M = mg. Solving for . T. gives . T w ma mg mg =+ =−= m my. 0N. This also follows from the fact that the tension in a rope is the same all along the rope. (b) If the two masses are reversed, the results will be the ... Free Body Diagram of Skydiving-Parachute system in TikZ 🥰🥰🥰 (1st comment Code and tutorial link)
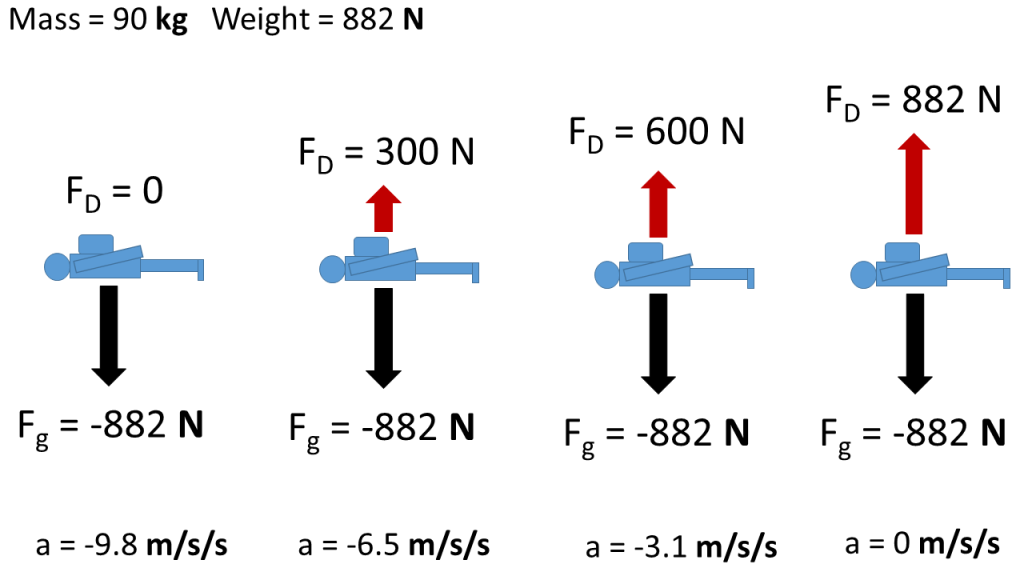
You are watching a skydiverwhose parachute is open and whose instantaneous height above ground level is indicated by digits on an electronic screen. The skydiverhas reached terminal speed. (Forthis question, assume the skydiver and the parachute togetheract as one body.) (a) Draw a system diagram and an FBD forthe situation. This processes is illustrated by free body diagrams for a skydiver with 90 kg mass in the following image: Free body diagrams of a person with 90 kg mass during a skydive. The initial speed is zero, so drag force is zero. As speed increases, the drag force grows, eventually cancelling out the person's weight. A skydiver has his parachute open and is floating downward through the air at a constant speed. Identify all the forces acting on the system skydiver-parachute. Check all that apply. Draw a free-body diagram of the system skydiver-parachute. Draw the vectors starting at the black dot. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. The exact length of your vectors will not be graded but the relative length of one to the other will be graded. Black dot is Mid screen Thank you; Question: Draw a free-body diagram ...
When a skydiver jumps out of a plane he starts accelerating downwards, until he reaches terminal speed. This is the speed at which the drag from air resistance exactly balances the force of gravity pulling him down. The figure below shows a free-body diagram of this. This TikZ tutorial is about drawing a free body diagram of a skydiver with parachute. Mainly, we will learn how to: 1) draw an arc in LaTeX using TikZ, 2) use foreach loop for repetitive objects, 3) draw animals using the package TikZlings, and much more! 29 Draw A Free Body Diagram Of The System Skydiver. Click Images to Large View 29 Draw A Free Body Diagram Of The System Skydiver 1. Draw a free body diagram of a parachutist who . a. has just stepped out of the airplane, and is accelerating toward the ground. b. has opened her parachute and is traveling downward with constant velocity. 2. Draw a free body diagram of a brick. a. at rest on a table. b. being pushed with constant velocity along a rough horizontal surface.
Free Body Diagram Simulator!! : A hockey puck glides to the right across the ice at a constant speed. ... Grav : A downward-moving skydiver who has just opened the parachute is slowing down. Situation (Diagram the forces on the skydiver/parachute combination.) Fair Grav : A rightward force is applied to a crate to push it across. the floor at a ...
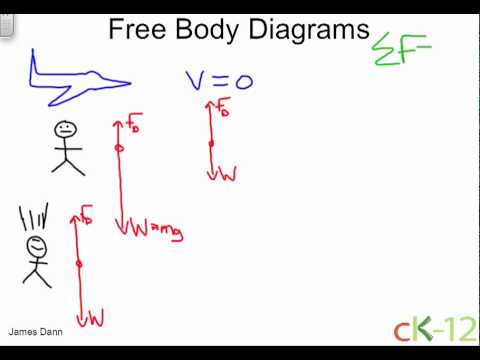
Acceleration. After the air resistance becomes large enough to balance out a skydiver's weight, they will have no net force. From Newton's First Law we already know that an object's inertia prevents a change in velocity unless it experience a net force, so from that point when the forces are balanced and onward, the skydiver continues at a constant velocity until they open their parachute.
The Physics Classroom serves students, teachers and classrooms by providing classroom-ready resources that utilize an easy-to-understand language that makes learning interactive and multi-dimensional. Written by teachers for teachers and students, The Physics Classroom provides a wealth of resources that meets the varied needs of both students and teachers.
Example 3.15 Using the same diagram as in the previous example, assume that m = 2 kg, M = 10 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the small block and the tabletop is 0.5. Compute the acceleration of the blocks. Solution. Once again, draw a free-body diagram for each object.
13. Free-Body Diagram Draw a free-body dia-gram of a water bucket being lifted by a rope at a decreasing speed. Specifically identify the system. Label all forces with their agents and make the arrows the correct lengths. Frope on bucket FEarth's mass on bucket System a Sugar Fhand on bag System FEarth's mass on bag a! 0
Problem 5 A skydiver is falling with a constant velocity. Consider air resistance. Draw a free-body diagram for the skydiver. Gravity pulls down on the skydiver, while air resistance pushes up as she falls. Problem 6 A man drags a sled across loosely packed snow with a rightward acceleration. Draw a free-body diagram of the forces acting on the ...
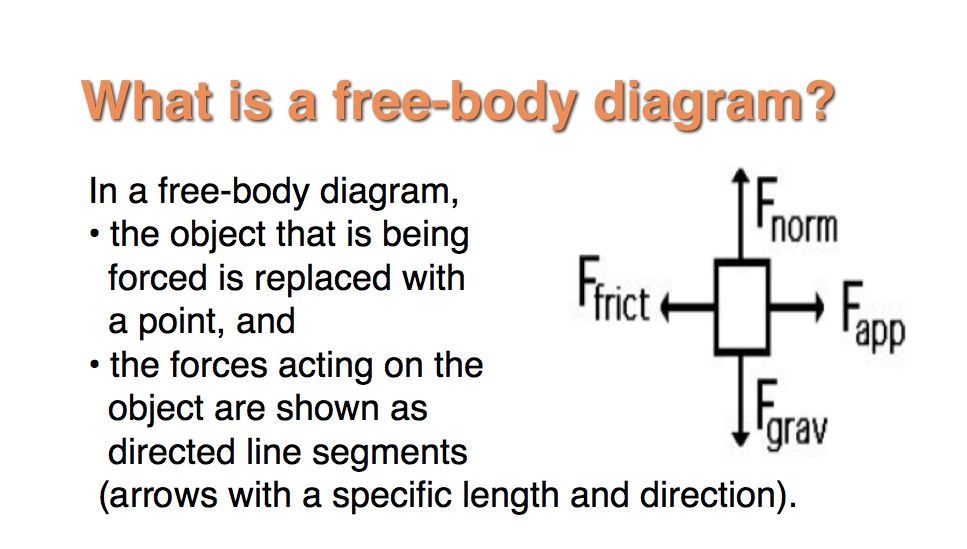
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
Figure 1 shows the free body diagram of the idealized skydiver a few seconds after leaving the airplane. The system of coordinates chosen associates the x direction with the horizontal and y direction with the vertical. Figure 1: Free body diagram of the idealized skydiver, a few seconds after jumping of the airplane.
When you draw a free body diagram, you draw longer arrows for stronger forces, and shorter arrows for weaker ones. If the skydiver's falling speed is still increasing, you can tell that the downward force of gravity acting on him is still greater than the upward force of air resistance.
10. A downward-moving skydiver who has just opened the parachute is slowing down. (Diagram the forces on the skydiver/parachute combination.) 11. The cabin of a small freight elevator is secured to a motor by a cable and is moving upward while slowing down. There is no contact between the cabin and the elevator shaft. Ignore air resistance. 12.
Step 4: Free Body Diagram. Now, we need to draw arrows that represent different forces applied on the skydiving-parachute system, namely, the gravity and the air resistance force. Here is the final LaTeX code of the free body diagram of this system: 1. 2.
chute has opened, the skydiver descends with constant speed. a. In the space provided below, draw separate free-body diagrams for the system consisting of the skydiver and parachute: i. immediately after the diver has jumped out of the plane, and ii. shortly after the skydiver (with parachute open) begins to move with constant speed.
A skydiver is falling straight down, along the negative y direction. During a later part of the fall, after the parachute has opened, her speed decreases from 48 to 26 m/s in 11s. Which of the following is correct? ... draw a Free Body Diagram (FBD) for the car. How many forces are acting on the car? 3 Fn = Normal Force W = Weight, the force of ...
This problem has been solved! See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. 1) A skydiver has his parachute open and is floating downward through the air at a constant speed. Identify all the forces acting on the system skydiver-parachute. Check all that apply.

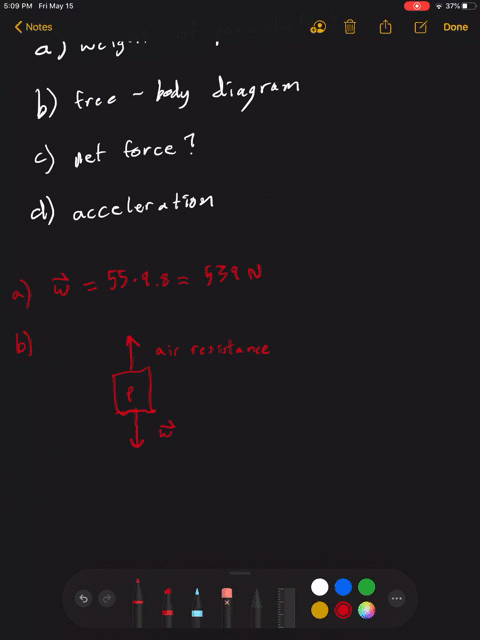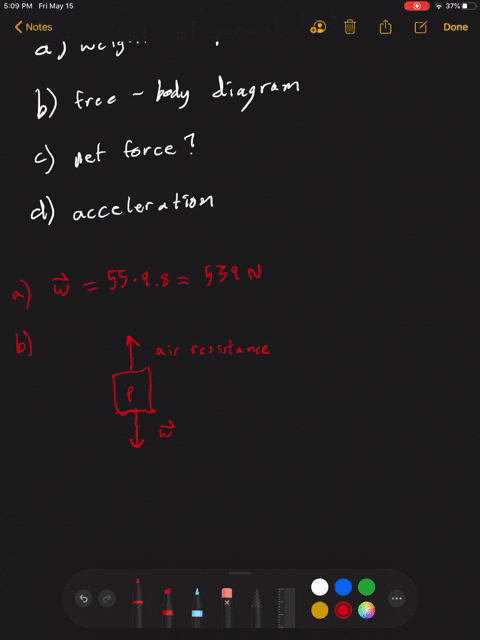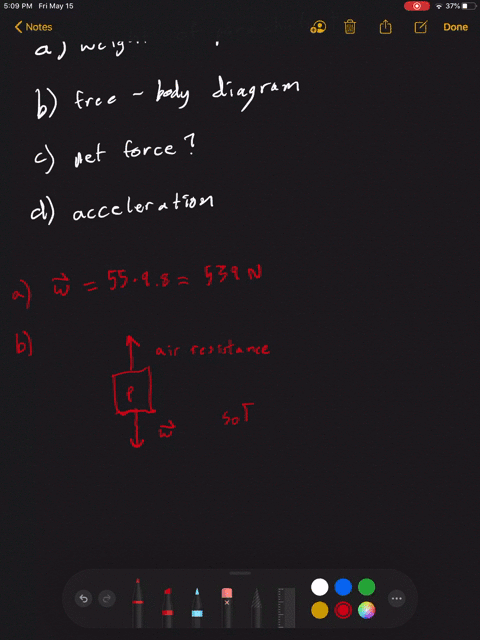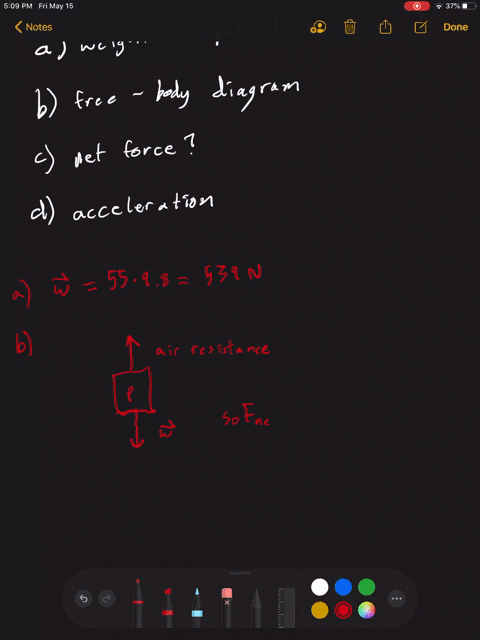






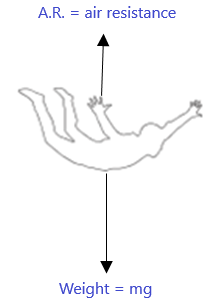










0 Response to "41 draw a free-body diagram of the system skydiver-parachute."
Post a Comment