39 crystal field energy level diagram
(Crystal field splitting energy also applies to tetrahedral complexes: Δ t.) It is important to note that the splitting of the d orbitals in a crystal field does not change the total energy of the five d orbitals: the two e g orbitals increase in energy by 0.6Δ o, whereas the three t 2 g orbitals decrease in energy by 0.4Δ o. Thus the total ...
AboutPressCopyrightContact usCreatorsAdvertiseDevelopersTermsPrivacyPolicy & SafetyHow YouTube worksTest new features · © 2021 Google LLC
Find step-by-step Chemistry solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: Draw the crystal-field energy-level diagrams and show the placement of d electrons for each of the following: $[IrCl_6]^{2-}$ (a low-spin complex),.
Crystal field energy level diagram
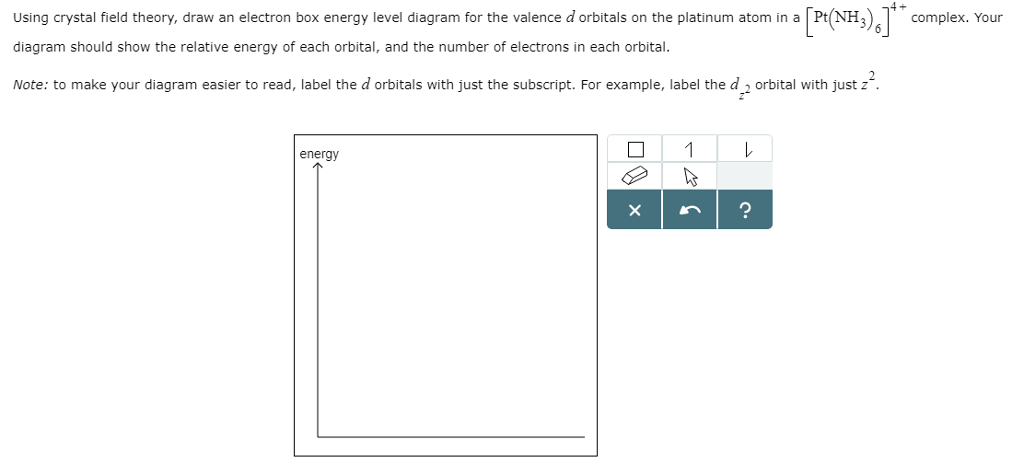
Answer to draw the crystal field energy level diagram for the 3d orbital of titanium in [Ti(H2O)6]^3+ indicate the crystal field s...
Textbook solution for General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course… 11th Edition Steven D. Gammon Chapter 22 Problem 22.57QP. We have step-by-step solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts!
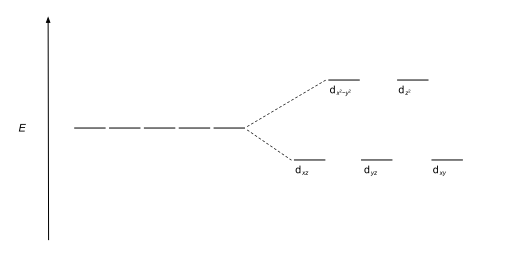
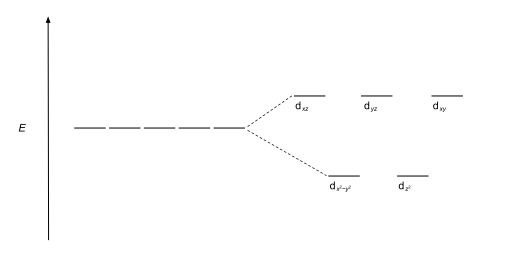
Hence, these three orbitals have less energy than the average energy in the spherical crystal field. Thus, the repulsions in octahedral coordination compound yield two energy levels: t 2g – set of three orbitals (d xy, d yz and d xz) with lower energy; e g – set of two orbitals (d x 2-y 2 and d z 2) with higher energy
Crystal field energy level diagram.
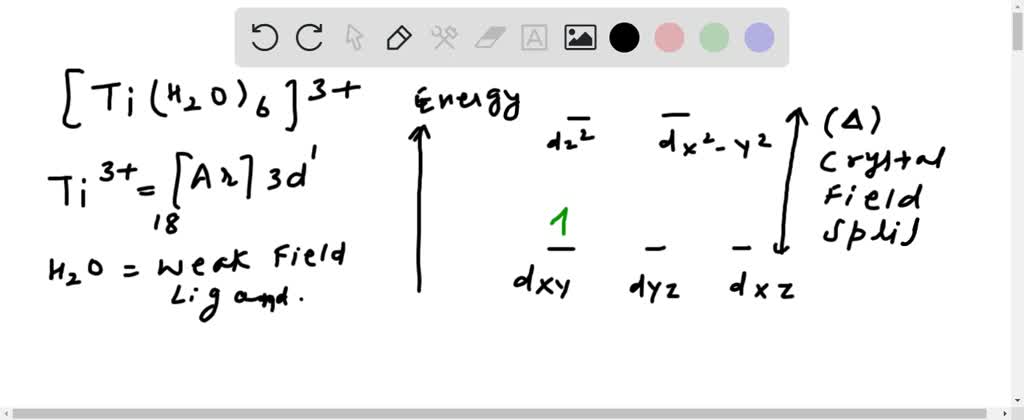
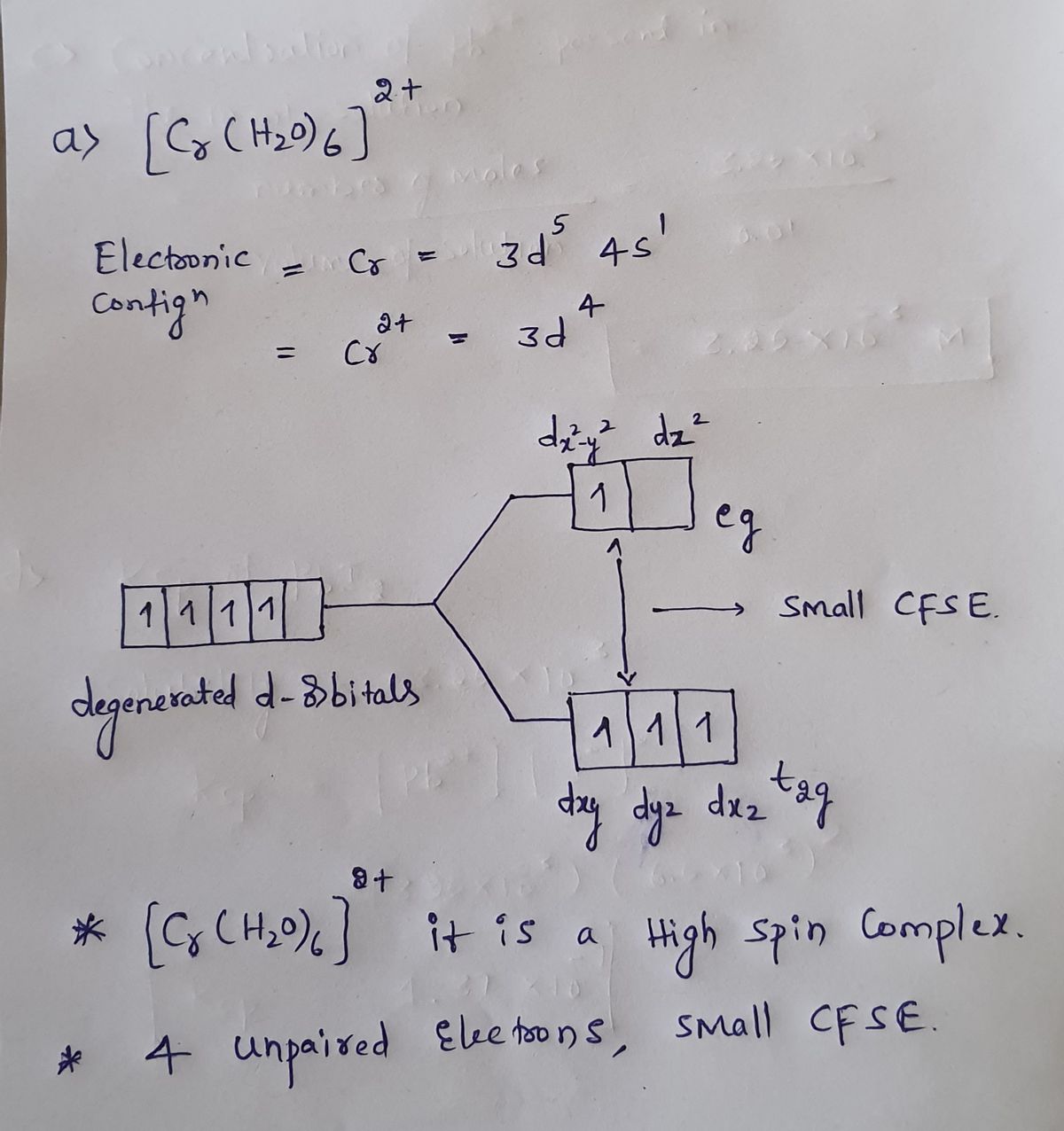
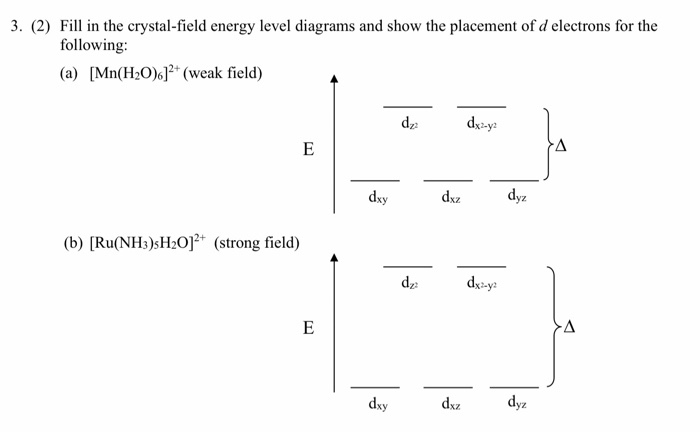
Draw the crystal-field energy-level diagrams and show the placementof d. Need more help! Draw the crystal-field energy-level diagrams and show the placementof d electrons for each of the following: (a) [Cr(H2O)6]2 + (four unpaired electrons), (b) [Mn (H2O)6]2+ (high spin),
But the two orbitals in the e g set are now lower in energy than the three orbitals in the t 2g set, as shown in the figure below.. To understand the splitting of d orbitals in a tetrahedral crystal field, imagine four ligands lying at alternating corners of a cube to form a tetrahedral geometry, as shown in the figure below. The d x 2-y 2 and d z 2 orbitals on the metal ion at the center of ...
Correct option is. B. Since cyanide ion is a strong field ligand, electrons pair up. All six electrons are present in lower t2g. . energy level.
The notation/symbol used for each ... no change in sign upon the symmetry operation inversion. The energy splitting is shown schematically in Fig. 2.7. Figure 2.7. Crystal field d orbital splitting diagrams for common geometries....
As a result, if there are any electrons ... ligand field by the amount known as the CFSE. Conversely, the eg orbitals are higher in energy. So, putting electrons in them reduces the amount of CFSE. Octahedral CFT splittingElectron diagram for octahedral d shell splitting. Crystal field ...
Energy level of hypothetical spherical field Crystal Field Splitting Energy, Δo! The energy gap between t2g and eg levels is designated Δo or 10Dq.! The energy increase of the eg orbitals and the energy decrease of the t2g orbitals must be balanced relative to the energy of the hypothetical spherical field (sometimes called the barycenter ...
We calculate the crystal field parameters from the crystal structure date and diagonalize the crystal field Hamiltonian to obtain the energy level structure of Cr 3+ ions in LiGa 5 O 8. The ...
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
Click here to get an answer to your question ✍️ Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electric configuration of the central metal ...2+: 5.3K2: 5.91 answer · Top answer: Number of unpaired electrons (n) = 4 Magnetic moment (mu) = √(4(4 + 2)) = √(24) = 4.9 BM
May 7, 2021 - It requires more energy to have an electron in these orbitals than it would to put an electron in one of the other orbitals. This causes a splitting in the energy levels of the d-orbitals. This is known as crystal field splitting. For octahedral complexes, crystal field splitting is denoted ...
So in this question is we draw the crystal filled energy level Diagram for 30 orbital off titanium complex That is B I ch teau six three post. So for this complex, we have broader crystal food. Energy level diagram. So, first off, all we discuss about the reluctantly configurations or titanium ...
Using crystal field theory, sketch the energy-level diagram for the d orbitals in an octahedral field; then fill in the electrons for the metal ion in each of the following complexes. How many unpaired electrons are there in each case? a [V(CN) 6] 3− b [Co(C 2 O 4) 3] 4− (high-spin). c [Mn(CN) 6] 3− (low-spin)
Hence, Co3+has a d6 configuration (1s22s22p63s23p63d6, while losing 1 3d and 2 4s electrons.) So the orbital energy level diagram is: And the number of unpaired ...1 answer · Top answer: (i)• In [CoF6]3–, the central metal atom is cobalt Co and oxidation state of Co in hereis: x=-6 times (-1)-3=+3Hence, Co3+has a d6 configuration ...
Goprep is providing NCERT Solutions for Class 8 to Class 12 and Online Coaching Classes for JEE/NEET Aspirants. Get CBSE & State Board Reference Book Solutions, Previous Year Question Papers and Live Sessions.
Hence, the crystal field splitting Δ o decreases when ligand to metal bonding takes place. The overall molecular orbital energy level diagram for this type of π-bonding in octahedral complexes can be shown as: Buy the complete book with TOC navigation, high resolution images and no watermark.
The crystal field splitting energy for tetrahedral metal complexes (four ligands) is referred to as Δ tet, and is roughly equal to 4/9Δ oct (for the same metal and same ligands). Therefore, the energy required to pair two electrons is typically higher than the energy required for placing electrons in the higher energy orbitals.
2. Draw the crystal field energies levels and electron occupancies for octahedral Cr3+ ions. Indicate the energy gap that corresponds to the transition that is being investigated. 3. Prepare a table of your data, including columns for λmax in nm and ∆O in cm-1, eV, and kJ/mol. Arrange the entries in order of increasing gap energy. 4.
Draw the crystal-field energy-level diagrams and show the placementof d electrons for each of the following: (a) [Cr (H2O)6]2 + (four unpaired electrons), (b) [Mn (H2O)6]2+ (high spin), (c) [Ru (NH3) 5H2O]2+ (low spin), (d) [IrCI6]2- (low spin), (e) [Cr (en)3]3+ , (f)... View Answer. Qualitatively draw the crystal field splitting of the d ...
Tomorrow's answer's today! Find correct step-by-step solutions for ALL your homework for FREE!
Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ion and determine the magnetic moment value in
Metal d orbitals in an O h crystal field • If a transition metal ion is placed in a spherical field equivalent to the charges on six ligands, the energies of all five d orbitals would rise together (degenerately) as a result of the repulsions between the negative charges on the ligands and the negative charges of the
The crystal field energy-level diagram. Label all orbitals and fill with the appropriate. number of electrons. (b) (2 pts.) Is the complex paramagnetic or diamagnetic? Circle one (c) (2 pts.) Calculate the crystal field stabilization energy (CSFE) in terms of "Dq" (where 10Dq is
Their blank d -splitting diagrams within the realm of crystal field theory are: [Ni(CN)4]2−: The d orbitals fill with 8 electrons, then, with a low spin configuration. You can see that an even number of d orbitals will get filled ( dyz,dxz,dz2,dxy) with an even number of 3d electrons. This gives rise to a diamagnetic configuration, as expected.
Certain Tanabe-Sugano diagrams (d 4, d 5, d 6, and d 7) also have a vertical line drawn at a specific Dq/B value, which is accompanied by a discontinuity in the slopes of the excited states' energy levels.This pucker in the lines occurs when the identity of the ground state changes, shown in the diagram below. The left depicts the relative energies of the d 7 ion states as functions of ...
For each of the following complexes, draw a crystal field energy-level diagram, assign the electrons to orbitals, and predict the number of unpaired electrons
Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ion and determine the magnetic moment asked Aug 26, 2019 in Chemistry by Anup Agrawal ( 17.5k points)
We find that the square planar complexes have the greatest crystal field splitting ligand field (left diagram) and the tetrahedral field (right diagram).D-orbital splitting diagrams Use crystal field theory to generate splitting diagrams of the d-orbitals for metal complexes with the following coordination patterns: 1. Octahedral 2. Tetrahedral 3.

Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central
(d) Draw the crystal field energy-level diagram for cisplatinum, labeling the d-orbitals. (e) Predict whether cisplatinum is diamagnetic or paramagnetic? Explain your answer. a) Pt Cl NH3 NH 3Cl Pt Cl NH Cisplatinum Transplatinum b) 90° c) Cisplatinum has four ligands. CN (coordination number) = 4 d) Pt is in group 10.
Crystal Field Splitting in an Octahedral Field eg Energy 3/5 o o 2/5 o t2g e g - The higher energy set of orbitals (d z2 and d x2-y2) t 2g - The lower energy set of orbitals (d xy, d yz and d xz) Δ o or 10 Dq - The energy separation between the two levels The eThe eg orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0 6orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0.6 Δo The t2gorbitals to be stabilized to the ...
4) Using crystal field theory, draw the crystal field d orbital energy level diagram for each of the following complexes by assigning electrons to 3d orbitals. [Co(en)2]2+ (square planar) [FeF6]3- (octahedral) 5) For the following complex, draw an orbital diagram for the isolated metal ion.
Iron(II) complexes have six electrons in the 5d orbitals. In the absence of a crystal field, the orbitals are degenerate. For coordination complexes with strong-field ligands such as [Fe(CN) 6] 4−, Δ oct is greater than P, and the electrons pair in the lower energy t 2g orbitals before occupying the eg orbitals. With weak-field ligands such as H 2 O, the ligand field splitting is less than ...
Ask any question and get an answer from our subject experts in as little as 2 hours.
Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ion and determine the magnetic moment value in the following. (i).[CoF 6 ] 3−,[Co(H 2 O) 6 ] 2+,[Co(CN) 6 ] 3− (ii).[FeF 6 ] 3−,[Fe(H 2 O) 6 ] 2+,[F(CN) 6 ] 4− Medium Solution Verified by Toppr Electronic configuration : Co 3+=Ar3d 6
The single d electron occupies an energy level 2/5 Δ o which is below the average energy of the d orbitals because of the CFSE of the d-orbitals. CFSE=2/5x243=97kJmol-1 As a result the complex is stable CRYSTAL FIELD STABILIZATION ENERGY (CFSE) The energy difference between the distribution of electrons in a particular crystal field and that for
Answer to Using crystal field theory, determine the energy-level diagram for the orbitals in an octahedral field for each of the f...
The most basic crystal field argument includes point-symmetric charges approaching the central metal in a way as the ligands would. Then, any orbitals that are symmetry-equivalent will end up at the same energy, and depending on how much these point towards the point-symmetric approaching charges they will be raised or lowered.
The magnitude of these energy separations, or crystal field splittings, depend on the valence of the transition metal ion and the symmetry, type and distances ...
Draw a crystal field energy level diagram for the 3d orbitals of titanium in leftoperatornametileftm
Answer in brief. With the help of the crystal field, energy-level diagram explain why the complex [Cr(en)3]3⊕ is coloured?
Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ion and determine the magnetic moment value i...
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ✍️ Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ ion and determine the magnetic moment value in the following: [CoF6]^3 - , [Co(H2O)6]^2 + . [Co(CN)6]^3 -
In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation
Energy-level diagram for C -3+ in an octahedral crystal field (L—S coupling not included) for the special choices and 30 (lowest doublet-levels only observed... Fig. 2. The simplified energy level diagram for Oj, 02, and 02 in their ground state. When a crystal field is present, the n, and nu levels are not degenerate.
Figure 3.7 Simplified energy level diagram for 3d6 ions (e.g., Fe2+ and Co3+) in an octahedral crystal field. The diagram shows that in a high intensity field the 1Alg crystal field state, corresponding to the low-spin configuration (t2gf, becomes the ground state.
Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ion and determine the magnetic moment value in the following <br> (a) [CoF_(6)]^(3-), [Co(H_(2)O)_(6)]^(2+), [Co(CN)_(6)]^(3-) <br> (b) FeF_(6)^(3-), [Fe(H_(2)O)_(6)]^(2+), ...
It requires more energy to have an electron in these orbitals than it would to put an electron in one of the other orbitals. This causes a splitting in the energy levels of the d-orbitals. This is known as crystal field splitting. For octahedral complexes, crystal field splitting is denoted by \(\Delta_o\) (or \(\Delta_{oct}\)).

















![Which of the following energy level diagram for [FeF6]3- is](https://cdn.tardigrade.in/img/question/chemistry/wmkts40pjptj-d.png)







0 Response to "39 crystal field energy level diagram"
Post a Comment