40 p2 molecular orbital diagram
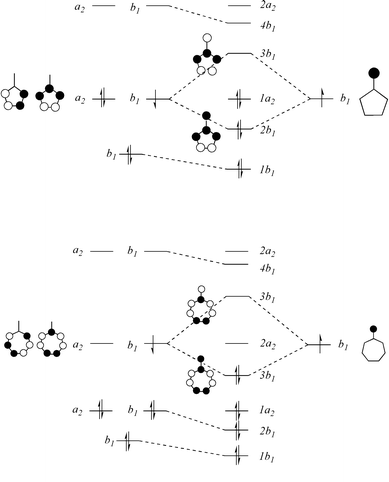
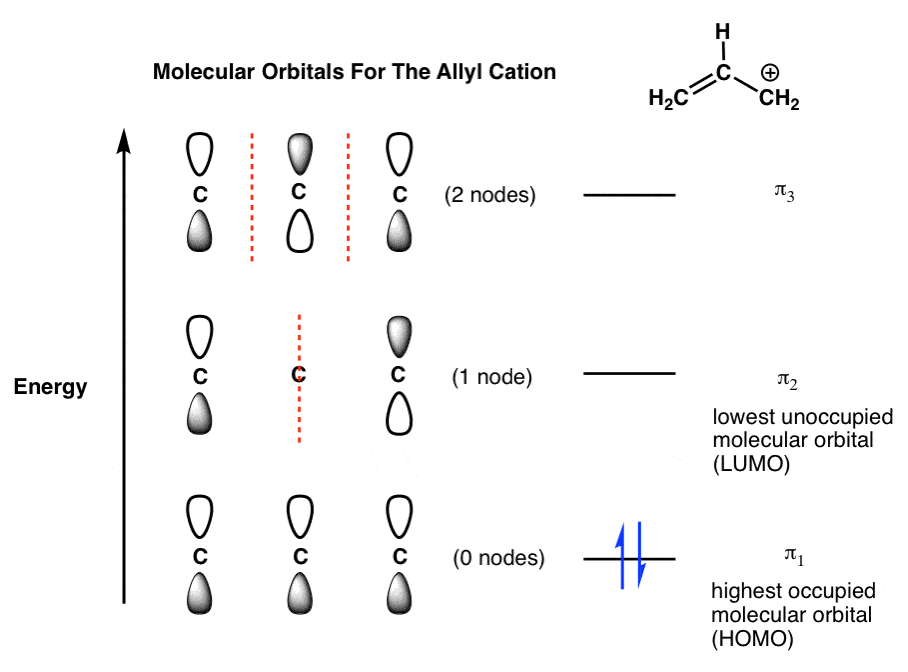
Molecular Orbital Diagrams. 1. Electrons preferentially occupy molecular orbitals that are lower in energy. 2. Molecular orbitals may be empty, or contain one or two electrons. Group theory is usually used to develop molecular orbital diagrams and drawings of more complicated molecules. 2. Building The Pi Molecular Orbital Diagram For Benzene: Hexatriene and Benzene Each Have Six Pi Molecular Orbitals. This is really the key difference in the molecular orbital picture of a cyclic system versus an acyclic system: two units can co-exist on the same floor.
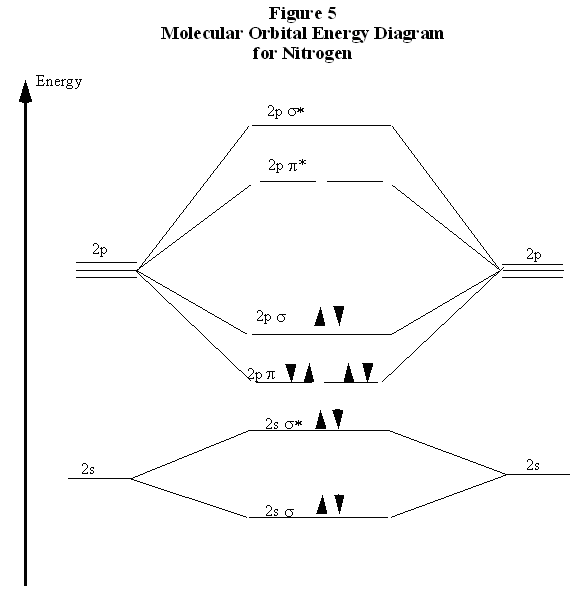
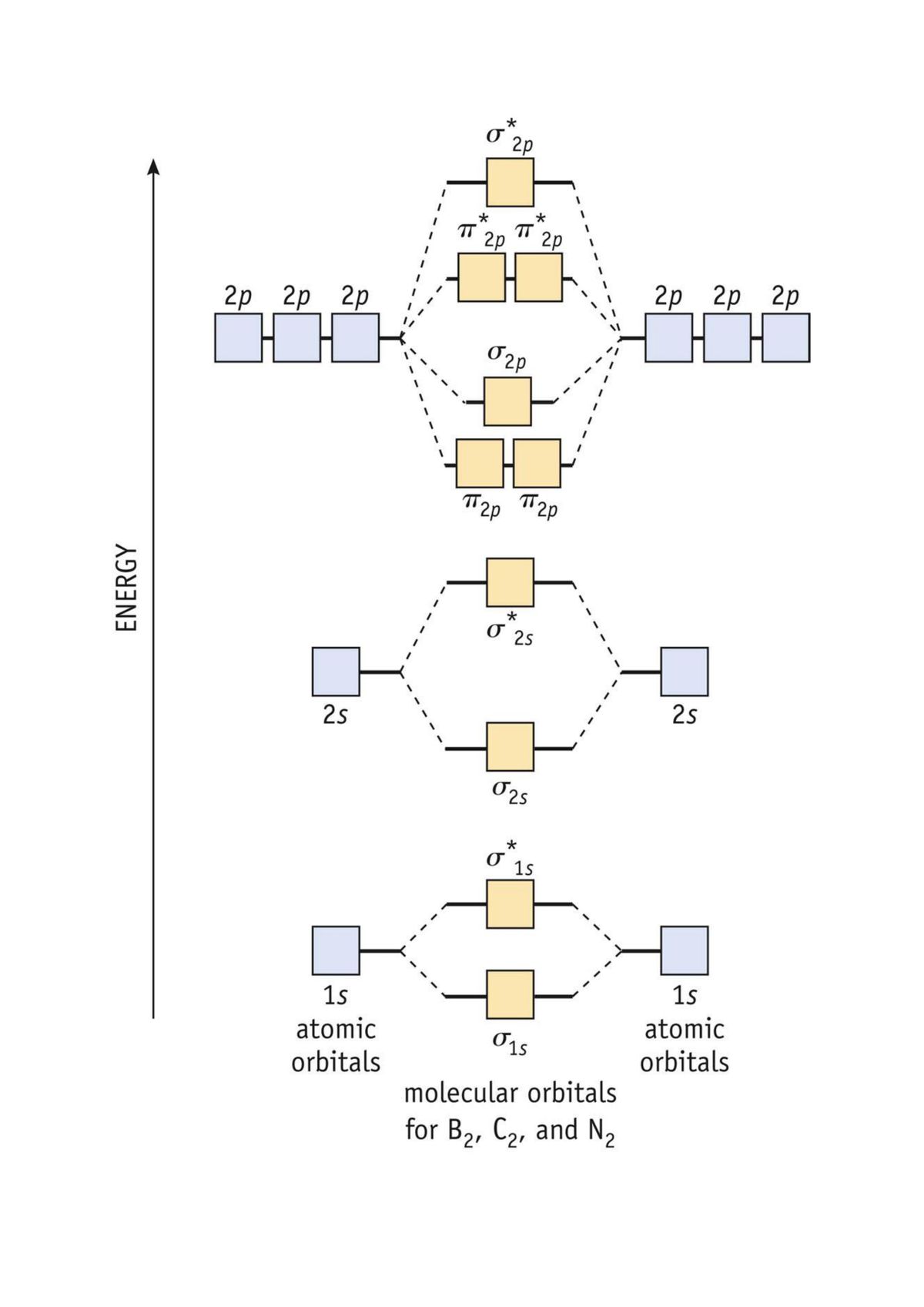
The molecular orbital energy- level diagram that results is constructed by putting the molecular orbitals in order of increasing number of Each valence shell has one 2s and three 2p orbitals, and so there are eight atomic orbitals in all and hence eight molecular orbitals that can be formed.
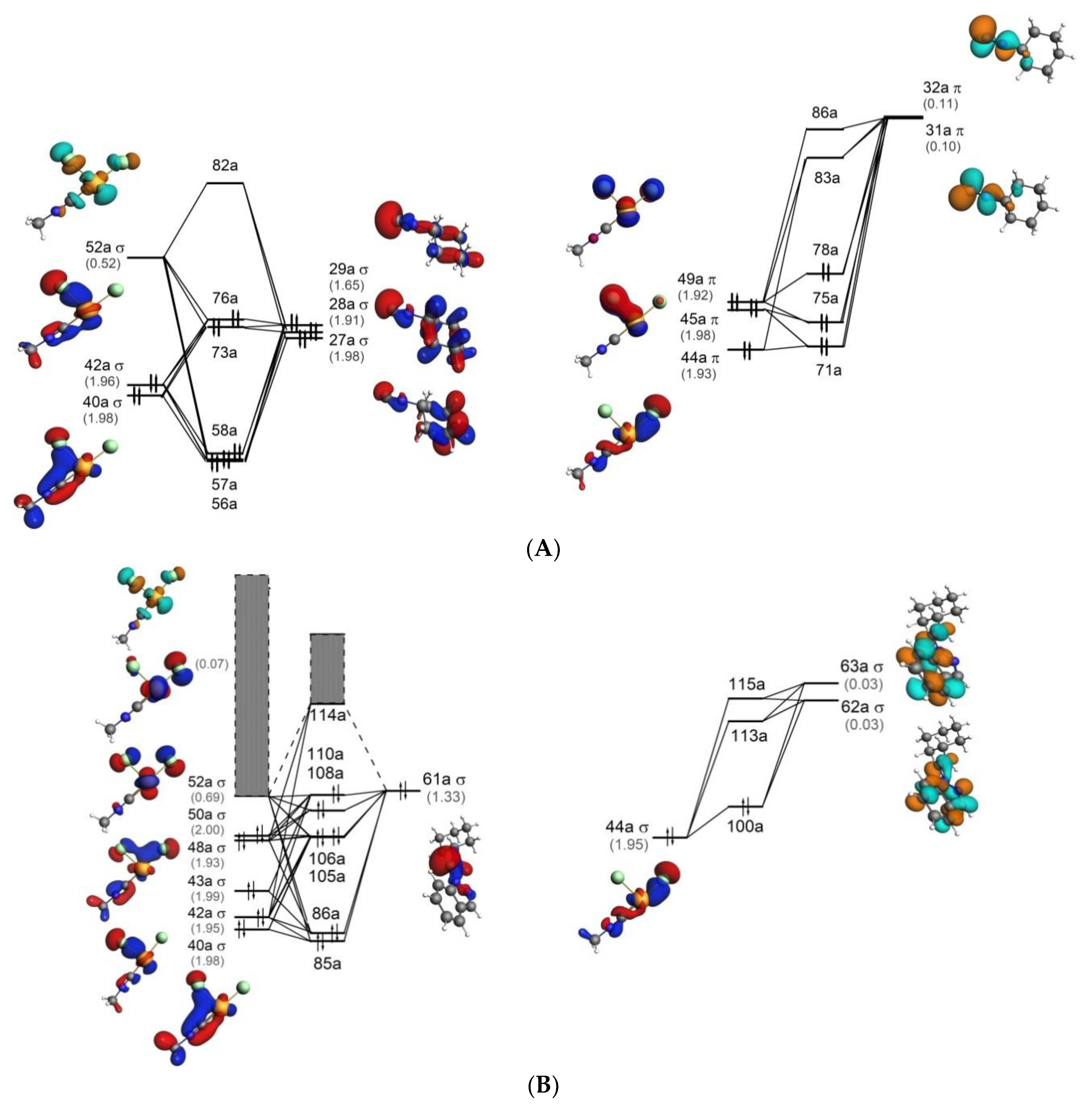
P2 molecular orbital diagram
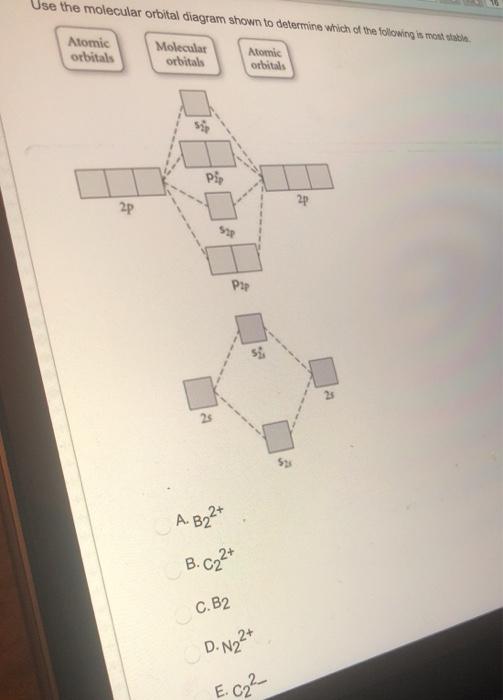
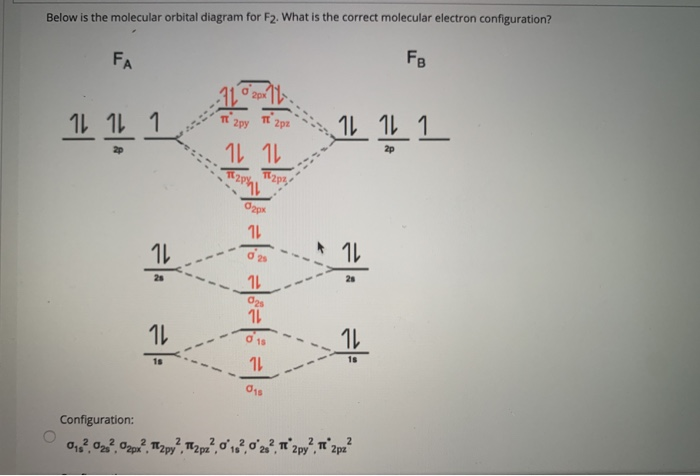
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked on the sides by constituent AO energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels ranging from low energy at the bottom to high energy at the top. draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2. the number of electrons in the pi2p molecular orbital is. their molecular orbital diagrams are more symmetrical than those of homonuclear diatomic molecules. which of the following statements about nitrogen oxide, NO, is FALSE.
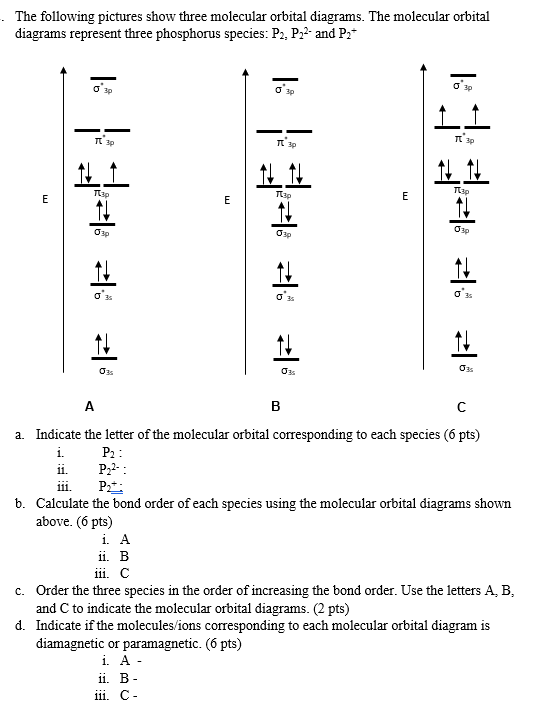
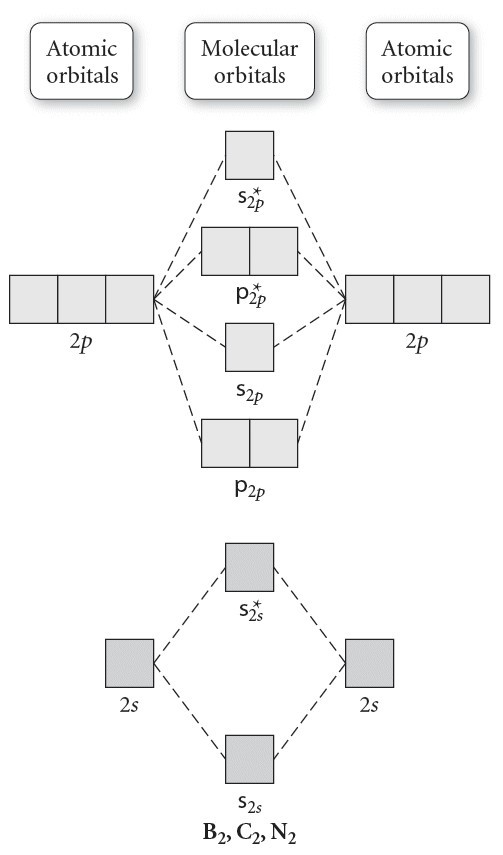
P2 molecular orbital diagram. Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (N2)Use aufbau and Hund to fill with 10 valence electronsYou get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2).Bond... • Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the H2 molecule. (b) The shapes of the molecular orbitals are obtained by squaring the wave functions for MO1 and... The problem is draw the molecular orbital diagram for P2, P2+, P2-. Rank these in terms of increasing bond strength. Thanks in advance for the help. 1. Sketch the qualitative molecular orbital diagram for XeF2. The molecule is linear and symmetric. Assume the valence 5s-orbitals of Xe are sufficiently lower in energy than the valence 5p-orbitals In other words, the bonding environment of the C-atom has a big effect on the shape of the 2p(C) orbital.
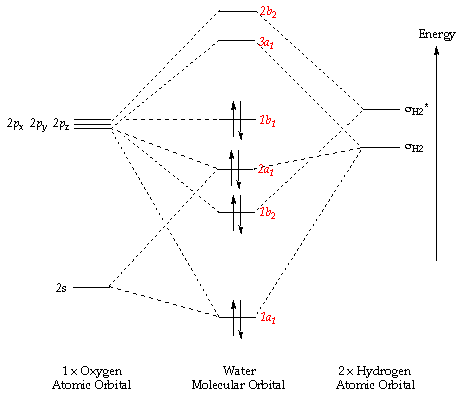
Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in LaTeX by means of the package MOdiagram. For information about the more traditional molecular structure... Here we have a molecular orbital diagram for the CO molecule. So when you're drawing on a global diagram like this, you have to draw it, it should be schematically shown lower energy than the carbon. Molecular Orbital Theory. I'm having a lot of trouble with this stuff. I don't really know how to start these questions (such as how to draw a correlation diagram) An orbital correlation attempts to show how the atomic orbitals belonging to the individual atoms in a molecule interact to form the molecular... ...molecular orbitals (LCAO), bonding / antibonding - Labelling of molecular orbitals (MOs) (σ, π and g, u) - Homonuclear diatomic MO diagrams - mixing of different AO's - More complex molecules (CO, H2O ….) • Energy is dependent on n2 and Z2 (2s and 2p the same - only true for 1 electron systems.
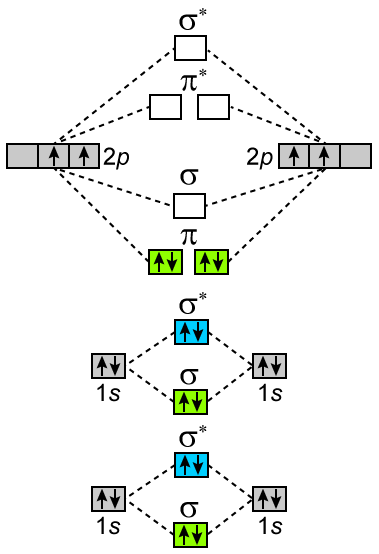
The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding electrons. Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. The #2p_y# and #2p_z# orbitals can overlap side-on to form degenerate pairs of #2pπ# and #2pπ"*"# orbitals. The bonding molecular orbital concentrates electrons in the region directly between the two nuclei. The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals. Figure 8.35 The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that H2 will be a stable molecule with lower energy than the separated atoms. Looking at Ne2 molecular orbitals, we see that the order is consistent with the generic diagram shown in the previous section.
Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons.
This second orbital is therefore called an antibonding orbital. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H2+.
The molecular orbital energy level diagram for dioxygen molecule is shown below Ans: The molecular orbital theory characterizes the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics. It is used to calculate bond order, bond length, bond strength, paramagnetic and...
The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored They completely fill all the orbitals except the highest-energy antibonding sigma 2p orbital. Thus, there will be 8 bonding electrons and 7 antibonding electrons...
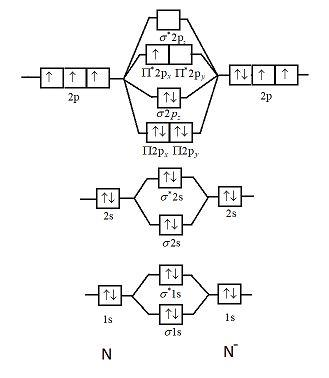
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen monoxide, the nitrosyl cation and the nitrosyl anion. Hot Network Questions. Why would one use "vous" when calling someone a racist?
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row
molecular orbital is the sum in an increased concentration. of two atomic orbitals, of electrons The diagram shows the order of energy levels for the molecular orbitals, assuming significant In the absence of mixing, the sg(2p) orbital would be expected to be lower in energy than the pu(2p)...
Figure 9-2 Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the combination of the 1s atomic orbitals on two identical atoms (at the left) to form two MOs. Each diagram is an extension of the. right-hand diagram in Figure 9-2, to which we have added the molecular orbitals formed. from 2s and 2p atomic...
The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. No. 9 Molecular Orbital Diagram for CO. Analysis done by Bond Order. If value of bond order is positive, it indicates a stable molecule and if the value is negative or zero, it means that the molecule is unstable.
A second molecular orbital is also created, which we simplistically show as a subtraction of the two atomic 1s orbitals [σ* = (1sa - 1sb)]. The energy diagram shows that 2s electrons are held more tightly than 2p electrons (because they are closer to the nucleus, on average).
Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams. Bond Orders and Stability of Molecules. Figure 1: Cartoons of the volume occupied by electrons in the 1s, 2s, and 2p hydrogen-like orbitals. Principles of Molecular Orbital Theory.
draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2. the number of electrons in the pi2p molecular orbital is. their molecular orbital diagrams are more symmetrical than those of homonuclear diatomic molecules. which of the following statements about nitrogen oxide, NO, is FALSE.
Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked on the sides by constituent AO energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels ranging from low energy at the bottom to high energy at the top.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.











0 Response to "40 p2 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment