38 bayes theorem tree diagram
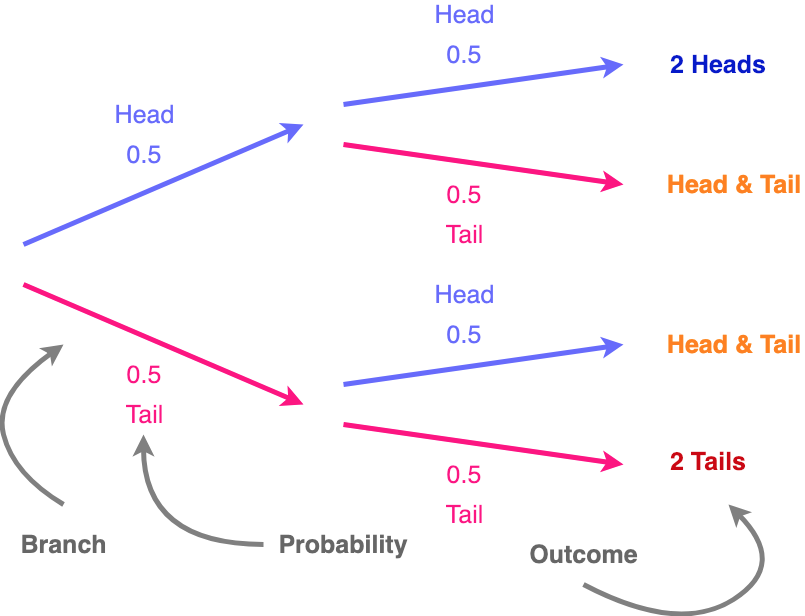
Conditional probability with Bayes' Theorem. Conditional probability using two-way tables. ... Conditional probability tree diagram example. Tree diagrams and conditional probability. This is the currently selected item. Next lesson. Independent versus dependent events and the multiplication rule. Sort by: Top Voted. In probability theory and statistics, Bayes' theorem (alternatively Bayes' law or Bayes' rule; ... The role of Bayes' theorem is best visualized with tree diagrams such as Figure 3. The two diagrams partition the same outcomes by A and B in opposite orders, to obtain the inverse probabilities. Bayes' theorem links the different partitionings.
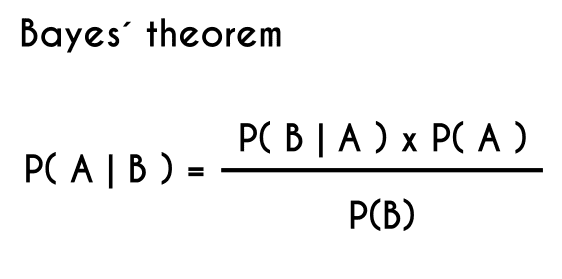
Bayes Theorem. Conditional probabilities provide a way to measure uncertainty when partial knowledge is assumed. Sometimes, we would like to reverse the roles of the partial knowledge and the unknown event. ... Therefore, we shall construct a tree diagram, with the lung cancer data in the first set of branches to take advantage of the given ...
Bayes theorem tree diagram
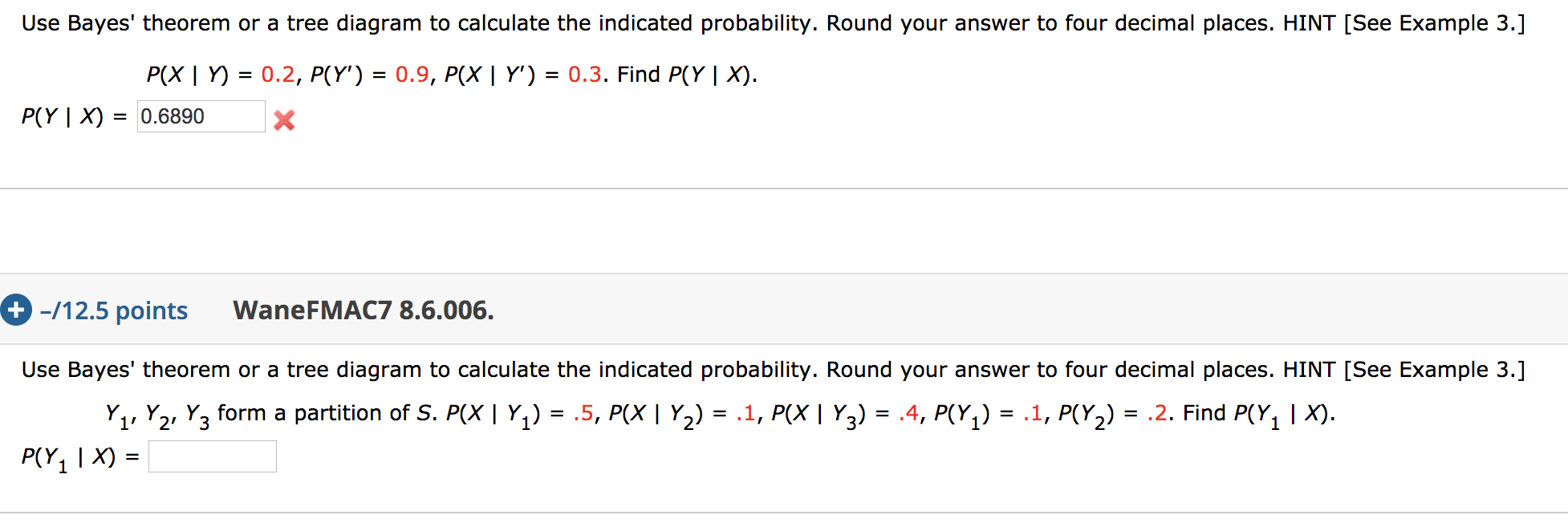
This lecture is part of an open online course on Managerial Statistics. See the course at http://openonlinecourses.com/ This course was organized by Alemi. Question: Use Bayes' theorem or a tree diagram to calculate the indicated probability. Round your answer to four decimal places. P (AB) = 0.7, P (B) = 0.8, P (AB) = 0.2. Find P ( BA). P ( BA) = :-/12.5 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES Use Bayes' theorem or a tree diagram to calculate the indicated probability. Round your answer to four decimal places. Solution using a tree diagram: As always, we will start by writing down all of the information. Definitions: 20 = choose the 20 sided die 5 = the value is a 5. Given: P(20) = ½, P(20C) = ½, P(5|20C) = 1 6, P(5|20) = 1 20 Want: P(20|5). Note that this is a Bayes' Theorem problem because the conditional probability is 'backwards' of what is given.
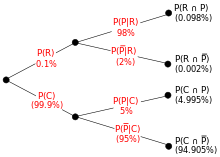
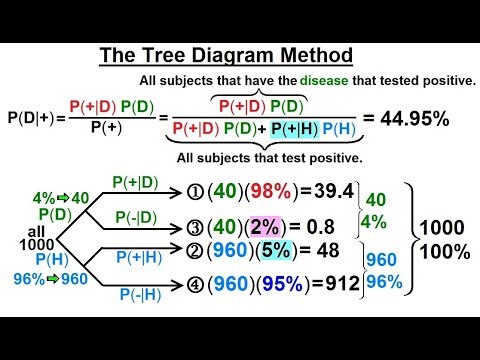
Bayes theorem tree diagram. The calculations are shown in the tree diagram. Notice that we have the probability of a positive test result given disease status, but we actually want to know the probability of having TB given a positive test result. ... Bayes' Theorem would give us the same answer as the probability tree flip.Feel free to use whichever method you find ... See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. 1. Use Bayes' theorem or a tree diagram to calculate the indicated probability. Round your answer to four decimal places. HINT [See Example 3.] 2. Use Bayes' theorem or a tree diagram to calculate the indicated probability. Bayes theorem tree diagram. Hot Network Questions If smooth tires provide the best grip, what exactly are mountain bike tires good for? Numerical integration in C++: Newton-Cotes formulas When and why did English stop pronouncing 'hour' with an [h] like its spelling still shows? The Problem of Evil/Suffering modified into Buddhism ... Bayes theorem tree diagram. Ask Question Asked 9 months ago. Active 3 months ago. Viewed 244 times 2 $\begingroup$ A bag I contain $4$ white and $6$ black balls while another Bag II contains $4$ white and $3$ black balls. One ball is drawn at random from one of the bags, and it is found to be black.
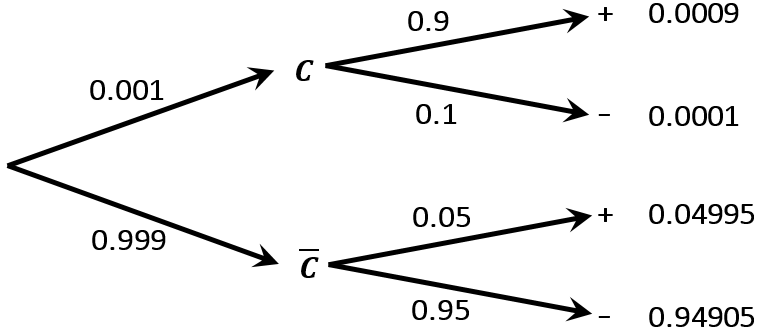
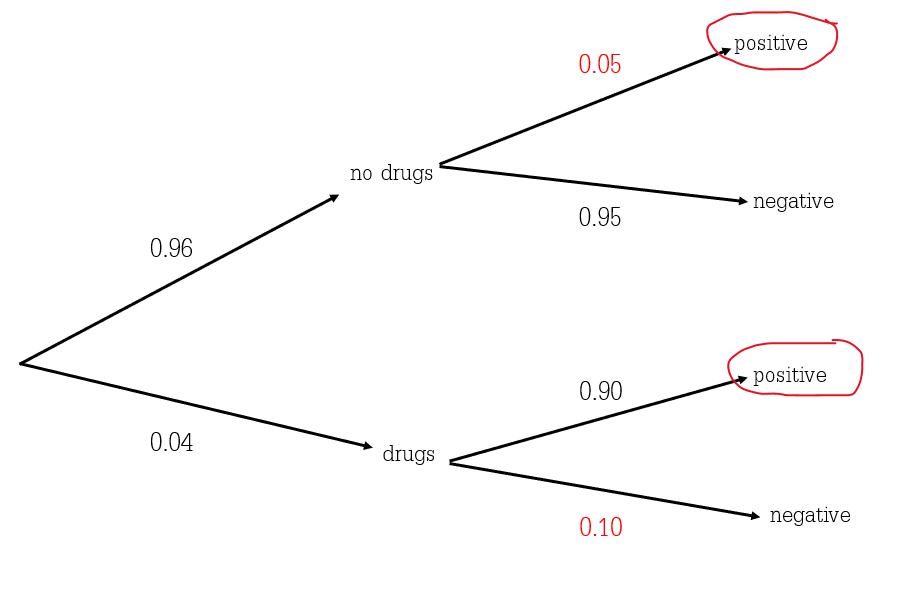
Bayes' Theorem Let's consider the events A and B. By the conditional probability formula we have P(A and B) = P(AjB)P(B) ... Buying a car: Bayes with Tree Diagram Suppose you need to buy a car. I Based on previous experience you know that 30% of the cars have FAULTY transmission. Bayes' Theorem and Probability Trees. ... The chance of any one overall outcome can found by multiplying the probabilities down one path in the tree diagram. Thus the chance of not being infected, and getting a negative test result is $0.98 \times 0.995 = 0.9751$. This can be done for all the paths. Read it Watch It Use Bayes' theorem or a tree diagram to calculate the indicated probability. Round your answer to four decimal places. HINT (See Example 3.] P(XIV) = This question hasn't been solved yet Ask an expert Ask an expert Ask an expert done loading. 1. Show transcribed image text Expert Answer. The definition of the Bayes theorem is: "Bayes theorem gives the probability of an event based on new information that is related to that event." In this topic, we will discuss the Bayes theorem from the following aspects: What is Bayes theorem? How to use the Bayes theorem? Tree diagrams. Bayes theorem formula. When to use Bayes theorem?
Bayes Theorem Tree Diagram Now, we are ready to answer the question, "supposing a defendant is convicted, find the probability the defendant is innocent." All this means is that we are being asked to find the probability of innocence, given conviction. We can formulate that as a rule for applying Bayes theorem on a probability tree, for P. . ( A ∣ B), naming A as 'cause' and B as 'data': Eliminate all the paths through the tree made impossible by the conditioning on data B. Denominator is sum of all path-probabilities consistent with B. Numerator is sum of all path-probabilities ... Visualizing Bayesian Theorem with Venn, Tree and Pie Diagrams. Get started. Open in app. ... Visualise Bayesian Theorem through Venn diagram and do not need to memorise it again. ... this method for the extraction of conditional probability from multiple features given a class label is called Naïve Bayes. Even without an exact Venn diagram, visualizing the diagram can help us apply Bayes' theorem: 1% of women in the group have breast cancer. \[P(A) = 0.01\] 80% of those women get a positive mammogram, and 9.6% of the women without breast cancer get a positive mammogram too.
Bayes theorem for beginners. Image by Author ... We can discuss expanding this to multi-class, multi-feature datasets and also about Naive Bayes in another article using a tree diagram for better ...
NOTE All the above calculations may be done with the help of a tree diagram shown below. Once the tree diagram have all the probabilities, it is easier to use these probabilities in Bayes' theorem in order to evaluate the final results. More References and links More on Probabilities.
Bayes' theorem and naive Bayes classifier. Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology: ABC of Bioinformatics; Elsevier Science Publisher: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp.403-412. Frosst, N. and Hinton, G., 2017. Distilling a neural network into a soft decision tree. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.09784.
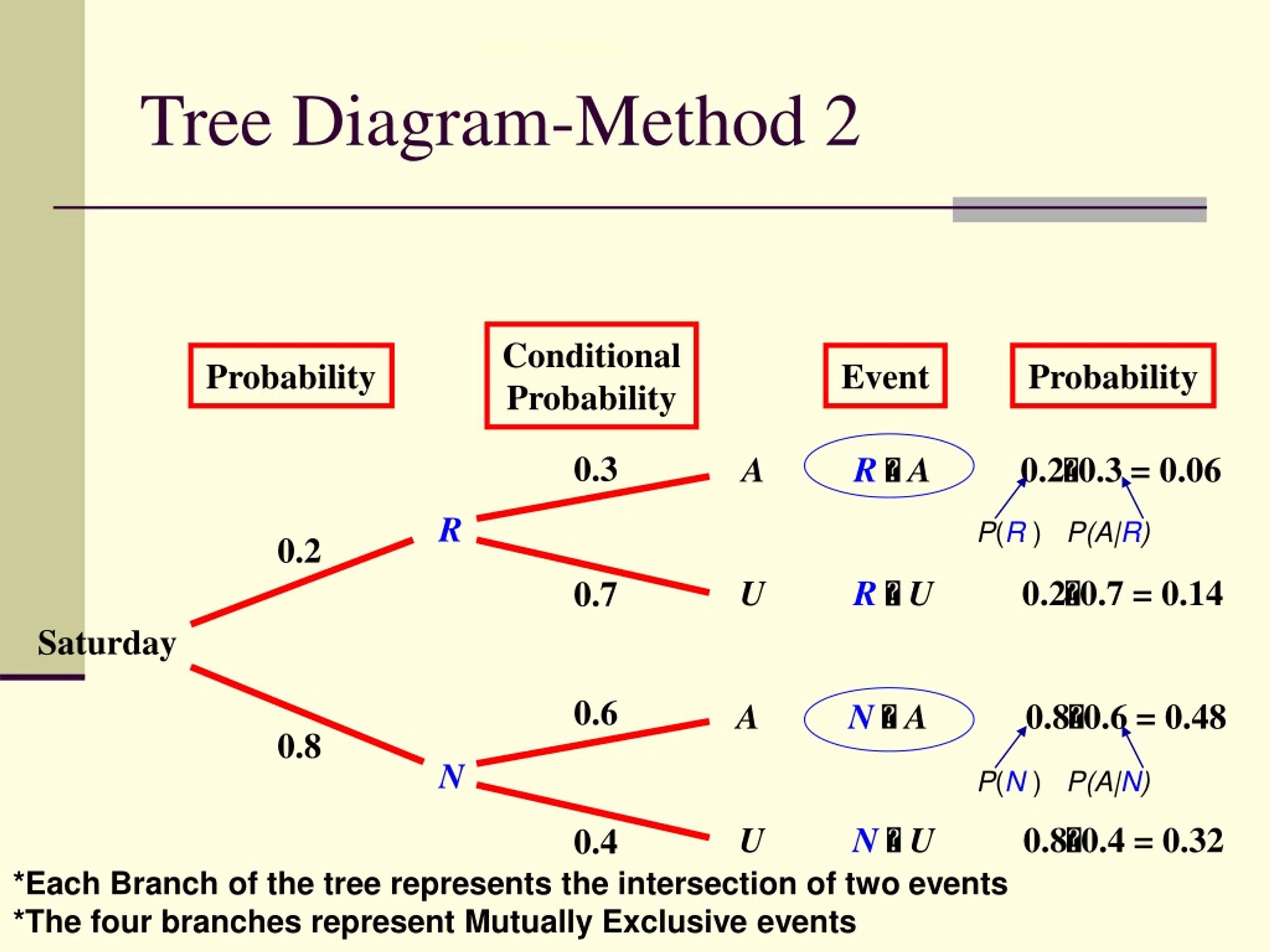
Here, we examine the above tree diagram. For section D, 75% of the class will pass, so the probability of passing given that a student is in section D is 0.75. ... pass), which CANNOT be read off the tree. Here, we need Bayes' theorem: find the probability of the intersection and divide by the probability of what we are given. In other words, ...
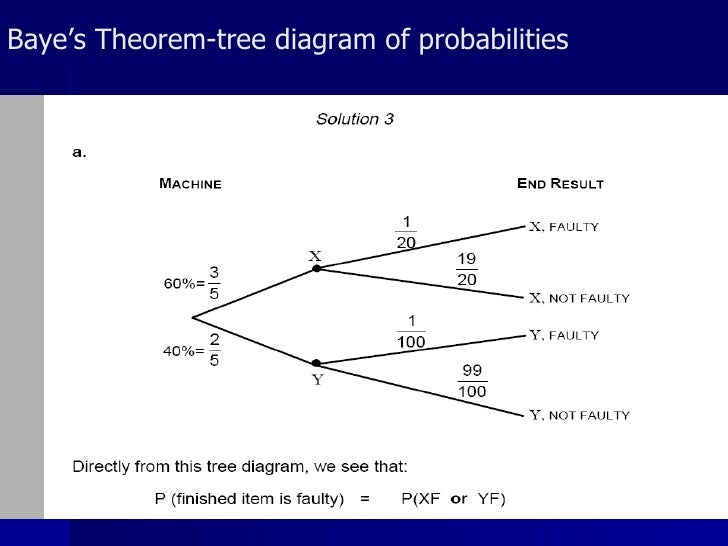
Bayes' Theorem We can draw a tree diagram representing the information we are given. If we choose a touch screen at random from those produced in the factory, we let MA be the event that it came from Machine A and let MB be the event that it came from Machine B. We let D denote the event that the
This video tutorial provides an intro into Bayes' Theorem of probability. It explains how to use the formula in solving example problems in addition to usin...
Bayes' theorem, also known as Bayes' law or Bayes' rule, tells us the probability of an event, given prior knowledge of related events that occurred earlier. ... If you're ever having trouble figuring out a conditional probability problem, a tree diagram is a great tool to fall back on, because it shows all of the sample space of the ...
the tree diagram. Please do so when you try to do them, or when you read the solutions {draw the diagram to try to follow what's happening. 2. solutions Exercise 1. A doctor is called to see a sick child. The doctor has prior information that 90% of sick children in that neighborhood have the u, while the other 10% are sick with 1
File:Bayes theorem tree diagrams.svg. Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 363 × 599 pixels. Other resolutions: 145 × 240 pixels | 291 × 480 pixels | 363 × 600 pixels | 465 × 768 pixels | 620 × 1,024 pixels | 1,240 × 2,048 pixels | 470 × 776 pixels. .
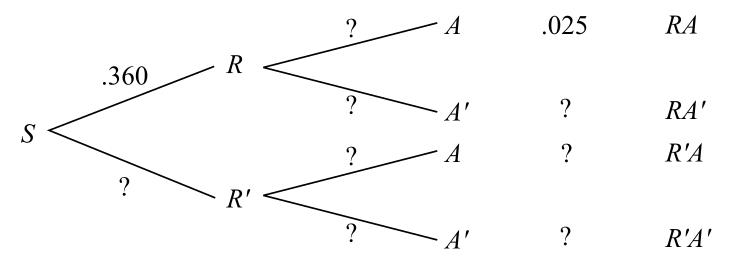
Bayes' Theorem Bayes' Theorem, named after the English mathematician Thomas Bayes (1702-1761), is an important formula that provides an alternative way of computing conditional probabilities. Before the formula is given, take another look at a simple tree diagram involving two events and as shown in Figure C.14. FIGURE C.14
Solution using a tree diagram: As always, we will start by writing down all of the information. Definitions: 20 = choose the 20 sided die 5 = the value is a 5. Given: P(20) = ½, P(20C) = ½, P(5|20C) = 1 6, P(5|20) = 1 20 Want: P(20|5). Note that this is a Bayes' Theorem problem because the conditional probability is 'backwards' of what is given.
Question: Use Bayes' theorem or a tree diagram to calculate the indicated probability. Round your answer to four decimal places. P (AB) = 0.7, P (B) = 0.8, P (AB) = 0.2. Find P ( BA). P ( BA) = :-/12.5 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES Use Bayes' theorem or a tree diagram to calculate the indicated probability. Round your answer to four decimal places.
This lecture is part of an open online course on Managerial Statistics. See the course at http://openonlinecourses.com/ This course was organized by Alemi.



















0 Response to "38 bayes theorem tree diagram"
Post a Comment