38 cellular respiration detailed diagram
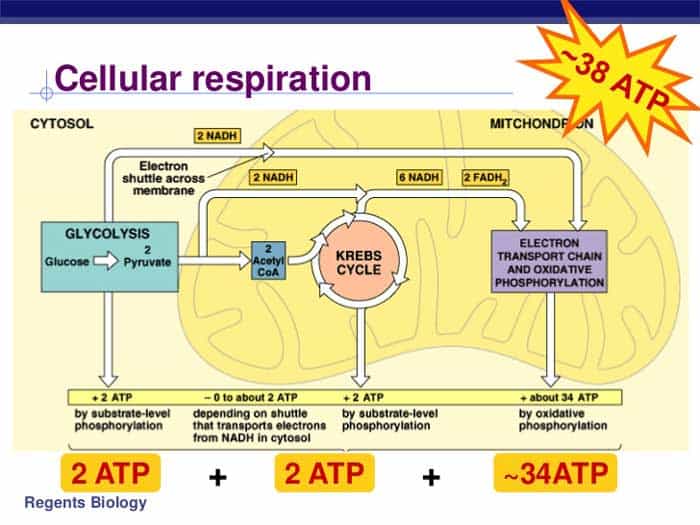
Thus, the total ATP yield in the cellular respiration process is 36 or 38 ATP molecules. Hope this article on simple cellular respiration diagram has helped you understand the process well. The process of cellular respiration is a very complex reaction that involves many enzymes, coenzyme, and molecules. 10.9.2015 · Mitochondrial respiration involves the carbon balance in the whole plant, with 20–80% of the carbon fixed in photosynthesis being released again through the respiration process. The respiration of the leaves in both the light and dark can account for ∼50% of the whole-plant respiratory CO 2 (Ayub et al., 2014).
Cellular Respiration ( Flowchart) Use Creately's easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. We were unable to load the diagram. You can edit this template on Creately's Visual Workspace to get started quickly. Adapt it to suit your needs by changing text and adding ...

Cellular respiration detailed diagram
Undergraduate Programs Without a doubt, the Biology degree is the most versatile of the many degrees in the life sciences. Over half of our majors (in all of our degrees) go on for an advanced degree such as the Master of Science or the Doctor of Philosophy Understanding Cellular Respiration Here are three visual depictions of cellular respiration - an equation, an output description and an illustration. 1) Equation: C 6 H 12 O 6 (1 glucose molecule) + 6 O 2 = 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + 36 ATP (ENERGY) carbohydrate + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + ATP energy 2) Description of the molecules created in all three stages of cellular respiration: Brachiopods (/ ˈ b r æ k i oʊ ˌ p ɒ d /), phylum Brachiopoda, are a group of lophotrochozoan animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs.Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, while the front can be opened for feeding or closed for protection. Two major groups are recognized, …
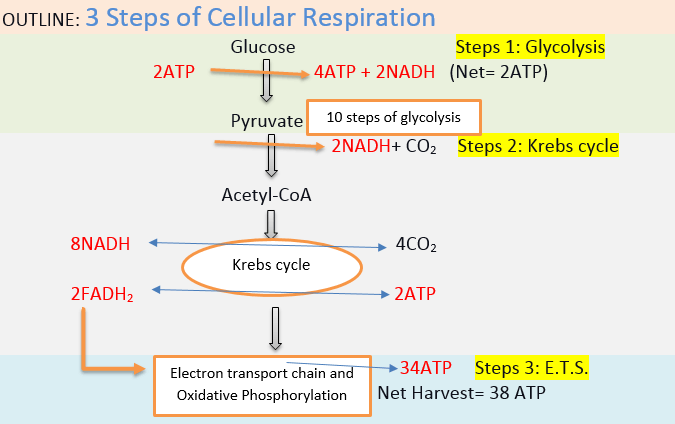
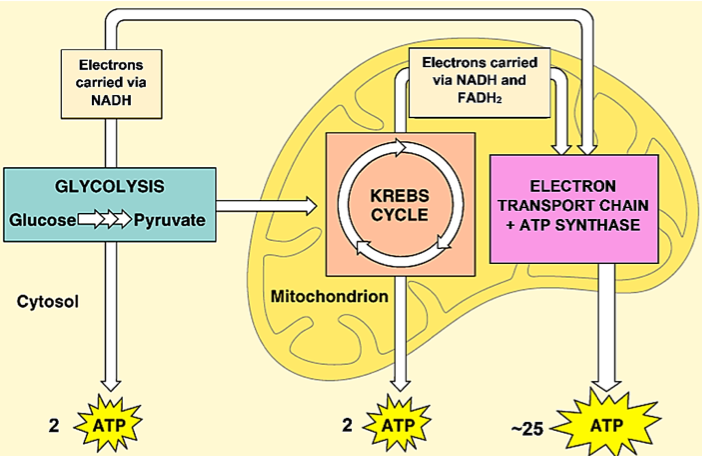
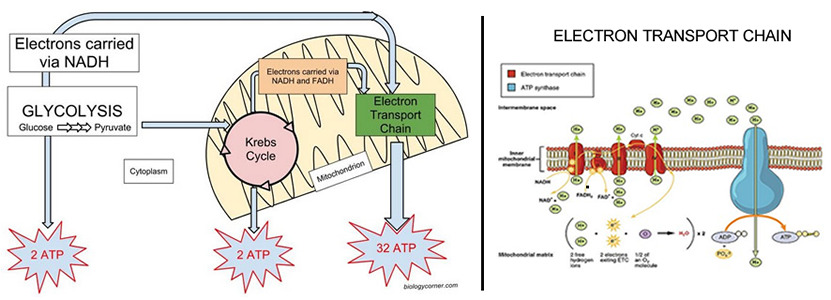
Cellular respiration detailed diagram. May 7, 2020 - Biology: Flow Chart for Cellular Respiration Complete respiration flow-chart Cellular respiration from glycolysis to the Krebs cycle, including co-enzymes and ATP production. Steps of cellular respiration Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The stages of cellular respi… Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, "biological machines" also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as ATP).Basically, ATP serves as the main energy currency of the cell. Metabolic pathways that contribute to the production of ATP molecules in cells are collectively referred to as cellular respiration. When a molecule of glucose undergoes aerobic cellular respiration, 36 molecules of ATP are produced. Glucose is an energy-rich molecule. The breakdown of glucose results in the formation of low-energy molecules and energy. And for this reason, actually, and I'll get back to kind of why we're unable to, you know, kind of nail down a number here but for this reason, you might often see quite a range of predictions for how much ATP's actually produced in one cycle of cellular respiration, just to give you an idea of that, you know, when I look at some textbooks, you can see a range of anywhere from 30 to 38 ...
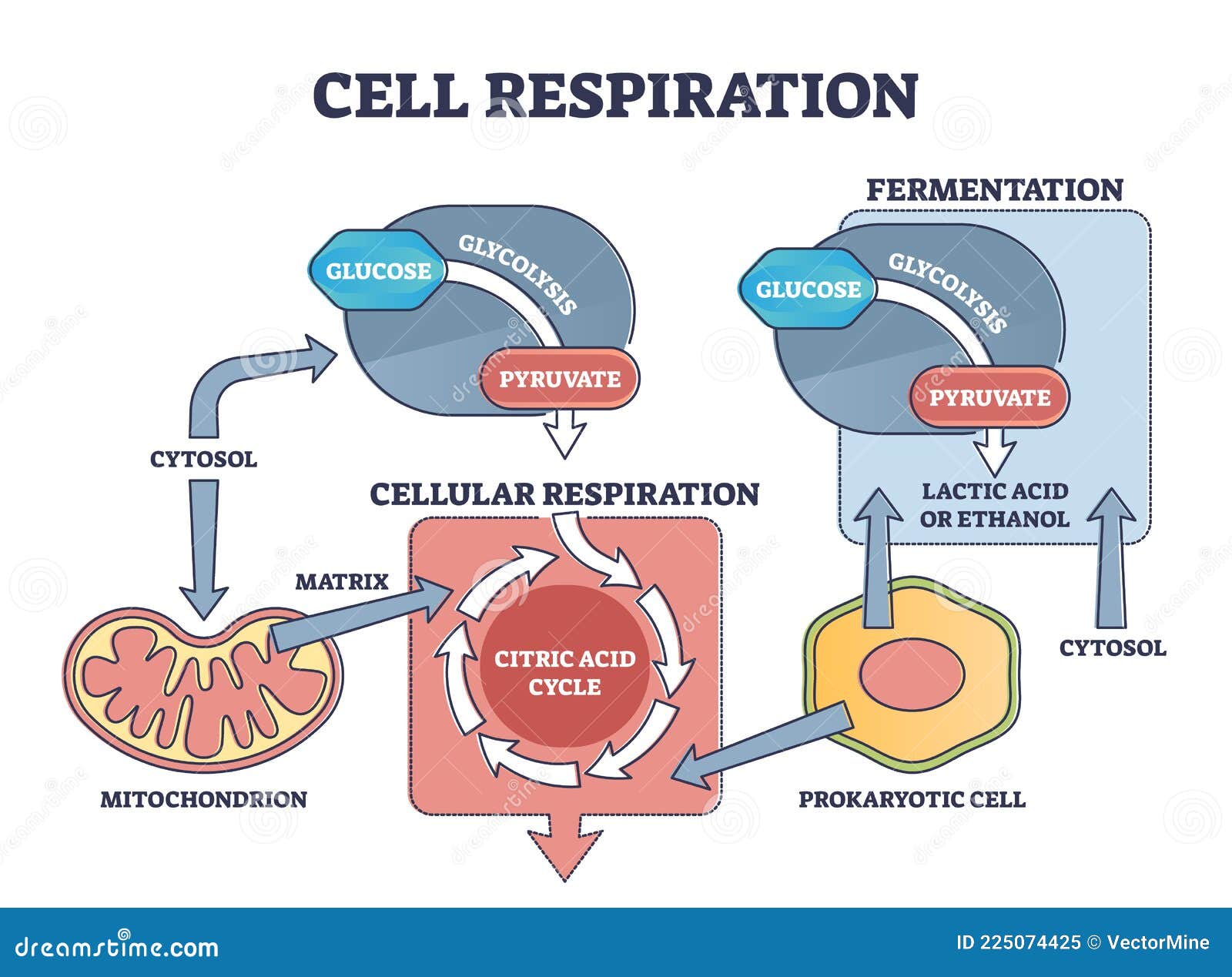
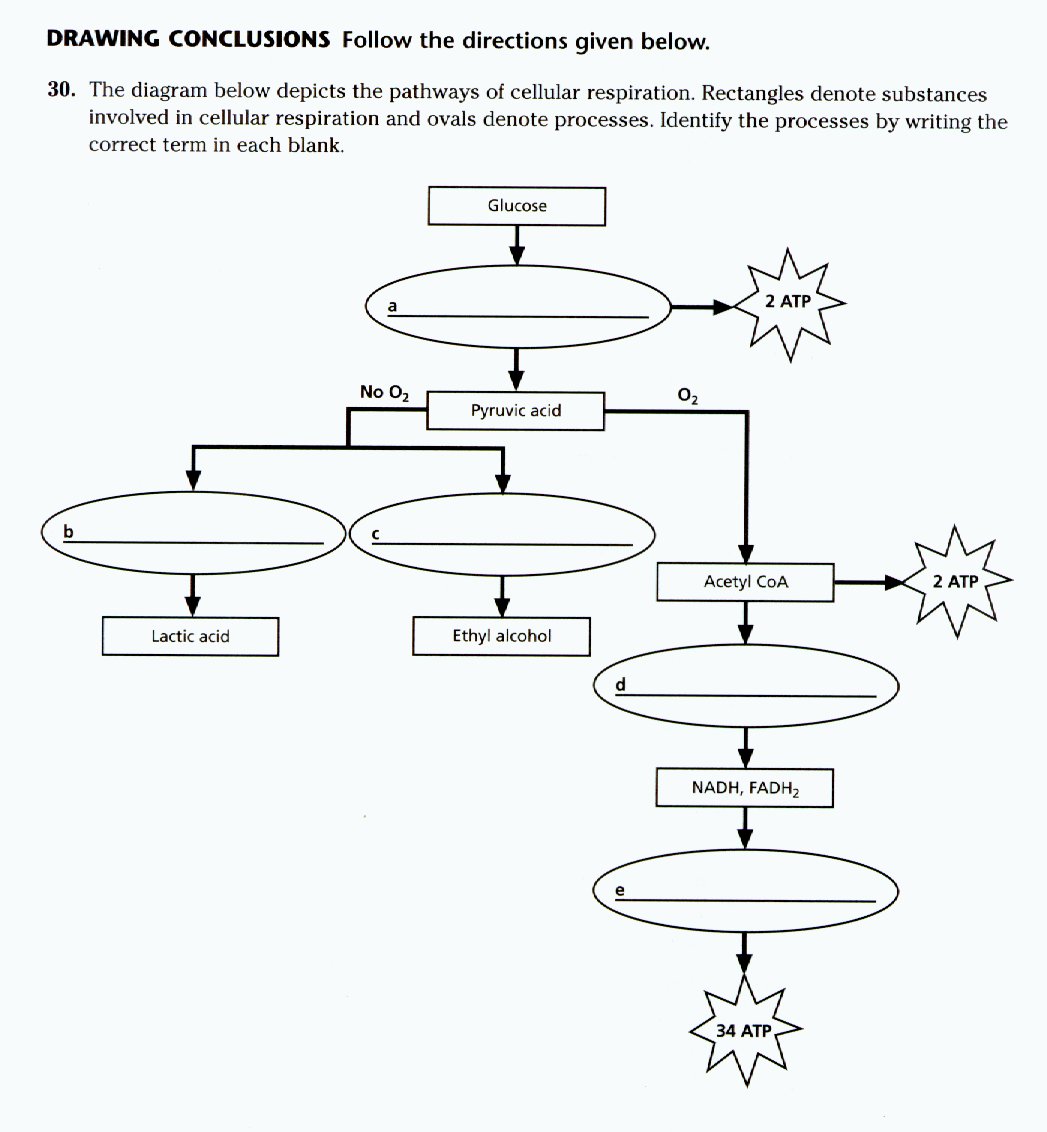
Start studying Respiration Diagram, Cellular Respiration.Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Detailed Diagram of Cellular Respiration Poster. A diagram of cellular respiration including glycolysis, Krebs cycle, citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain Cellular respiration is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place ... A mitochondrion (/ ˌ m aɪ t ə ˈ k ɒ n d r i ə n /; pl. mitochondria) is a double-membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic organisms. Mitochondria generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy. They were first discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1880 in the voluntary muscles of insects. 3 ) Construct an explanation of the function (e.g., mitochondria releasing energy during cellular respiration) of specific cell structures (i.e., nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and vacuoles) for maintaining a stable environment. Respiration. What is the overall purpose of cellular respiration? Write the equation for cellular respiration below. Label the reactants and the products. What are the 3 phases of the cellular respiration process? Where in the cell does glycolysis occur? Label the location on the cell diagram (Where in the cell does the Krebs (Citric Acid ...
Detailed Diagram of Cellular Respiration Poster. A diagram of cellular respiration including glycolysis, Krebs cycle, citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain Cellular respiration is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine ... Mitochondria are a double-membrane-bound cell organelle found in most eukaryotic organisms. In all living cells, these cell organelles are found freely floating within the cytoplasm of the cell. The diagram of Mitochondria is useful for both Class 10 and 12. It is one among the few topics having the highest weightage of marks and is majorly ... Diagram; Steps; Key Points; Respiration is of two types, aerobic respiration, and anaerobic respiration. Aerobic Respiration: It is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food. This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals, birds, humans, and other mammals. Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Diagram Project. Students must create a model/diagram of photosynthesis and cellular respiration to represent the processes. All steps should be labeled correctly, and a well written detailed summary should be included. Rubric Code: VX7694B.
Adjective. living, active, or occurring in the absence of free oxygen. ATP. Noun. (adenosine triphosphate) chemical found in most living cells and used for energy. cellular respiration. Noun. process by which cells turn nutrients into useful energy. coenzyme.
This video discusses Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain.Teachers: You can purchase this PowerPoint from my online store. Follow the li...
What is Cellular Respiration? It is the process by which organisms use energy from "food" (e.g., glucose, fatty acids) to fuel the endergonic synthesis of ATP. • requires (O 2), occurs in most organisms (plants, too!) • provides a supply of usable energy for cells (ATP) C 6 H 12 O 6 6HCO 2 2 OATPs Glucose Oxygen gas Carbon dioxide 6 ...
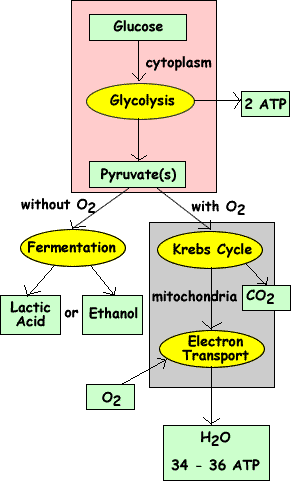
Cellular Respiration needs Oxygen to occur. Cellular Respiration takes place in the mitochondria; the powerhouse of the cell. Glycolysis. Glycolysis is the first step of cellular respiration and commonly begins with the simple sugar glucose. Through a series of steps a single molecule of glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of Pyruvic Acid ...
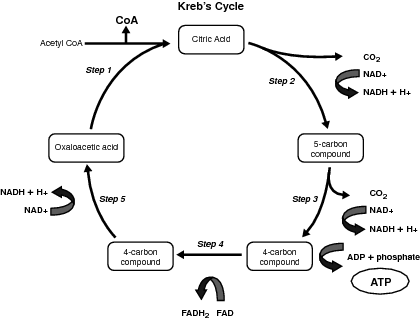
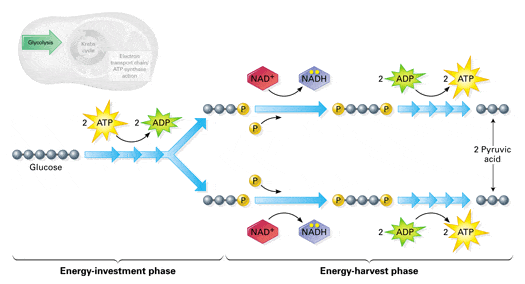
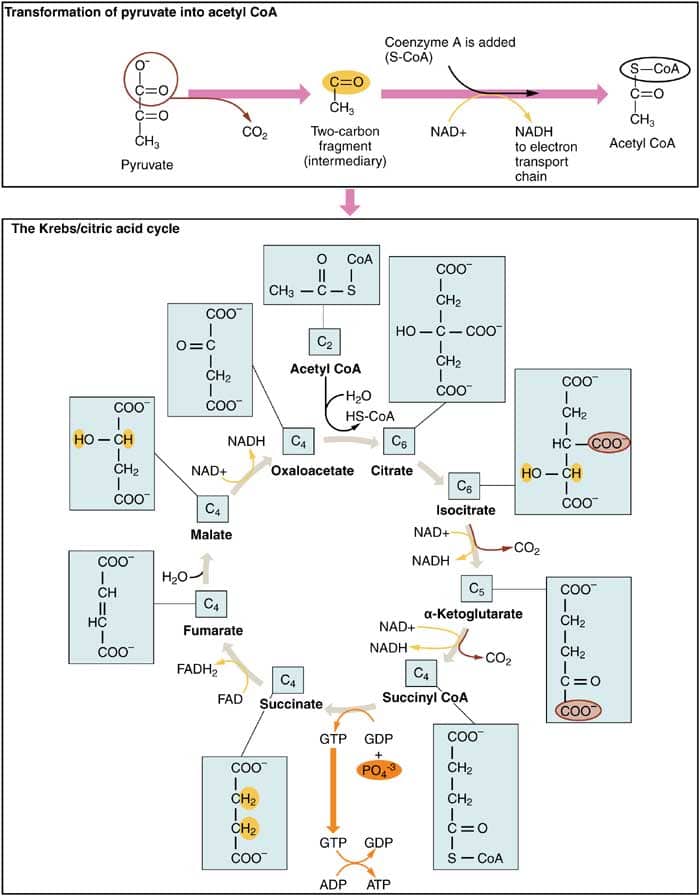
Steps of cellular respiration. Overview of the steps of cellular respiration. Glycolysis. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). ATP and NADH are made. These reactions take place in the cytosol. Pyruvate oxidation. Pyruvate travels into the mitochondrial matrix and is converted to a two-carbon molecule bound to ...
Glycolysis. The name glycolysis means "sugar-splitting," and sure enough, this metabolic pathway splits glucose into two three-carbon molecules. Learn more about the steps of glycolysis and how it is used in both cellular respiration and fermentation.
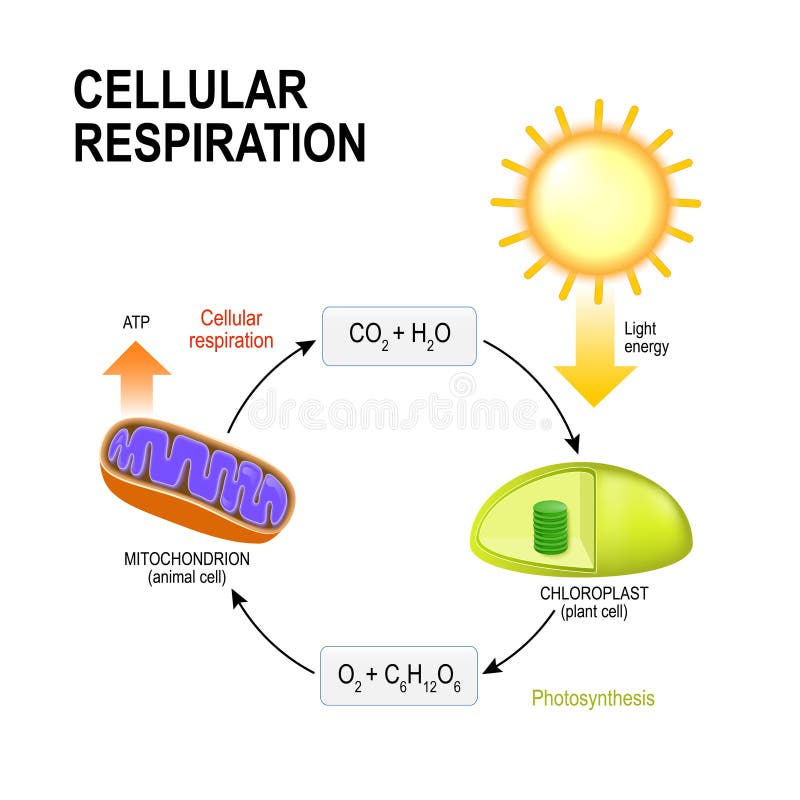
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, some bacteria, and some protistans use the energy from sunlight to produce sugar, which cellular respiration converts into ATP, the "fuel" used by all living things.
cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules, diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding, as waste products, carbon dioxide and water. Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation. (For longer treatments of various aspects of cellular respiration ...
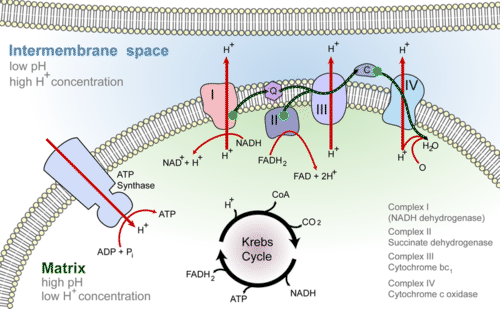
Detailed discussion on the steps of cellular respiration The reactants of the Electron Transport chain hold 10 NADH electron carrier molecules, 2FADH2, six oxygen atoms from the initial glucose molecule, and especially, 34 ADP and P to bond with ATP Synthase.
It occurs in the presence or absence of oxygen. Any type of cellular respiration begins with glycolysis where a 3-C molecule, pyruvic acid is formed as the end product. Different cells handle this pyruvate in two major ways, fermentation is one of them. Let us have a detailed look at the fermentation, its types and anaerobic respiration.
Cellular Respiration Questions and Answers. Get help with your Cellular respiration homework. Access the answers to hundreds of Cellular respiration questions that are explained in a way that's ...
Krebs Cycle and Link Reaction: Interactive Tutorial. 1. Introduction. If oxygen is present in a cell where respiration is occurring, then glycolysis is followed by a series of reactions that completely oxidize pyruvate (pyruvic acid) and the molecules it gets broken down into. You can see this in steps "2" and "3" in the diagram below.
The detailed glycolysis diagrams are illustrated in clear pictures. ... Glycolysis is the first of the main metabolic pathways of cellular respiration to produce energy in the form of ATP. Through two distinct phases, the six-carbon ring of glucose is cleaved into two three-carbon sugars of pyruvate through a series of enzymatic reactions ...
Tree respiration is similar to respiration in animals. In animals, glucose (6C sugar) is the primary respiration substance. In trees, sucrose (12C double sugar) is the primary transport and initial respiration substance. Sucrose is broken into 6C* units once in a cell. Complete respiration of one sucrose mol-
in a separate box or draw a cell and mitochondria and add all steps to the diagram in the appropriate location(s). No matter which option you choose, number the boxed sections or the steps. Your numbered diagram or drawing of the steps much include the following: 2. glycolysis, kreb cycle and electron transport chain 3. the movement of electrons 4.
Start studying Respiration Diagram, Cellular Respiration. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Oct 19, 2018 - Cellular respiration is essential for sustaining life at a cellular level. This BiologyWise article provides you with its diagram and some brief information. Have a look!
Cellular respiration involves four main steps in converting glucose molecules to harvest energy in one's body cells. These are: 1. Glycolysis - The glucose undergoes chemical processes where it gets converted into pyruvate. The energy released in these reactions is ATP.
Cellular respiration 2 Aerobic respiration Aerobic respiration (red arrows) is the main means by which both plants and animals utilize energy in the form of organic compounds that was previously created through photosynthesis (green arrow). Aerobic respiration requires oxygen in order to generate energy (ATP). Although carbohydrates, fats, and ...
Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert fuel into energy and nutrients. To create ATP and other forms of energy that they can use to power their life functions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy from that fuel into a useable form.
Brachiopods (/ ˈ b r æ k i oʊ ˌ p ɒ d /), phylum Brachiopoda, are a group of lophotrochozoan animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs.Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, while the front can be opened for feeding or closed for protection. Two major groups are recognized, …
Understanding Cellular Respiration Here are three visual depictions of cellular respiration - an equation, an output description and an illustration. 1) Equation: C 6 H 12 O 6 (1 glucose molecule) + 6 O 2 = 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + 36 ATP (ENERGY) carbohydrate + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + ATP energy 2) Description of the molecules created in all three stages of cellular respiration:
Undergraduate Programs Without a doubt, the Biology degree is the most versatile of the many degrees in the life sciences. Over half of our majors (in all of our degrees) go on for an advanced degree such as the Master of Science or the Doctor of Philosophy

















0 Response to "38 cellular respiration detailed diagram"
Post a Comment