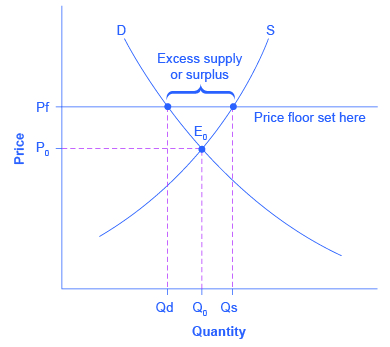
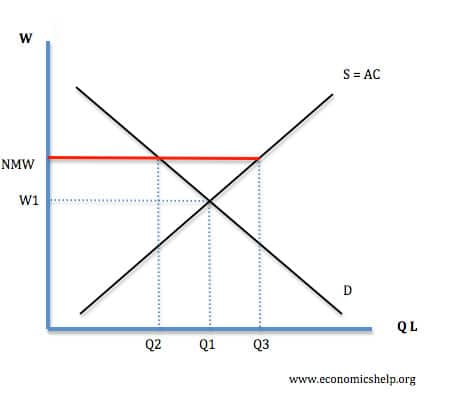
37 in the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the minimum wage at point a?
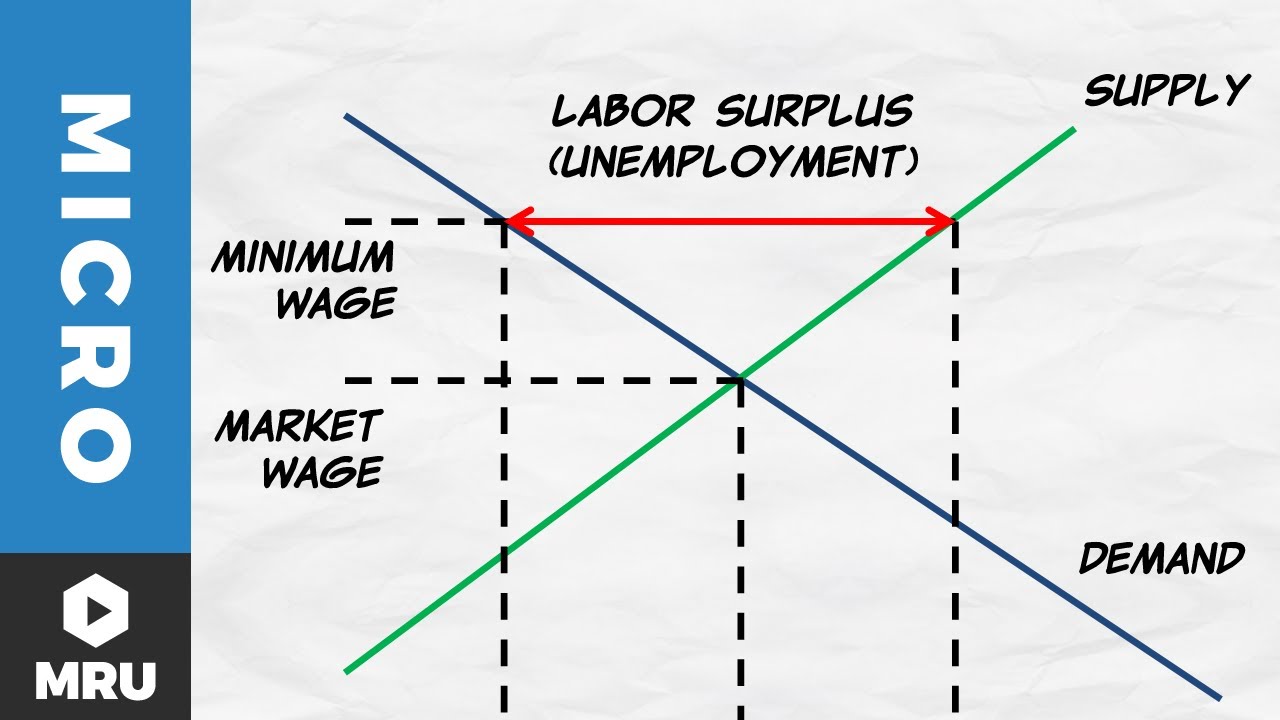
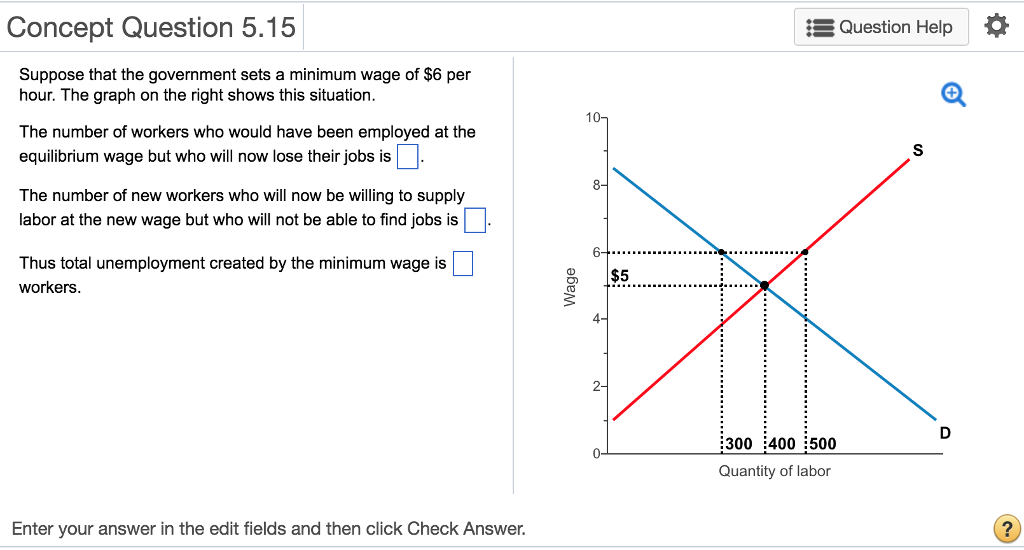
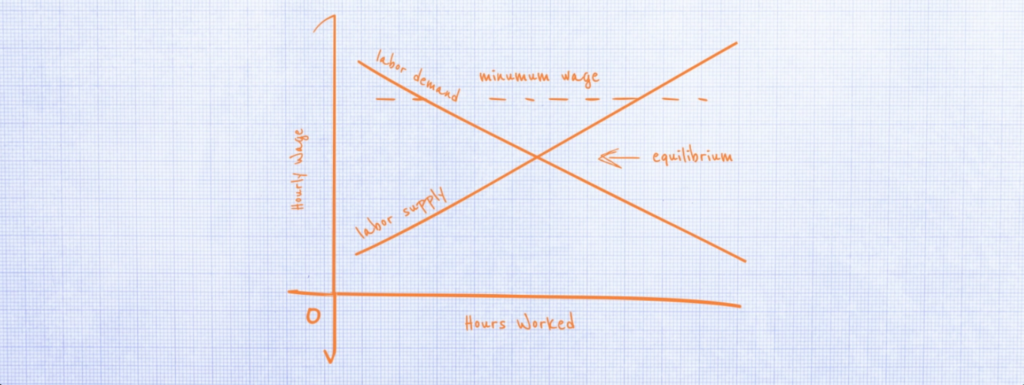
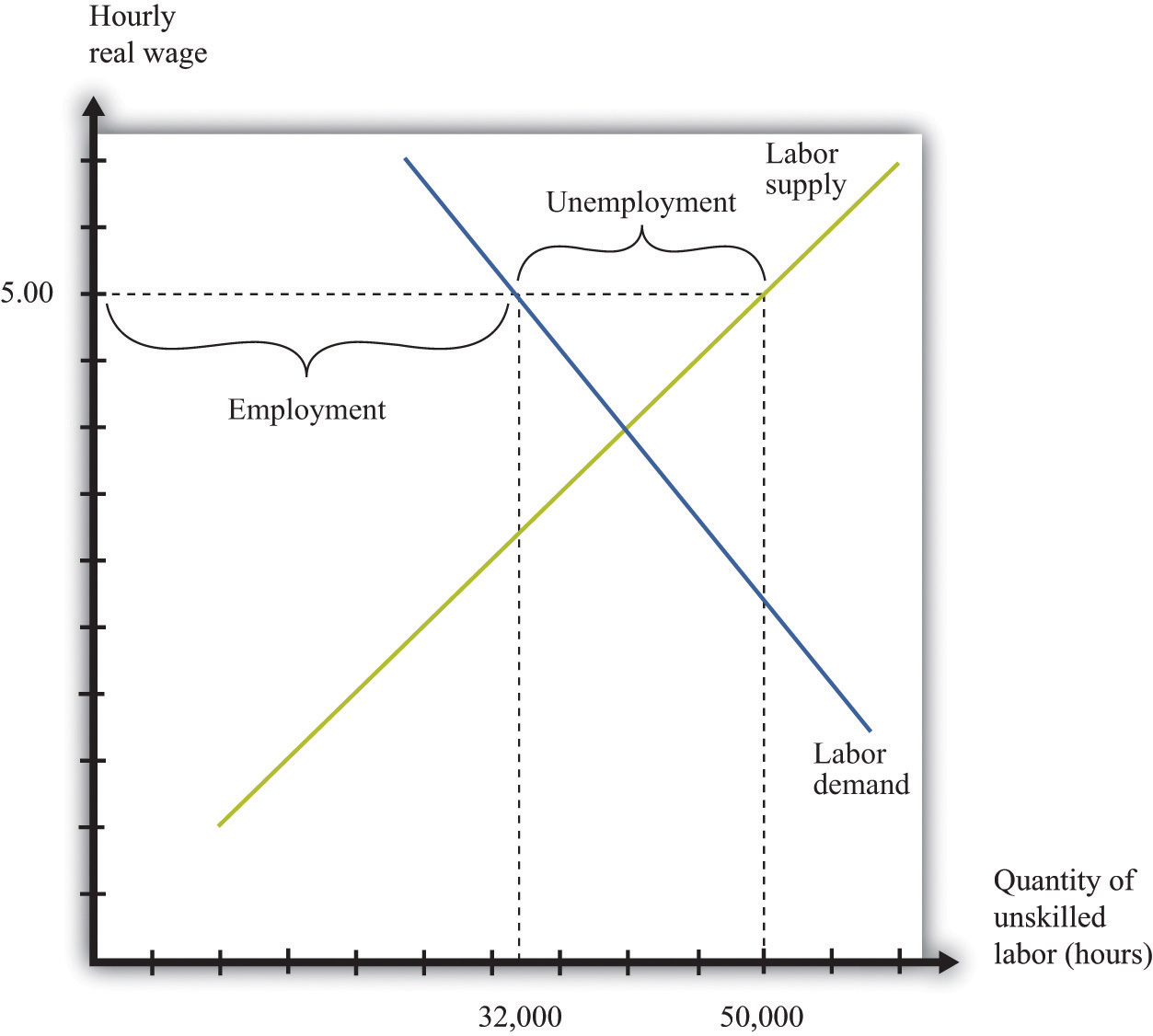
In particular the government imposes a minimum wage making it illegal for an employer to pay a worker less than a certain amount per hour. Because this is the most popular and recognizable example of a price floor, we will concentrate on it for the rest of this lesson.[2] ... In the diagram, the equilibrium wage is $5 per hour. At this wage ...
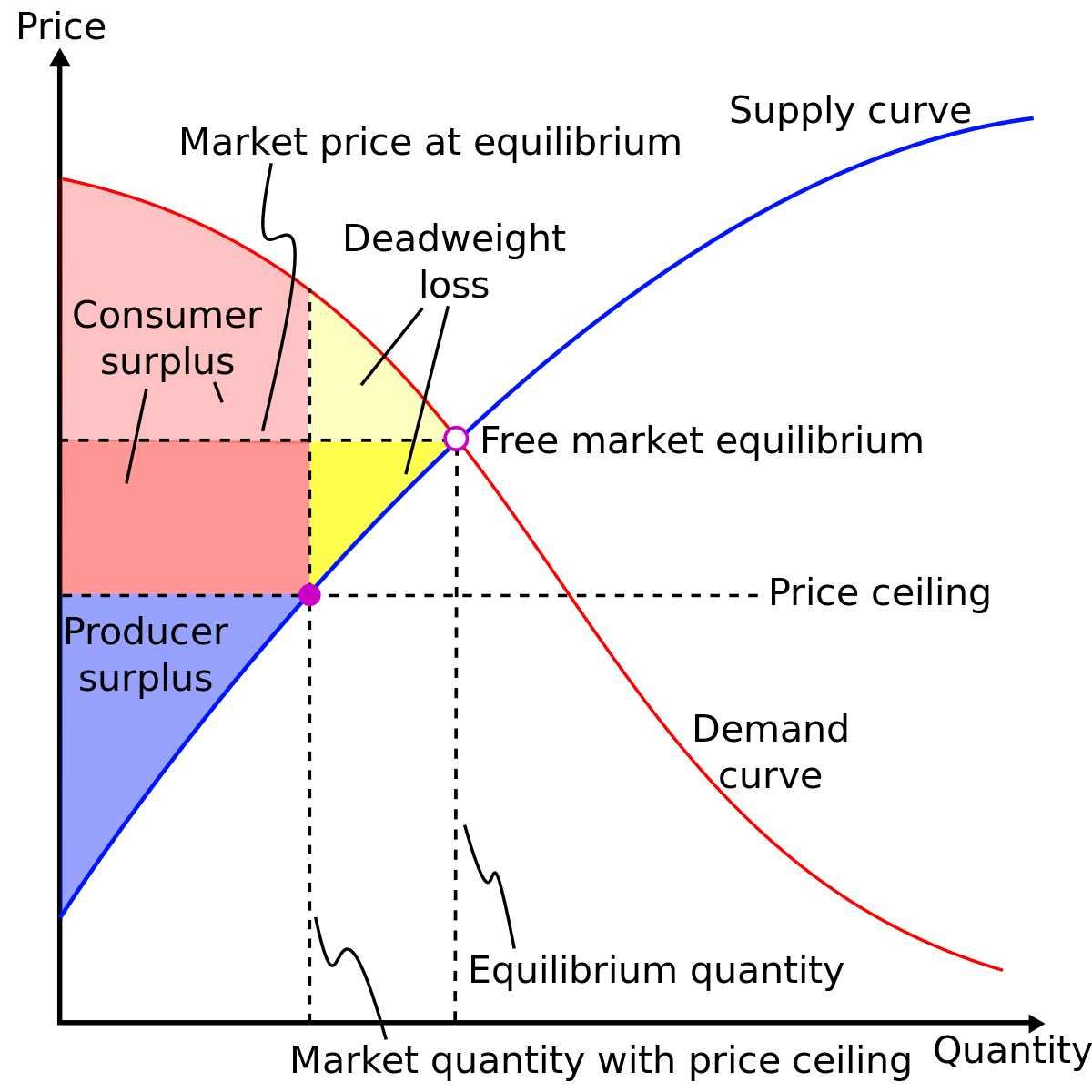
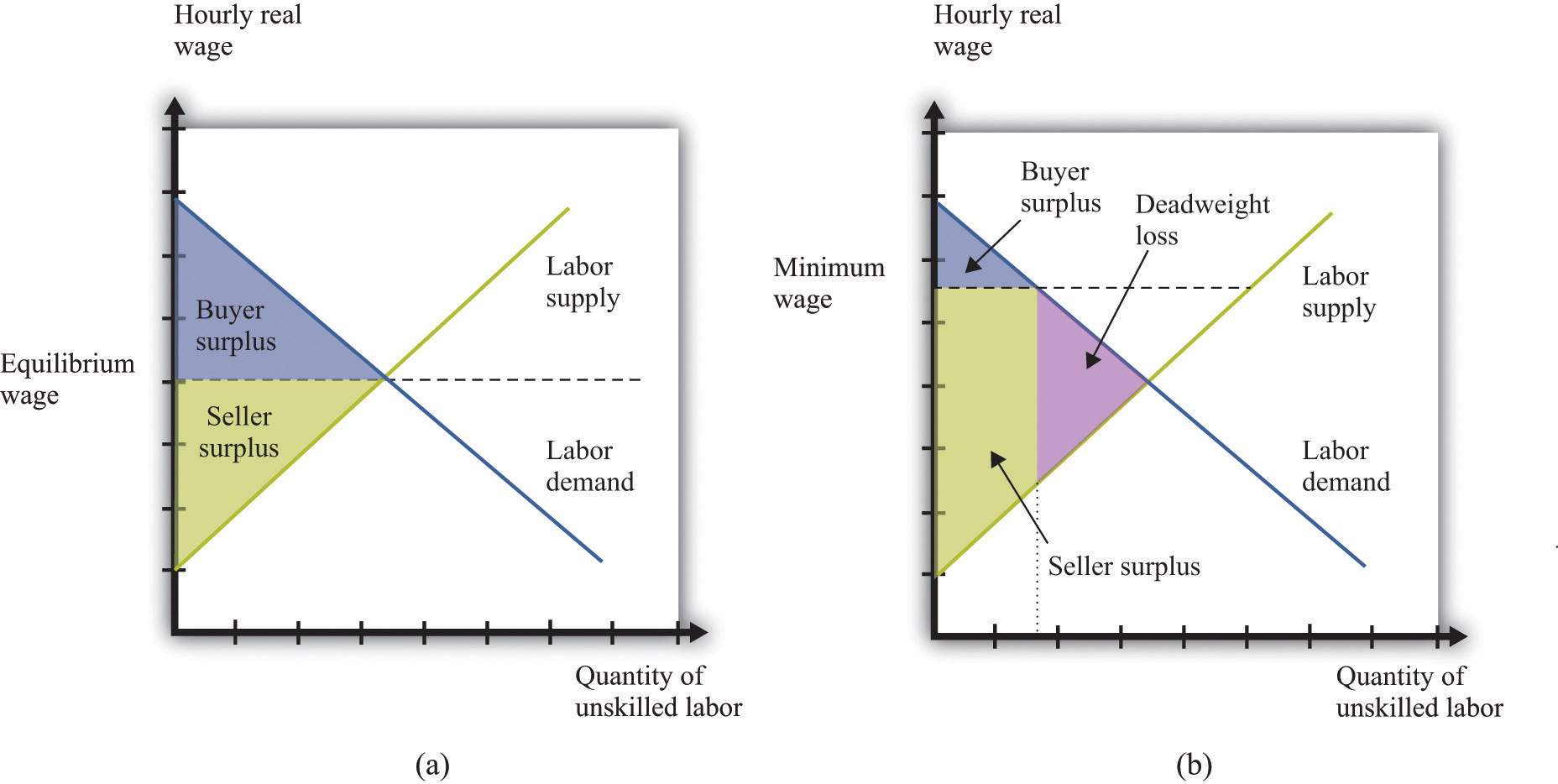
Causes of Deadweight Loss. Price floors: The government sets a limit on how low a price can be charged for a good or service. An example of a price floor would be minimum wage.; Price ceilings: The government sets a limit on how high a price can be charged for a good or service. An example of a price ceiling would be rent control - setting a maximum amount of money that a landlord can ...
In the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the minimum wage at Point A? There will be a surplus of workers. Use this image to answer the following question.
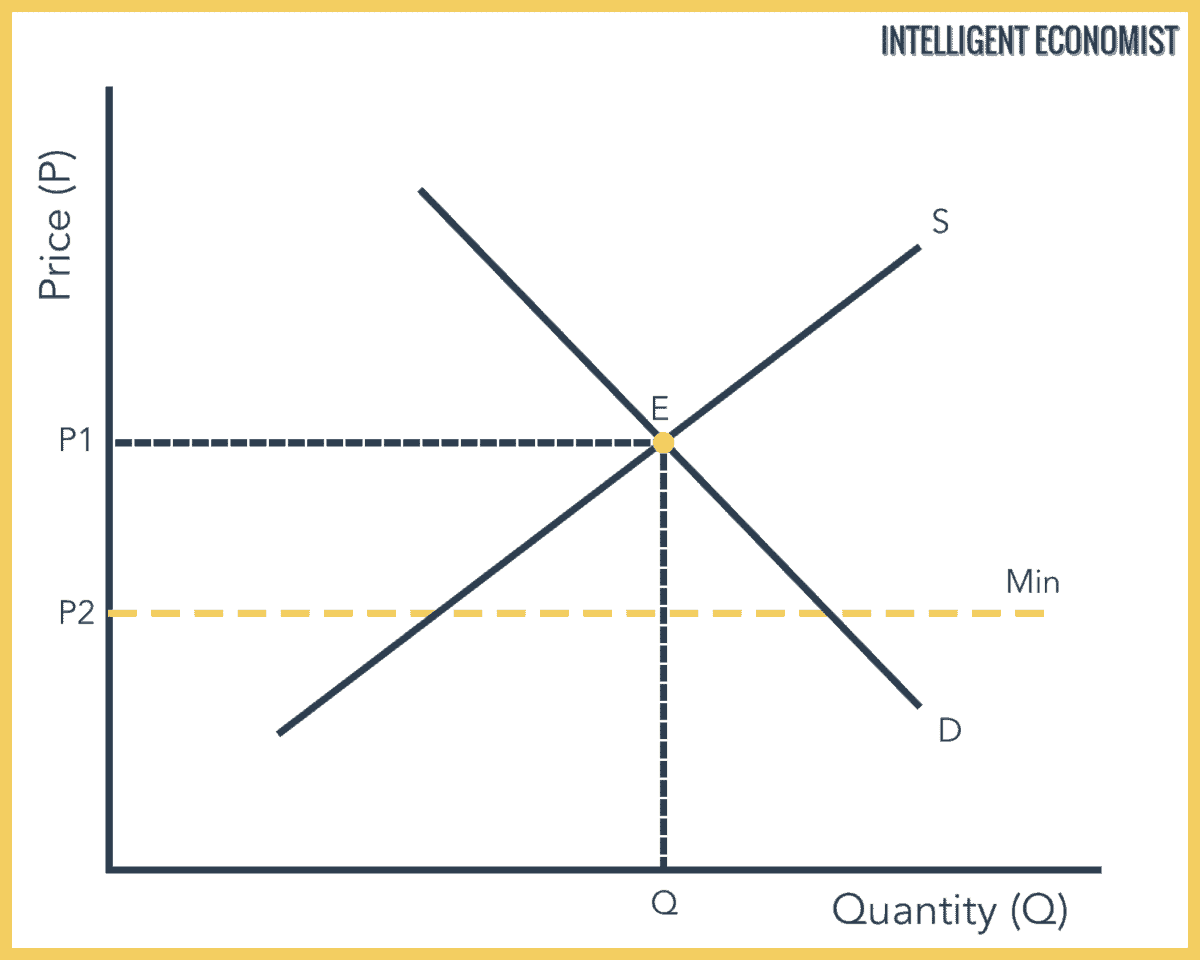
In the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the minimum wage at point a?
In the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the minimum wage at Point B? There will be a shortage of workers. There will be a surplus of workers. The minimum wage will rise to meet equilibrium. The minimum wage will fall to meet equilibrium. Question 2 (Multiple Choice Worth 5 points)
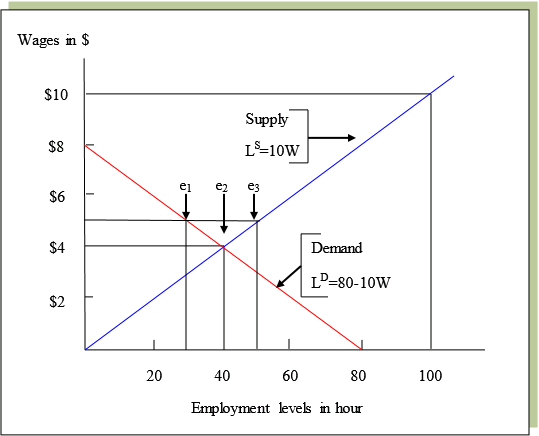
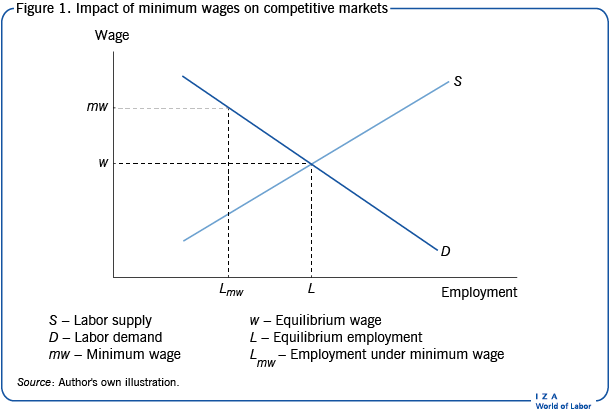
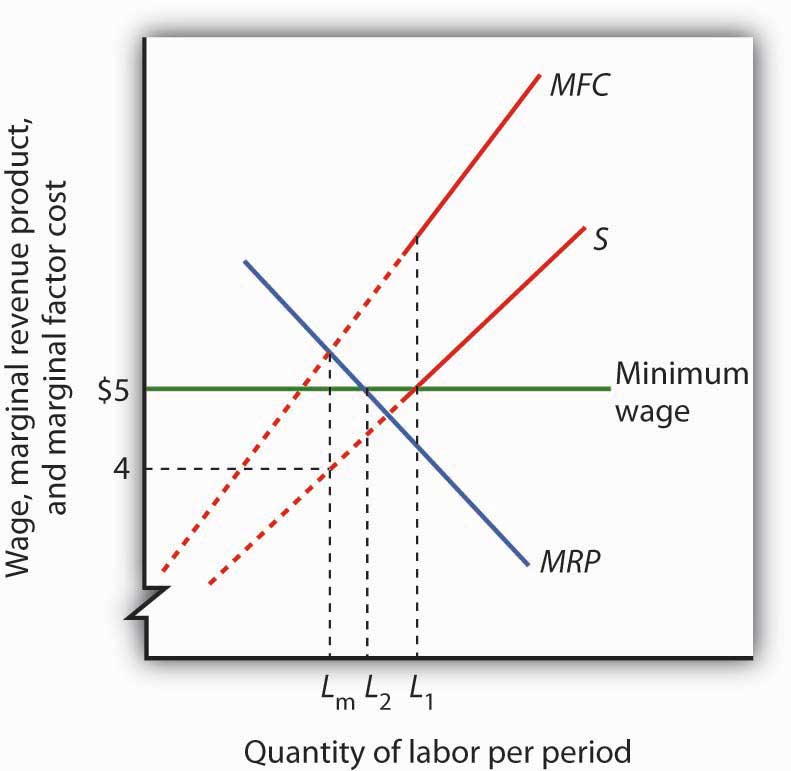
A minimum wage (W min) that is set above the equilibrium wage would create a surplus of unskilled labor equal to (L 2 - L 1). That is, L 2 units of unskilled labor are offered at the minimum wage, but companies only want to use L 1 units at that wage. Because unskilled workers are a substitute for a skilled workers, forcing the price of ...
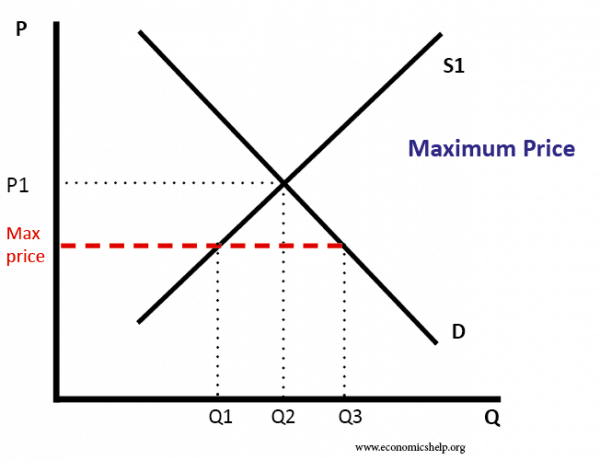
Government price controls are situations where the government sets prices for particular goods and services. Types of price controls. Minimum prices - Prices can't be set lower (but can be set above); Maximum price - Limit to how much prices can be raised (e.g. market rent); Buffer stocks - Where government keep prices within a certain band; Limiting price increases - In a privatised ...
In the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the minimum wage at point a?.
Price floors are used by the government to prevent prices from being too low. The most common price floor is the minimum wage--the minimum price that can be payed for labor. Price floors are also used often in agriculture to try to protect farmers. For a price floor to be effective, it must be set above the equilibrium price.
In the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the minimum wage at Point B? a) There will be a shortage of workers. b) There will be a surplus of workers. c) The minimum wage will rise to meet equilibrium. d) The minimum wage will fall to meet equilibrium. Lowering the discount rate can promote full employment because
In the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the minimum wage at point A? The minimum wage will rise to meet equilibrium. The minimum wage will fall to meet equilibrium. There will be a surplus of workers. There will be a shortage of workers. Question 18 (Multiple Choice Worth 3 points)
rate in a recession should be above the long-run average. Explain whether each of the following events will increase, decrease, or have no effect on long-run aggregate supply. a. The United States experiences a wave of immigration. b. Congress raises the minimum wage to $10 per hour. c. Intel invents a new and more powerful computer chip. d.
a. Use the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply to illustrate the initial equilibrium (call it point A). Be sure to include both short-run and long-run aggregate supply. b. The central bank raises the money supply by 5 percent. Use your diagram to show what. happens to output and the price level as the economy moves from the initial ...
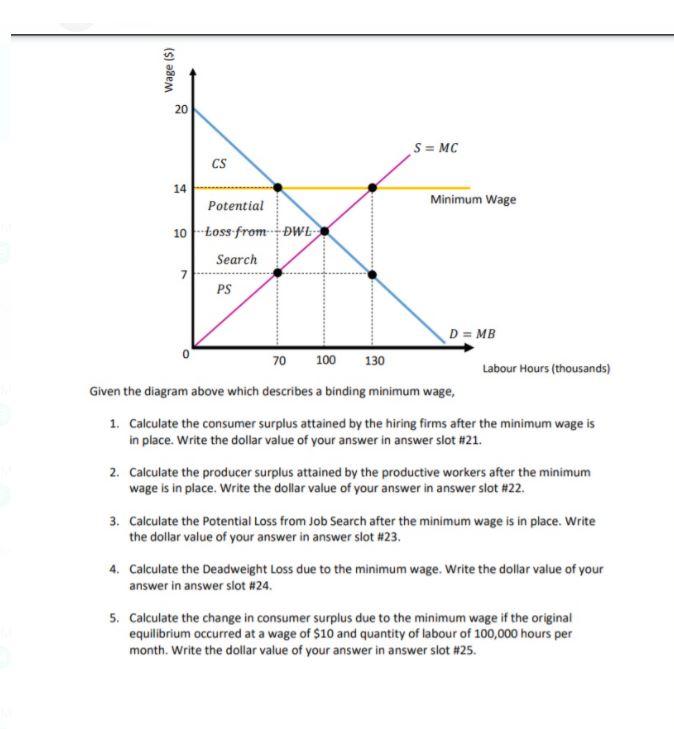
Two things happen when the government imposes a minimum wage: The amount of labor hired in the market decreases. In our example, the number of unskilled workers employed decreases from 1,000 to 800. Thus while those who have jobs earn a higher wage, there are now some individuals who no longer have jobs.
in the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the minimum wage at point b? asked Apr 29 in Other by gaurav96 Expert (68.9k points) 0 votes. 1 answer. a binding minimum wage tends to. asked Nov 21 in Other by megha00 Expert (40.9k points) 0 votes. 1 answer.
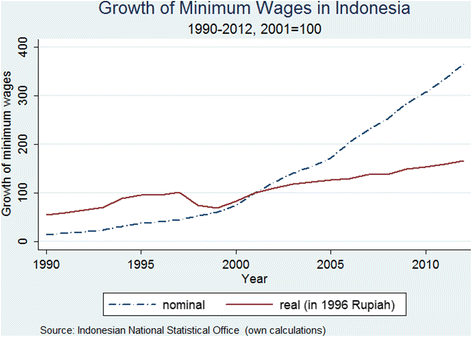
The U.S. government sets a minimum wage, a price floor that makes it illegal for an employer to pay employees less than a certain hourly rate. In mid-2009, the U.S. minimum wage was raised to $7.25 per hour. Local political movements in a number of U.S. cities have pushed for a higher minimum wage, which they call a living wage. Promoters of ...
Price Floor. A price floor or a minimum price is a regulatory tool used by the government. More specifically, it is defined as an intervention to raise market prices if the government feels the price is too low. In this case, since the new price is higher, the producers benefit. For a price floor to be effective, the minimum price has to be ...
Show in a supply and demand diagram how minimum wage can increase unemployment. In our supply and demand analysis, a minimum wage is a simple application of a binding price floor. In this case, the "price" which is typically on the y-axis is the wage which gets paid to workers. In this simplistic model, it is best to think of the wage as how ...
2. In the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the price for potatoes at Point B? A. There will be a shortage of potatoes. B. There will be a surplus of potatoes. C. The price of potatoes will rise to meet equilibrium. D. The price of potatoes will fall to meet equilibrium.
In the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the minimum wage at Point A? There will be a surplus of workers. Which of these is not a result of the federal government spending more than it earns? Increased taxes INCORRECT. Inflation is low but the unemployment rate is the highest seen in several years.
Government intervention through minimum wages. A minimum wage is the lowest hourly, daily or monthly wage that employers may legally pay to employees or workers. The main aim of introducing minimum wages is to reduce poverty and the exploitation of workers who have little or no bargaining power with their employers.
15 In the diagram, the ARP L curve is the average revenue product of labour curve of a profit-maximising monopsony and the MRP L curve is its marginal revenue product of labour curve. The firm pays its workers the minimum wage, OW, set by the country's government. The curves AFC L and MFC
The government does not like it and maybe many of their voters are people making that wage, so they say, "Hey, you know what? "We are going pass some well-intentioned legislation. "We are going to pass a minimum wage. "We are going to pass a law, minimum wage, "that says any employer has to pay at least $7 an hour." $7 an hour.
Answers: 1 on a question: In the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the minimum wage at Point B? There will be a shortage of workers. There will be a surplus of workers. The minimum wage will rise to meet equilibrium. The minimum wage will fall to meet equilibrium.
In the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the minimum wage at Point B? a. There will be a shortage of workers. 5. The government sets the price of wheat for the coming year above the equilibrium price. What effect would this have on supply and demand? a.
In the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the price for potatoes at point A? A. There will be a shortage of potatoes. B. There will be a surplus of potatoes. C. The price of potatoes will rise to meet equilibrium. D. The price of potatoes will fall to meet equilibrium.
In the diagram above what will happen if the government sets the minimum wage at point a. The price of internet access will rise to meet equilibrium. In our example the number of unskilled workers employed decreases from 1000 to 800. But with a minimum wage b some gains from trade are lost because there are. 102 the effects of a minimum wage.
In the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the minimum wage at Point A? The minimum wage will rise to meet equilibrium. The minimum wage will fall to meet equilibrium. There will be a surplus of workers. There will be a shortage of workers. Question 18 (Multiple Choice Worth 5 points) [04.02 MC]
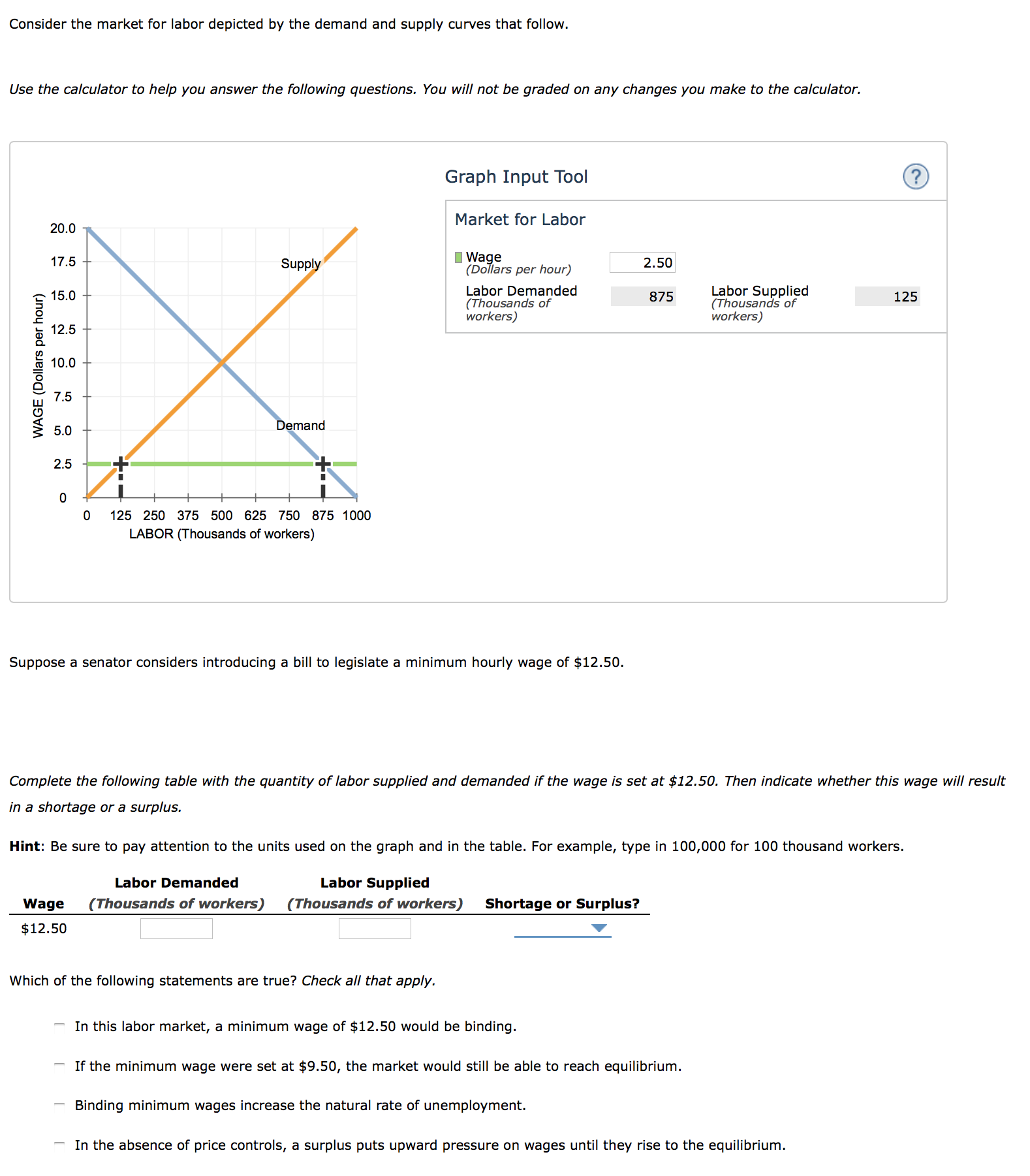
A minimum wage is very similar to a price floor because it is set above the market wage. According to this illustration of the labor market, the equilibrium wage is at $9, while the quantity of ...
in the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the minimum wage at point b? asked Apr 29 in Other by gaurav96 Expert (68.9k points) 0 votes. 1 answer. a minimum wage set below the equilibrium wage _____. asked Apr 22 in Other by gaurav96 Expert (68.9k points) 0 votes. 1 answer.
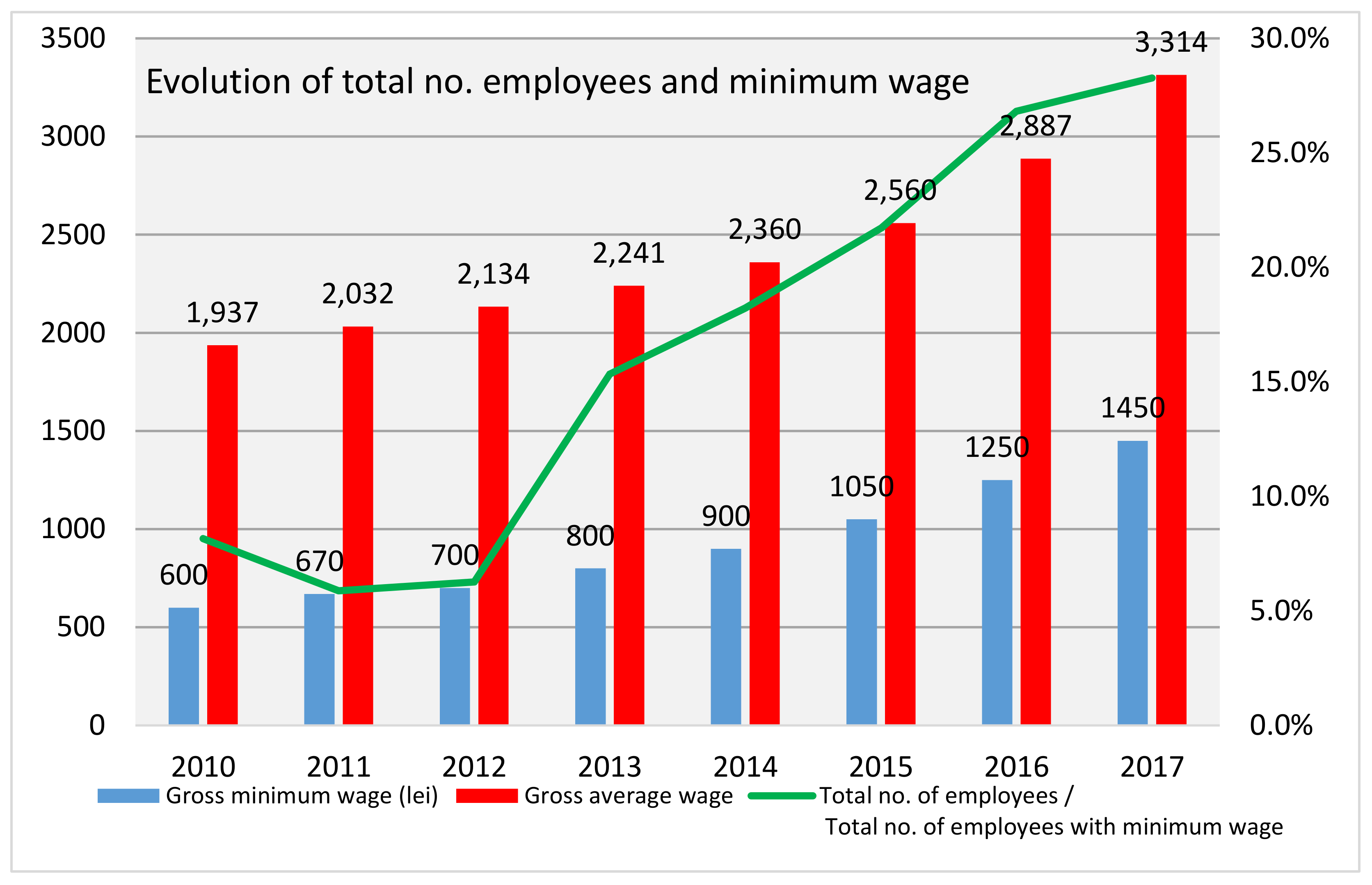
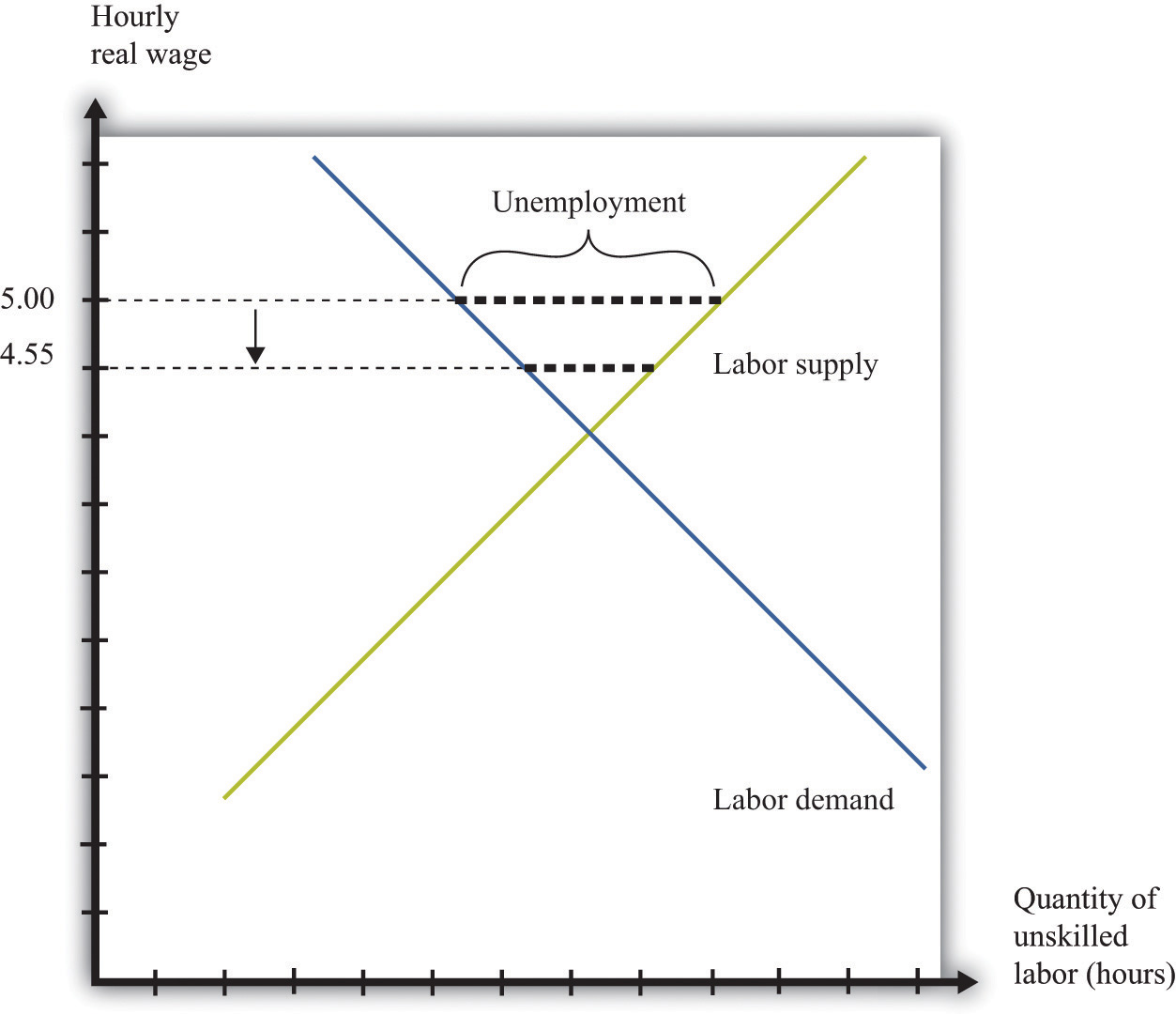
Even if the government increases minimum wage by enough so that it rises slightly above the equilibrium wage and becomes binding, there will be only a small excess supply gap between the quantity demanded and quantity supplied. These insights help to explain why U.S. minimum wage laws have historically had only a small impact on employment.




/disequilibrium-498e9ba4154c4a7c8739b3443da14b17.png)






/media/img/posts/2013/12/EPI_1010_Raise/original.png)

0 Response to "37 in the diagram above, what will happen if the government sets the minimum wage at point a?"
Post a Comment