41 diagram of eukaryotic cell
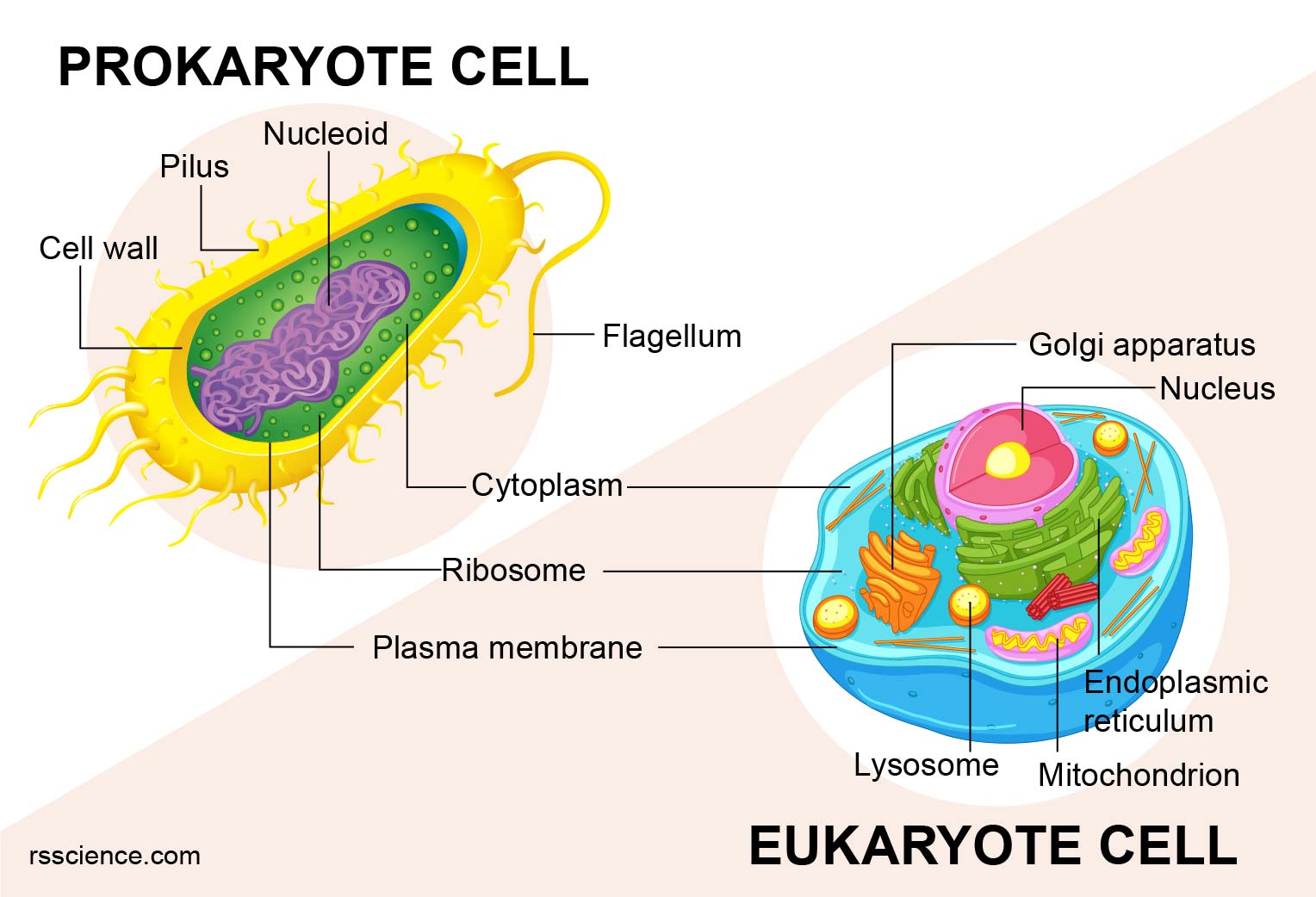
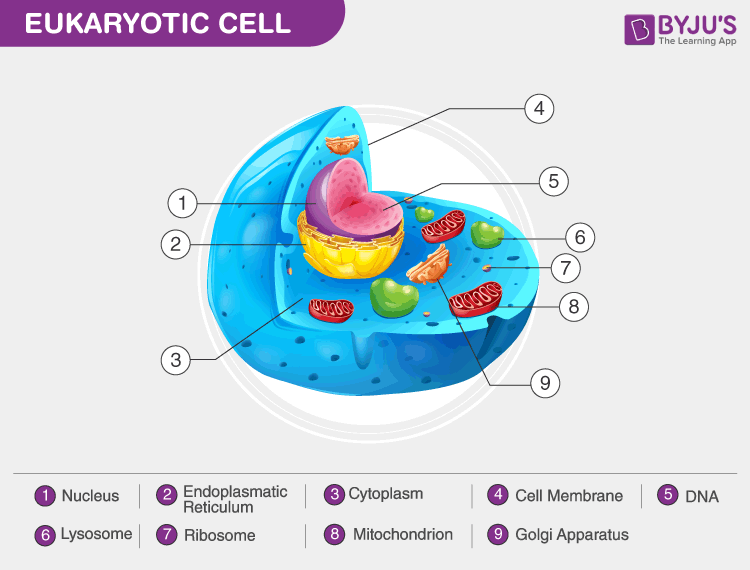
Eukaryotic cells have the nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane. The cell has mitochondria. Flagella and cilia are the locomotory organs in a eukaryotic cell. A cell wall is the outermost layer of the eukaryotic cells. The cells divide by a process called mitosis. The eukaryotic cells contain a cytoskeletal structure. Eukaryotic Cell. Eukaryotic cells are defined as cells containing organized nucleus and organelles which are enveloped by membrane-bound organelles. Examples of eukaryotic cells are plants, animals, protists, fungi. Their genetic material is organized in chromosomes. Golgi apparatus, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Nucleus are parts of Eukaryotic Cells.
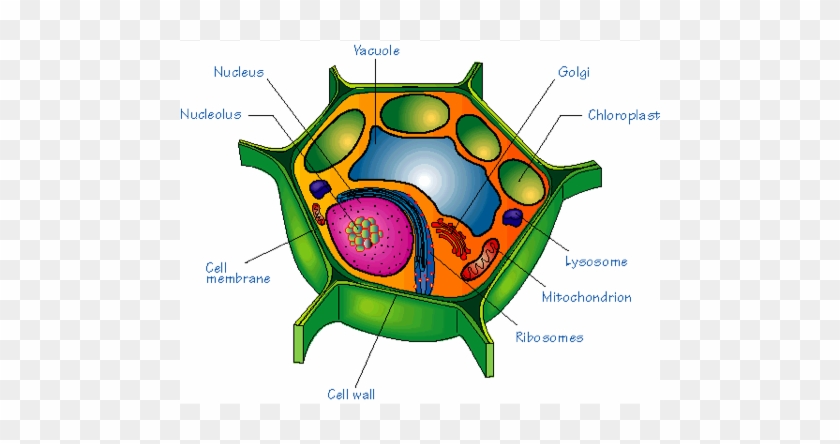
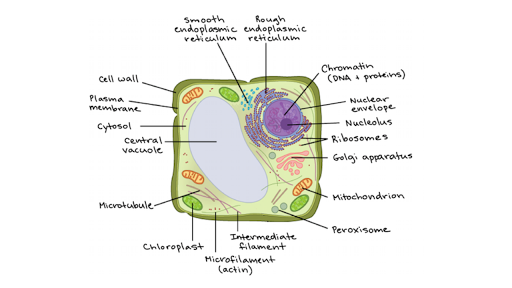
Structure of eukaryotic cells: The ultra cellular structure of a eukaryotic cell (animals and plants)must be known with the functions of organelles: Cell surface membrane is selectively permeable to control the exchange and is mainly made up of lipids and proteins.

Diagram of eukaryotic cell
Eukaryotic Nucleus: Structure and Function. The nucleus is an important eukaryotic cell organelle. It functions as the administrative centre and coordinates and controls the cell functions such as protein synthesis, metabolism and cell division. The nucleus is the seat of the genetic material, the DNA. The nucleus is the largest of all cell ... During the 1950s, scientists postulated the concept of prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell, with earlier groundwork being laid by Edouard Chatton, a French Biologist in 1925. Anatomically, cells vary with respect to their classification, therefore, prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells differ from each other quite drastically. The plasma membrane. Like bacteria and archaea, eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates the internal contents of the cell from its surrounding environment.The plasma membrane controls the passage of organic molecules, ions, water, and oxygen into and out of the cell.
Diagram of eukaryotic cell. The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Eukaryotes have two major types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. ... There, the vesicles fuse and coalesce from the center toward the cell walls; this structure is called a cell plate. As more vesicles fuse, the cell plate enlarges until it merges with the cell walls at the periphery of the cell. Enzymes use the ... and eukaryotic cells 1. Create a Venn diagram or concept map that clearly distinguishes bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic cells in terms of their genome organization, organelles, cell envelopes, ribosome size and component molecules, and cytoskeleton. 2. Determine the type of microbe when given a description of a newly discovered microbe. 56 Phases of the Cell Cycle. A typical eukaryotic cell cycle is illustrated by human cells in culture, which divide approximately every 24 hours. As viewed in the microscope, the cell cycle is divided into two basic parts: mitosis and interphase.Mitosis (nuclear division) is the most dramatic stage of the cell cycle, corresponding to the separation of daughter chromosomes and usually ending with ... Structure (components/ parts) of Eukaryotic cell Eukaryotic cells are much larger in size when compared with prokaryotic cells, having the volume about 10,000 times higher than prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are formed of a number of membrane-bound and membrane-less organelles that all perform together to support the cell's organization ...
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles; prokaryotic cells do not. All cells share certain characteristics. •Cells tend to be microscopic. •All cells are enclosed by a membrane. •All cells are filled with cytoplasm. •All cells have DNA Bacterium (colored SEM; magnification 8800x) cell membrane cytoplasm Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells . Title: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Venn Diagram Worksheet Author: Brandon Linn Created Date: 9/19/2018 6:59:56 PM ... November 12, 2021. Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes Venn Diagram Venn Diagram Teaching Middle School Science Prokaryotes. Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Intp Careers Intp Personality Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration. Prokaryote Eukaryote Animal Plant Cell Prokaryotes Plant Cell Eukaryotic Cell. Meiosis Lessons Mitosis Meiosis Mitosis Vs Meiosis Mitosis. Eukaryotic cells which contain nucleus are called nucleated whereas those who don't possess nucleus are called anucleated. The DNA found in the nucleus has various function such as metabolism, growth, reproduction, homeostasis, differentiation and death.
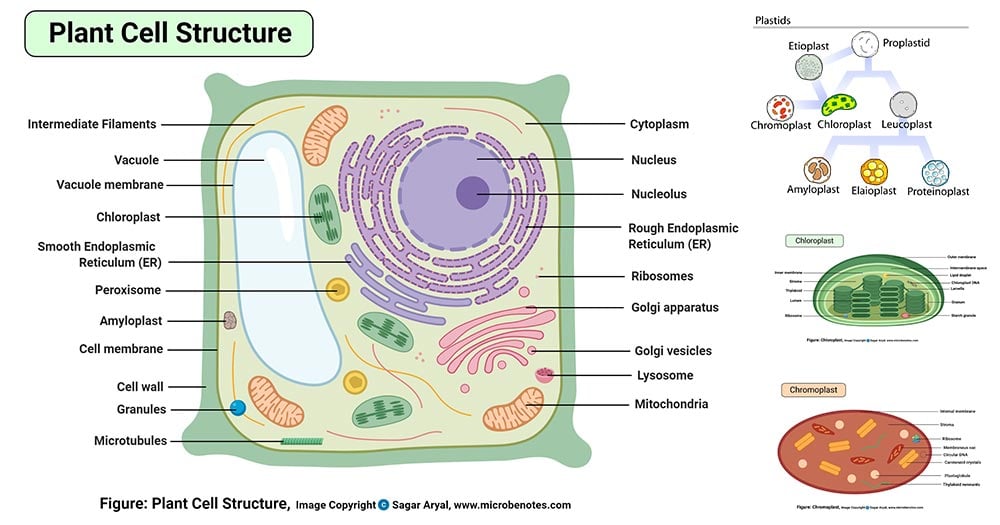
Eukaryotic Cell Envelope & External Structures Cell Wall: The cells of plants, algae and fungi have thick, protective cell walls, which provide support, help maintain the shape of the cell, and prevent the cell from taking in too much fresh water and bursting. Feversham College. Q1.The diagram shows a eukaryotic cell. (a) Complete the table by giving the letter labelling the organelle that matches the function. (b) Use the scale bar in the diagram above to calculate the magnification of the drawing. Show your working. Eukaryotic Cell Structure Animal Cell Plant And Animal Cells Eukaryotic Cell. Royalty Free Stock Photos A Typical Cell Labeled Cell Diagram Animal Cell Cells Worksheet. This Schematic Diagram Shows A Generic Animal Cell And The Organelles Including The Nucleus En Animal Cells Worksheet Human Cell Diagram Human Cell Structure. The eukaryotic cell is surrounded by a plasma membrane which is made of protein and phospho-lipids. Some of the eukaryotic cells are surrounded by a cell wall like in fungal cells, some protists, and in plant cells. Cell walls give strength and rigidity to the cell. The Nucleus is centrally placed which is a double membranous structure.
The eukaryotic cells are too complex than prokaryotic cells and evolved from them about 1.5 billion years ago (BYA). Size: Eukaryotic cell size varies greatly from 10 mm to 500 mm. Ostrich egg is the largest eukaryotic cell known measuring 170 mm X150 mm.
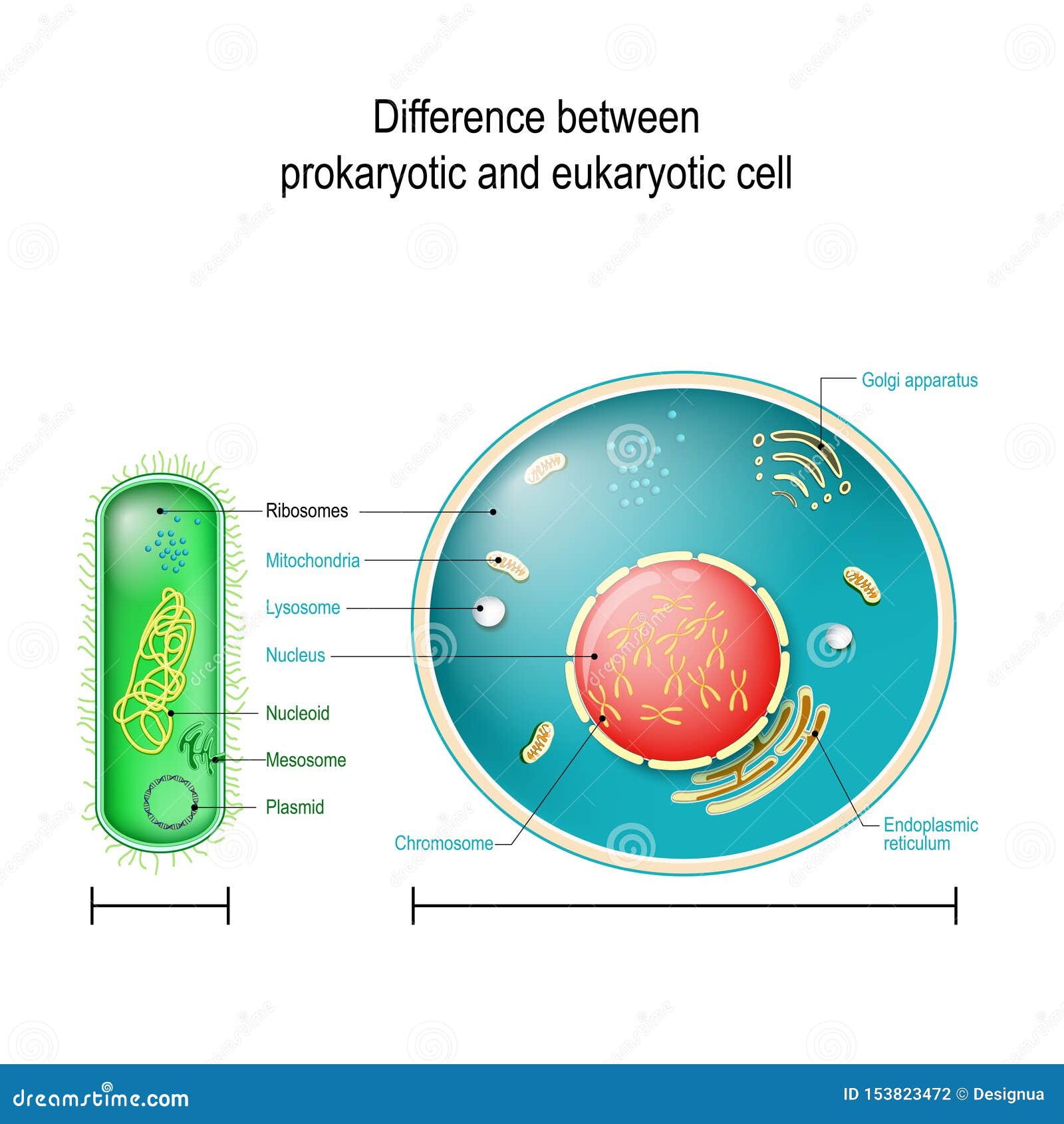
Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Differences Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Stock Vector Illustration Of Golgi Disease 153823472
A eukaryotic cell is one of two different types of cells. Organisms that are based on the eukaryotic cell are called "eukaryotes" and include plants, animals, fungi, and protists. The only organisms that are not based on the eukaryotic cell are organisms based on a prokaryotic cell structure. Those organisms are found in the domains Archaea ...
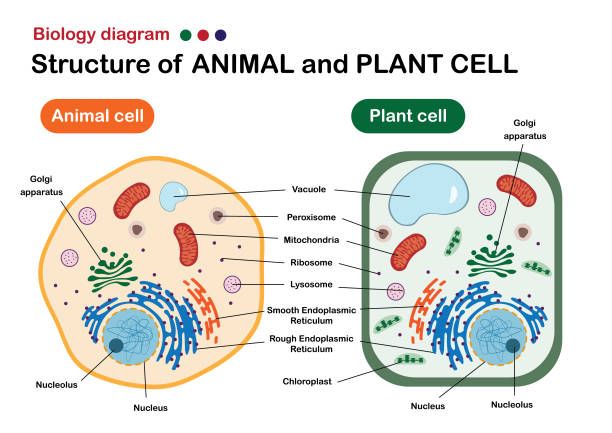
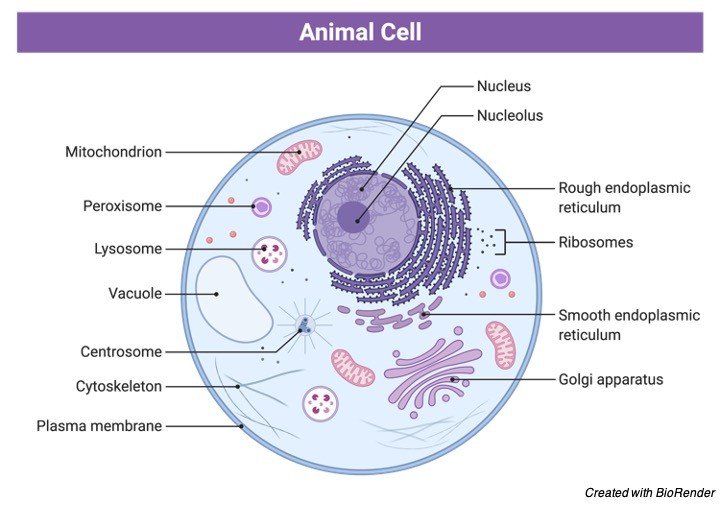
The nucleus is the site of most cellular genetic material, DNA. The Golgi Apparatus processes and packages proteins. The endoplasmic reticulum is the site of protein and lipid production. The mitochondrion is the site where energy stored. The plasma membrane composed of a phospholipid bilayer controls cellular traffic. The Eukaryotic Cell.
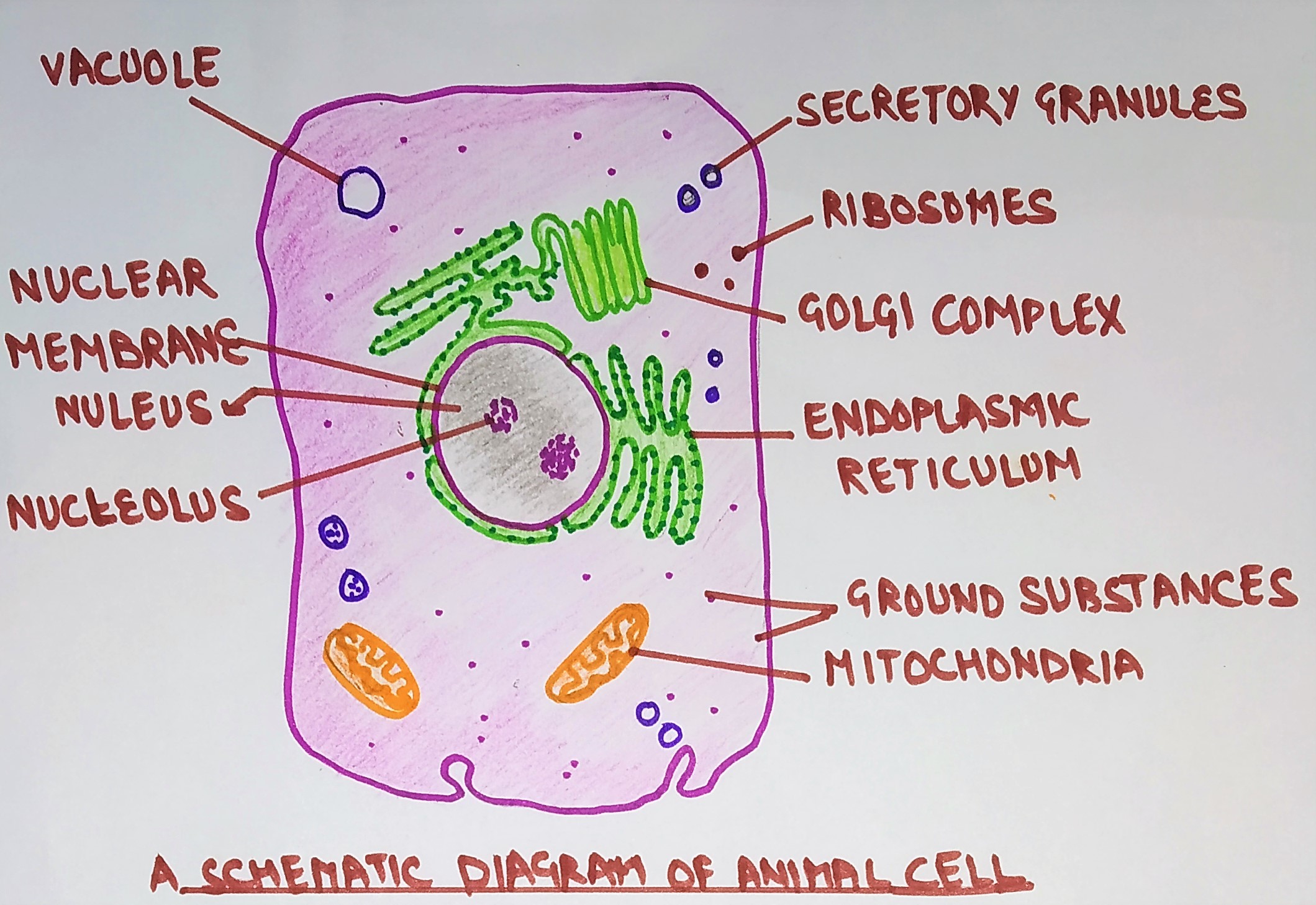
Animal Cell Structure. Animal cells are typical of the eukaryotic cell, enclosed by a plasma membrane and containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Unlike the eukaryotic cells of plants and fungi, animal cells do not have a cell wall. This feature was lost in the distant past by the single-celled organisms that gave rise to the ...
Eukaryotic Cell Structure. Eukaryotic cell are the developed, advanced and complex forms of cells. They are the building block or smallest unit of life of organisms as simple as amoeba and protozoa to the most complicated plants and animals. Significantly bigger than the prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have diameter ranging from 10µm -100µm.

2 3 Eukaryotic Cells Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Ultrastructure Of A Liver Cell As An Example Of An Animal Cell Ppt Download
Other Eukaryotic Cell Components and Organelles. Cytoplasm: The inside of the cell, between the nucleus and plasma membrane, is filled with a gel-like fluid in which the organelles are suspended. Cytoplasm includes both the liquid (called cytosol) and the suspended organelles. Cytoskeleton: Composed of microtubules, intermediate filaments and ...
Eukaryotic Cell (With Diagram) Article Shared by. ADVERTISEMENTS: The below mentioned article provides biology notes on Eukaryotic Cell. A eukaryote cell is the one which has an organised nucleus and several membrane covered cell organelles. Except monera, the cells of all other kingdoms have eukaryotic organisation. ...
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Venn Diagram Prokaryotes Both Prokaryotes Eukaryotes and Eukaryotes *No Nucleus *Cells have a nucleus *Small and simple *Cells have organelles *No organelles *Can be unicellular or *Are very abundant *Have ribosomes multicellular
While all eukaryotic cells contain a cytoskeleton, some types of cells - like plant cells - have a cell wall for even more protection. Unlike the cell membrane, which is relatively fluid, the cell wall is a rigid structure that helps maintain the shape of the cell.
Two Types of Cells. There is another basic cell structure that is present in many but not all living cells: the nucleus. The nucleus of a cell is a structure in the cytoplasm that is surrounded by a membrane (the nuclear membrane) and contains, and protects, most of the cell's DNA. Based on whether they have a nucleus, there are two basic types of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells.
The eukaryotic cells types are generally found in animals, plants, algae, and fungi. For the purpose of this article, the primary focus will be the structure and histology of the animal cell. The major differences between animal and plant cells will be explored as well. As previously stated, the fundamental components of a cell are its organelles.
The plasma membrane. Like bacteria and archaea, eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates the internal contents of the cell from its surrounding environment.The plasma membrane controls the passage of organic molecules, ions, water, and oxygen into and out of the cell.
During the 1950s, scientists postulated the concept of prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell, with earlier groundwork being laid by Edouard Chatton, a French Biologist in 1925. Anatomically, cells vary with respect to their classification, therefore, prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells differ from each other quite drastically.
Eukaryotic Nucleus: Structure and Function. The nucleus is an important eukaryotic cell organelle. It functions as the administrative centre and coordinates and controls the cell functions such as protein synthesis, metabolism and cell division. The nucleus is the seat of the genetic material, the DNA. The nucleus is the largest of all cell ...
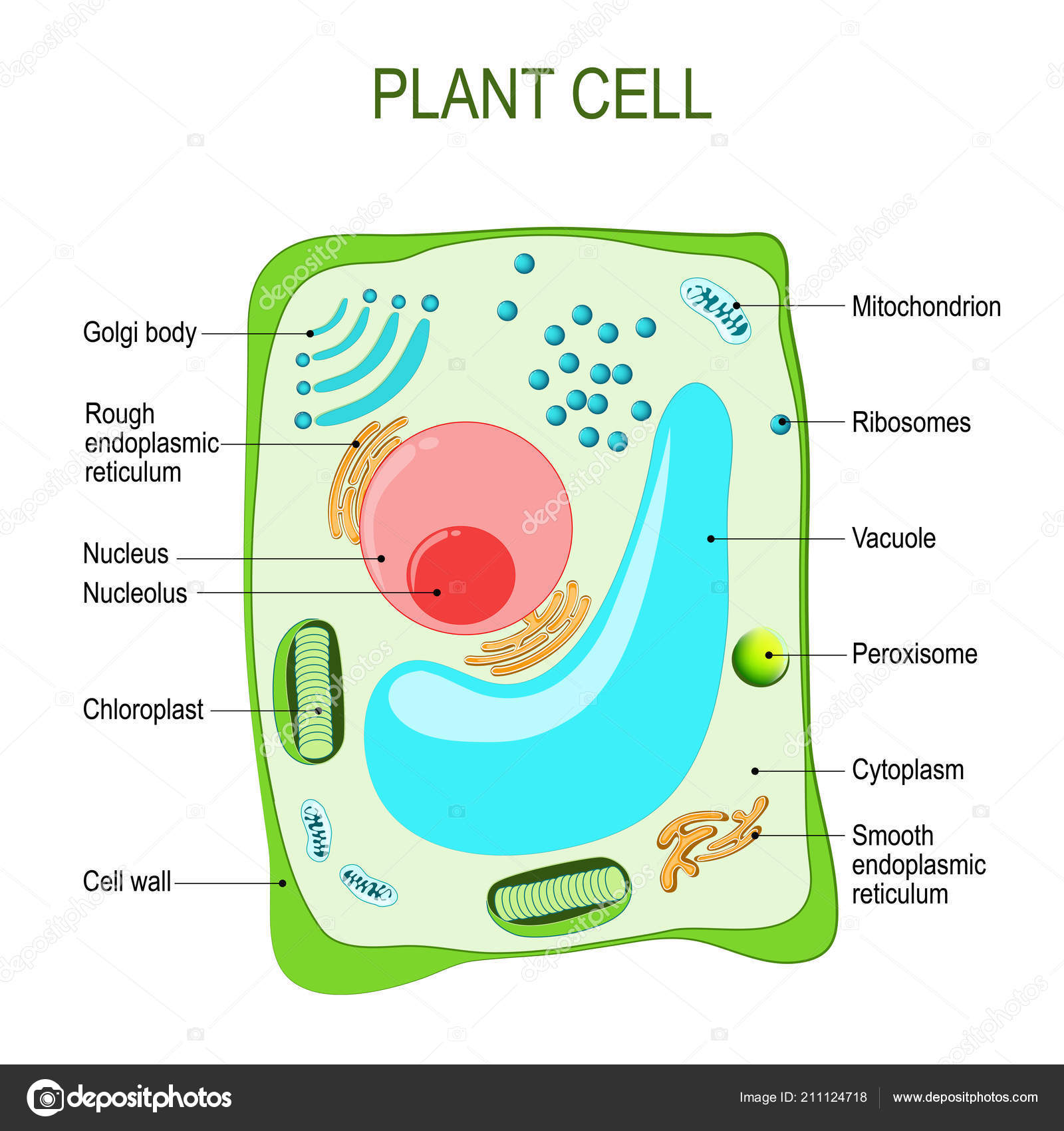
Plant Cell Anatomy Cross Section Structure Eukaryotic Cell Vector Diagram Stock Vector Image By C Edesignua 211124718

Animal Cell Cross Section Structure Of A Eukaryotic Cell Vector Diagram Stock Vector Vector And Low Budget Royalty Free Image Pic Esy 035791791 Agefotostock






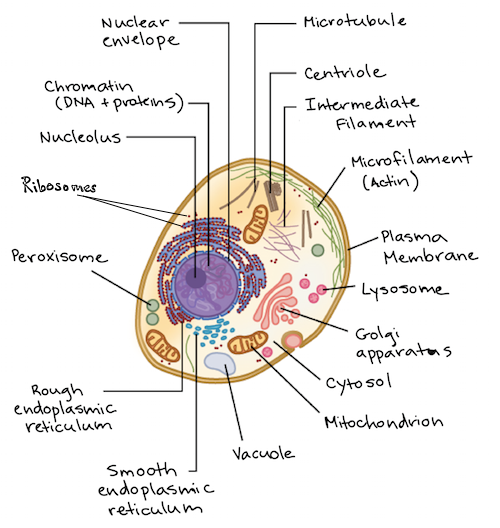





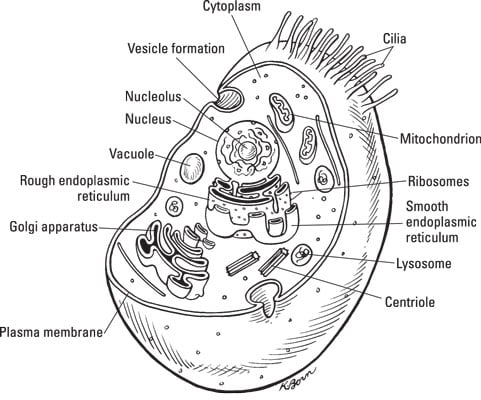










0 Response to "41 diagram of eukaryotic cell"
Post a Comment