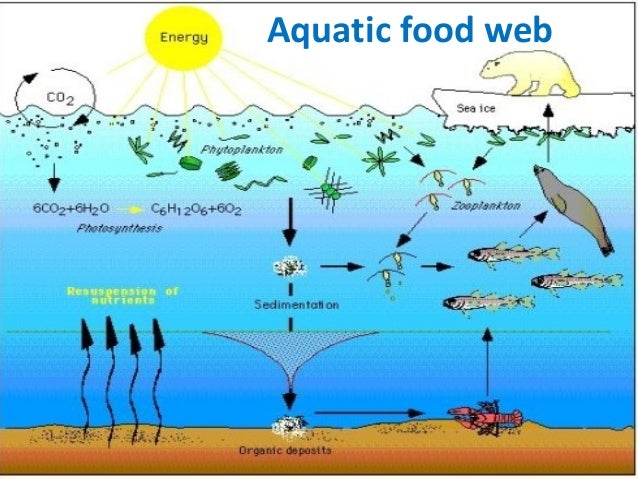
39 aquatic food web diagram
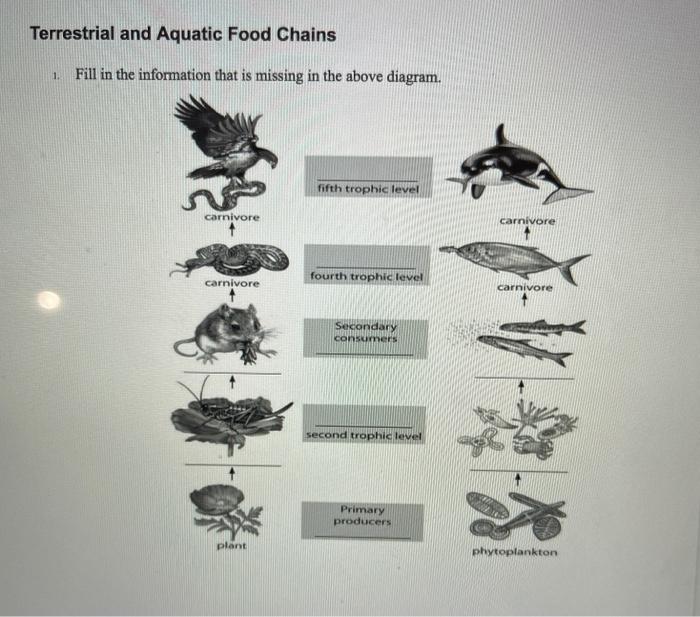
A food chain in a grassland ecosystem may consist of grasses and other plants, grasshoppers, frogs, snakes and hawks (Figure 8.3). In a freshwater aquatic ecosystem like a pond, the organisms in the food chain include algae, small animals, insects and their larvae, small fish, big fish and a fish-eating bird or animal (Figure 8.4).
In aquatic ecosystems, food webs involve organisms that live in water. Aquatic ecosystems make up the largest part of our biosphere, the part of Earth that is able to support life. Aquatic ecosystems include marine and freshwater ecosystems. Marine ecosystems are saltwater environments such as oceans, coral reefs, and salt marshes.
A food web is an ecological concept based on food and energy transfer. It shows the relationship of animals present in a particular habitat or ecosystem. A food web is a combination of several food chains. This food flow also depicts the flow of energy from the producers to the consumers. The terrestrial food web is different from an aquatic ...
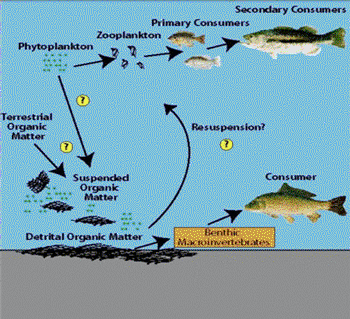
Aquatic food web diagram
Food webs describe who eats whom in an ecological community. Made of interconnected food chains, food webs help us understand how changes to ecosystems — say, removing a top predator or adding nutrients — affect many different species, both directly and indirectly. Phytoplankton and algae form the bases of aquatic food webs. They are eaten by primary consumers lik
QUESTION 2 The diagram below shows an aquatic food web. Study the diagram and then answer the questions which follow: Great White Shark Dolphin Sea Turtle Moon Jellyfish Clowrffish Ang Decomposers: Sea Cucumber Starfish Seaweed Algae Plankton Identify the following from the diagram: а. i. A primary consumer ii. Microscopic autotrophs ii.
In a food chain, each organism occupies a different trophic level, defined by how many energy transfers separate it from the basic input of the chain. Food webs consist of many interconnected food chains and are more realistic representation of consumption relationships in ecosystems. Energy transfer between trophic levels is inefficient—with ...
Aquatic food web diagram.
A food web is a diagram of the links among species in an ecosystem - essentially who eats what. A food chain shows only the organisms that contribute to the diet of the top consumer. Figures 1 and 2 show examples of typical terrestrial and aquatic food webs, respectively. The triangular diagram in Figure 1 is an example of the main components ...
In the Aquatic Food-Web domain, animals, namely, fish, are a consistent focus, and there is more emphasis on terms related to species interactions (i.e. 'predator', 'food web', 'trophic'; Fig. 3). The central location of these two research domains reflects common word use and interests of many scientists.
Patterns of energy flow through different ecosystems may differ markedly in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems (Shurin et al. 2006). Food webs (i.e., energy flow webs) can be used to reveal these ...
Students complete a lake food web challenge, learn how all organisms in the lake ecosystem are interconnected, and explain how aquatic invasive species can impact the food web. Objectives Students will be able to: build a lake food web. explain how aquatic invasive species impact the lake food web.
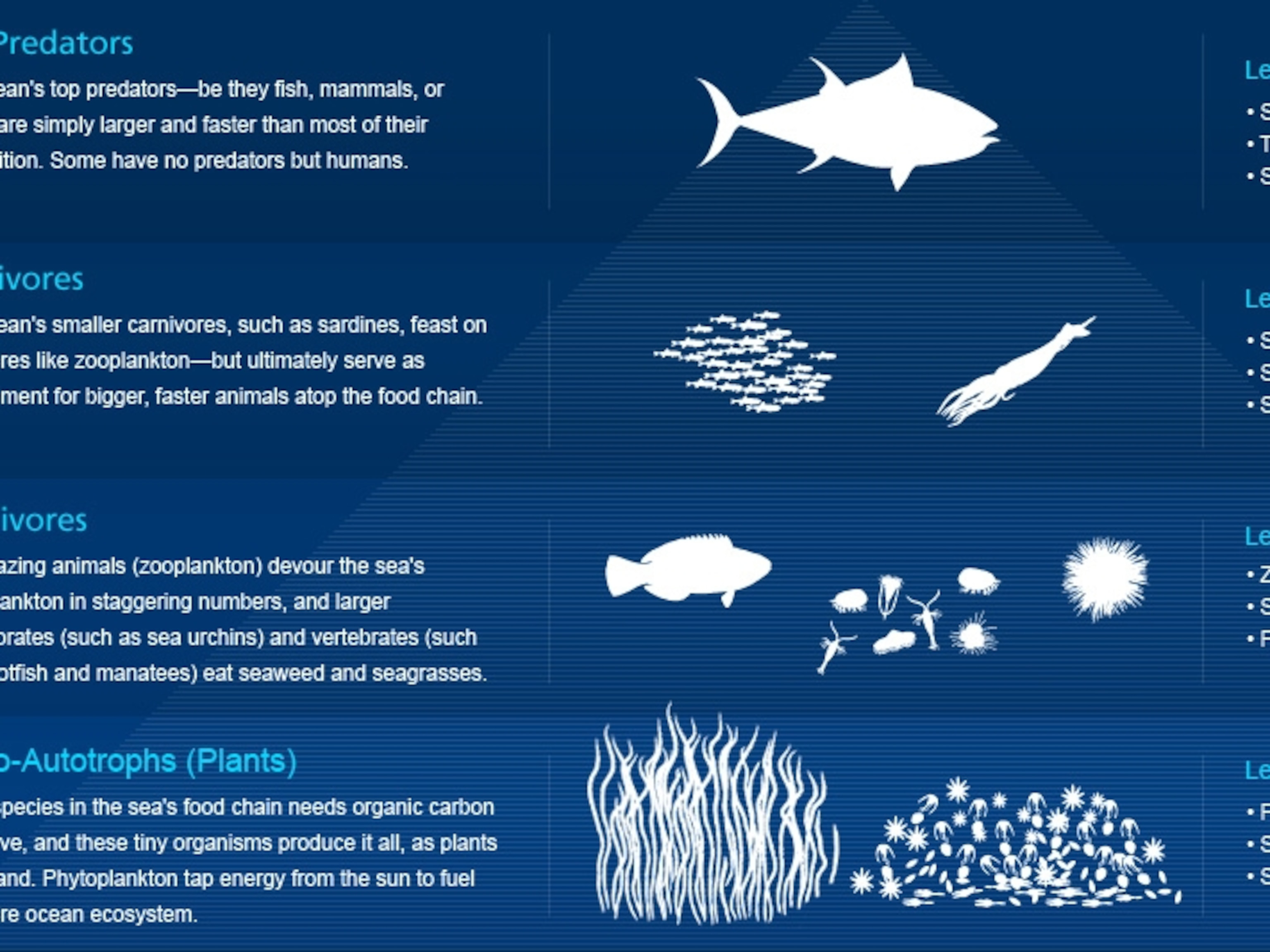
At the base of the ocean food web are single-celled algae and other plant-like organisms known as phytoplankton.Phytoplankton are a group of microscopic autotrophs divided into a diverse assemblage of taxonomic groups based on morphology, size, and pigment type.Marine phytoplankton mostly inhabit sunlit surface waters as photoautotrophs, and require nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus ...
Great Lakes Food Web Diagrams. GLERL has developed food web diagrams for all of the Great Lakes and Lake St. Clair. The major species in each lake are briefly described, along with a diagram summarizing the ecosystem energy flow (who eats or is eaten by whom!). These diagrams are based on a model from a paper published in 2003 supported by both ...
The Food Web Aquatic Ecology. Aquatic Ecology Page 2. Aquatic Ecology Page 3 aquatic vegetation covers the waters surface. The pond has reached the age of senescence. Willows, cypress, cattail and other shoreline plants advance toward the ponds center. Eventually rooted plants cover the pond bottom
Ecosystem (With Diagram) Article Shared by. ... Food Web-Interlocking Pattern of Organisms: ... The animals include snow petrel and penguins which depend on the aquatic food chain. In a tropical region, on the other hand, the ecosystems have a rich species diversity and therefore, the food webs are much more complex. ...
A food web is a diagram of the links among species in an ecosystem - essentially who eats what. A food chain shows only the organisms that contribute to the diet of the top consumer. Figures 1 and 2 show examples of typical terrestrial and aquatic food webs, respectively.
A food web is a "who eats whom" diagram that shows the complex feeding relationships for a particular ecosystem. Learn about the different types of food webs, examples, and how it differs from a ...
A food chain is a network of links in a food web. Here, the producers are consumed by the predators-primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. When many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as Food Web. A food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms.
Marine food webs. Feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains - in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term 'food web' more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers. A food web diagram illustrates 'what eats what' in a particular habitat.
Creating a food web is a really great way to learn more about how organisms and animals live in their natural habitats. While a food chain shows how ecosystems function in a linear way, a food web is a more visual approach with multiple animals connected to one another. To create a food web, write ...
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community.Another name for food web is consumer-resource system.Ecologists can broadly lump all life forms into one of two categories called trophic levels: 1) the autotrophs, and 2) the heterotrophs.To maintain their bodies, grow, develop, and to reproduce, autotrophs ...
Food webs describe who eats whom in an ecological community. Made of interconnected food chains, food webs help us understand how changes to ecosystems — say, removing a top predator or adding nutrients — affect many different species, both directly and indirectly. Phytoplankton and algae form the bases of aquatic food webs.
& provide food for a wide range of organisms including whales, shrimp, snails, zooplankton & jellyfish. Insects are invertebrates. They are part of the base of the food web. They feed on plants & bacteria & are eaten by many species of fishes & birds in rivers & estuarine environments. Aquatic or terrestrial insects that are transported into Puget
Food chain and Food Web ,definition, diagram and examples and Food Chain and Food Web, Food Chain and Food Web- food chain is a series of interlinked organism for food taking from one another and Food Web is interconnected food chain that make web like structure. Food chain is necessary for ecological balance in nature in which no one species can found in nature but all the species are found ...
aquatic habitat. Evaluating the food webs will determine if the students were able to organize the plants and animals to create an accurate food web. Evaluating student responses during follow-up discussions will identify misconceptions. Additional activities to address misconceptions should be provided. ... See food web diagram for answers 3 ...
The diagram below is an example of a food web. To explore food webs in more detail, try the Interactive Food Web component (located on the right-hand side of this page). Next: Aquatic Ecosystems: Biomass and Production
Marine Food Webs. 1. Build background about marine trophic pyramids and food webs. Review with students that food chains show only one path of food and energy through an ecosystem. In most ecosystems, organisms can get food and energy from more than one source, and may have more than one predator. Healthy, well-balanced ecosystems are made up ...
Food Webs The concept of a food chain is an abstraction or generalization. Ecosystems are more complicated than a single food chain would indicate. Most aquatic ecosystems contain many more species than those in a single food chain, and all of these species interact and are interdependent.
The diagram shows part of an aquatic food web for a stable lake ecosystem in Connecticut. What is the source of energy for the algae? A. waves B. sunlight C. bacteria D. rotifers, water eas and tadpoles 23. Ecosystems are composed of all living and nonliving components in an area. Food webs
Freshwater food web. This food web shows the role played by invertebrates (animals without backbones), such as mayflies and stoneflies, in freshwater ecosystems. The arrows indicate what eats what. Invertebrates feed on living and dead plant matter, and on each other. Invertebrates are an important link in the food web as they convert the ...


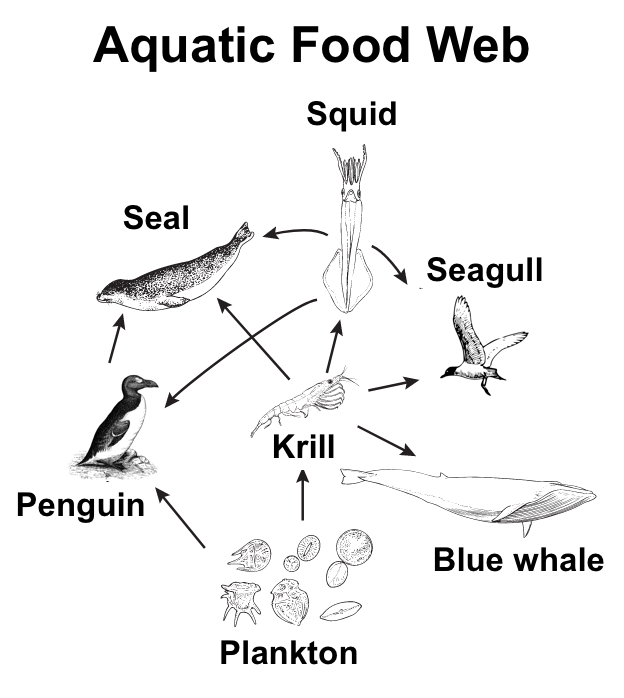





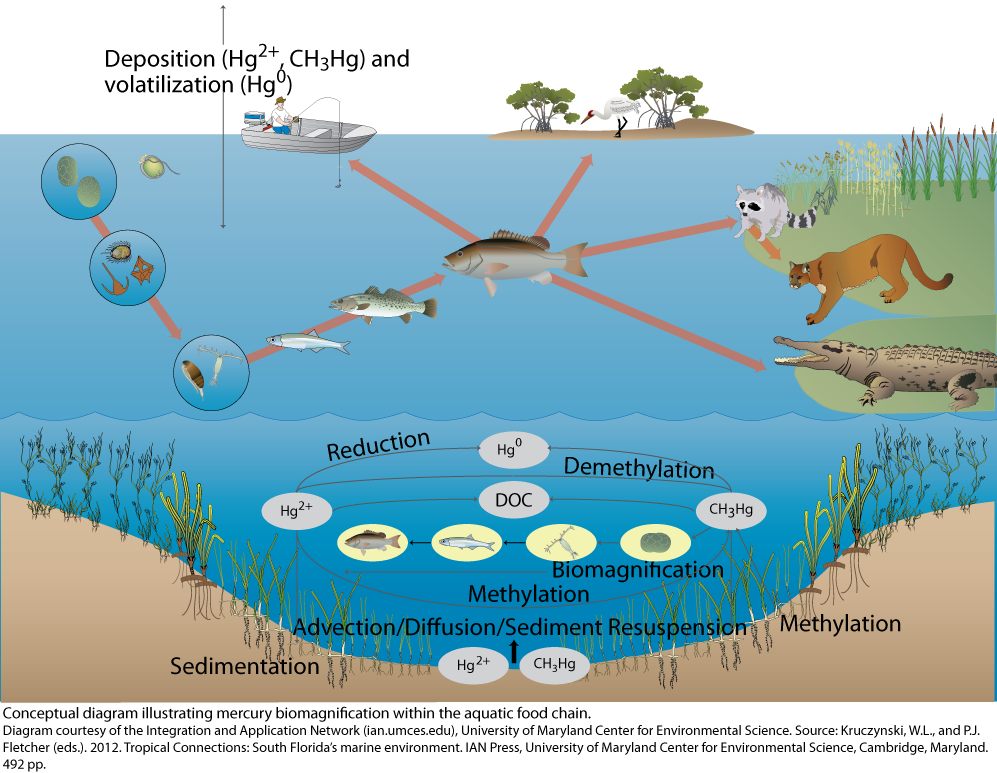



![PDF] Distribution of phthalate esters in a marine aquatic food web ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/f1701eecab6b99bbcde5a6839806bce3b9366a75/5-Figure2-1.png)











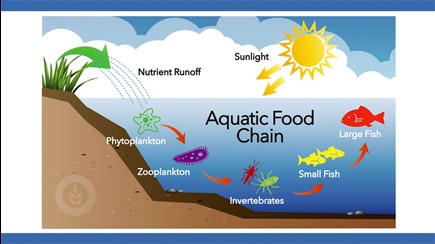




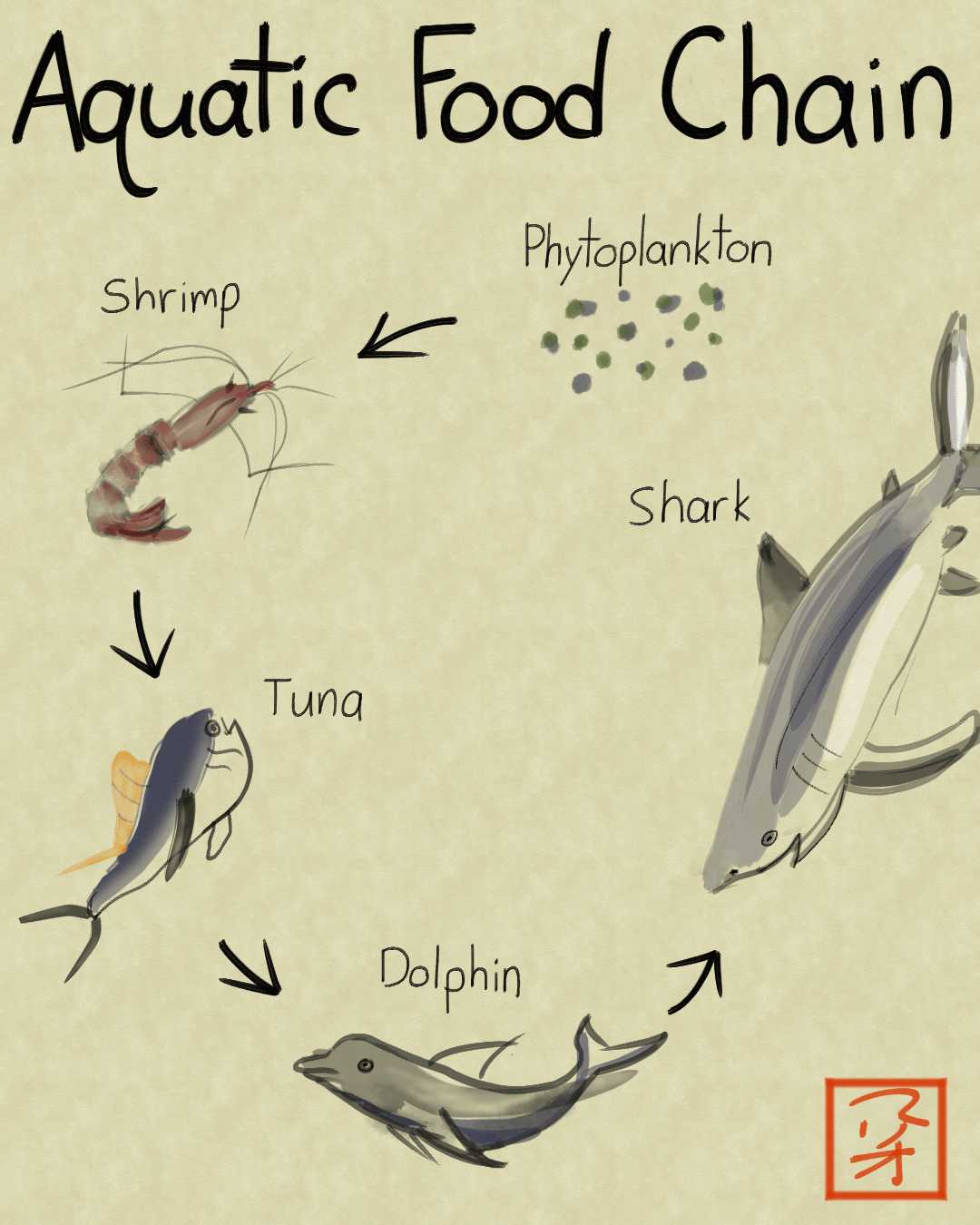
0 Response to "39 aquatic food web diagram"
Post a Comment