37 pv diagram practice problems
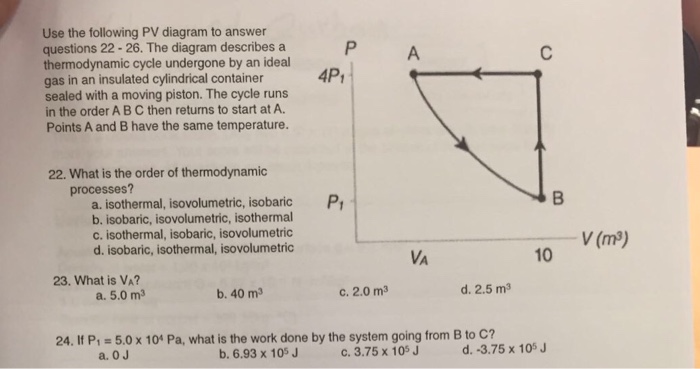
Or you could think about the problem a bit and use PV=nRT. N 2 O is placed in a piston. Initially the volume of the piston is 3.0 L, and the pressure of the gas is 5.0 atm. The piston is used to compress the gas to a volume of 1.5 L; determine the pressure of the N 2 O. well, before the compression. P 1 V 1 = n 1 R 1 T 1. or. after expansion. P ... What scientific concept do you need to know in order to solve this problem? Our tutors have indicated that to solve this problem you will need to apply the Work & PV Diagrams concept. You can view video lessons to learn Work & PV Diagrams. Or if you need more Work & PV Diagrams practice, you can also practice Work & PV Diagrams practice problems.
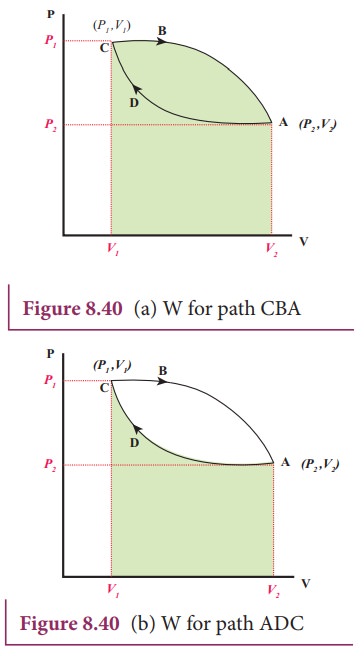
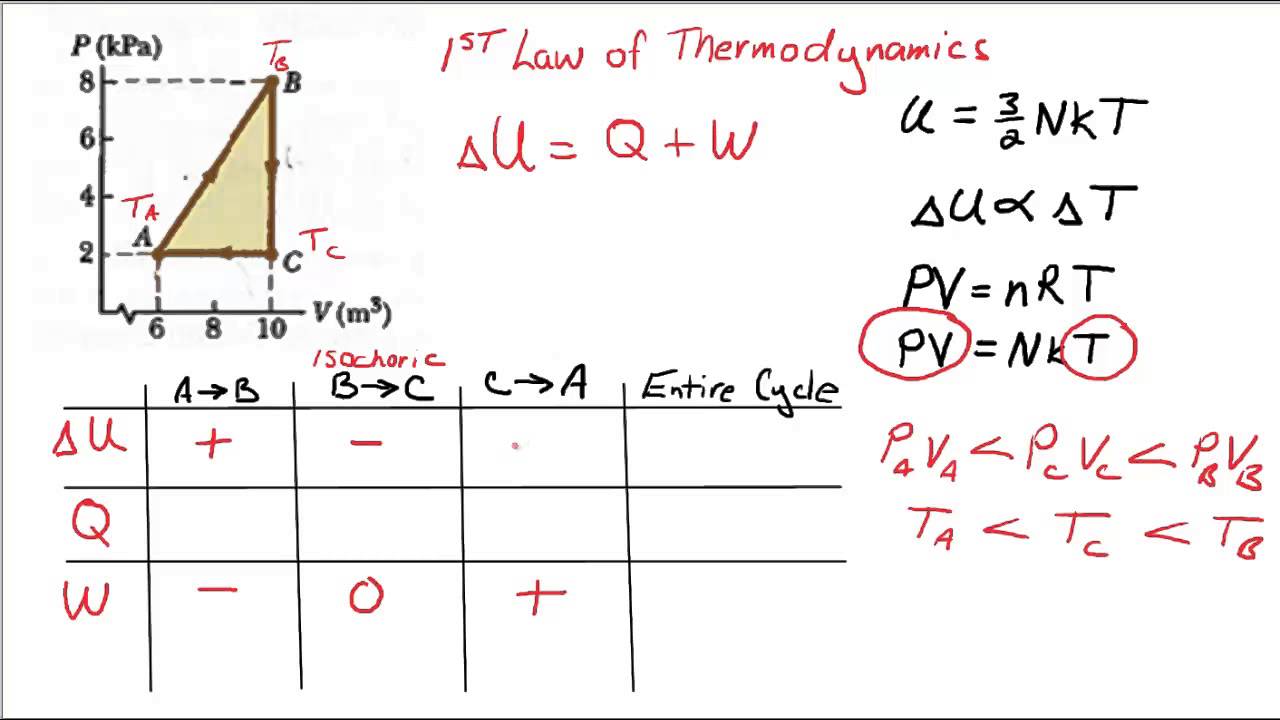
(iii) On a single pV diagram, show and label both processes. PSS 17.1: The Bermuda Triangle Description: Find the work done on an ideal gas in a simple isochoric-isobaric-constant pV process. (PSS 17.1: Work in ideal-gas processes) Learning Goal: To practice Problem-Solving Strategy 17.1 for problems involving calculating work done on an ideal gas.

Pv diagram practice problems
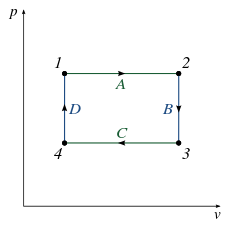
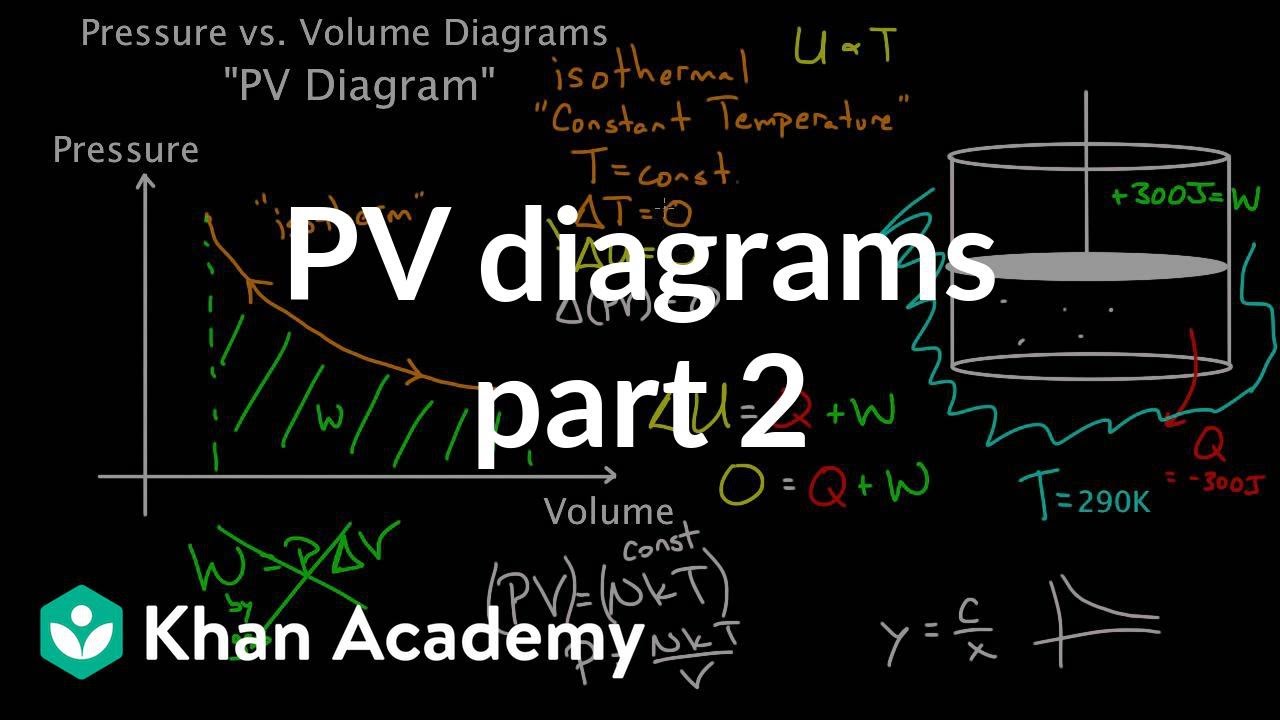
Practice solving Work & PV Diagrams problems. Master even the most complex scientific problems with our step-by-step explanation videos. This physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into PV diagrams. It explains how to calculate the work done by a gas for an isobaric process, iso... Practice Problems, Chapters 1 - 4 1. Use the P-V diagram below to answer the following questions 1a) The Net Work for the cyclic process is: a) Zero b) Positive c) Negative d) Cannot tell from the diagram 1b) The processes from states 1 to 2 and 3 to 4 are: a) Isothermal b) Isobaric c) Isochoric d) Isometric
Pv diagram practice problems. EXAMPLE 8.15 (PV diagram) A gas expands from volume 1m3 to 2m3 at constant atmospheric pressure. (a) Calculate the work done by the gas. (b) Represent the work done in PV diagram. Solution (a) The pressure P = 1 atm = 101 kPa, V f =2 m 3 and V 1 = 1m 3. From equation (8.17) W = Since P is constant. It is taken out of the integral. Processes (Ideal Gas) A steady flow compressor handles 113.3 m 3 /min of nitrogen (M = 28; k = 1.399) measured at intake where P1= 97 KPa and T1= 27 C. Discharge is at 311 KPa. The changes in KE and PE are negligible. For each of the following Thermodynamics Unit - Practice Thermodynamics problems True/False T F For an isothermal process, ∆S SYS can never decrease. False. For example vaporization. T F For all phase transitions, ∆H = 0 False. ∆H is never zero for a phase transition T F A process that doubles the number of microstates of system will double the ... This physics video tutorial explains the concept of the first law of thermodynamics. It shows you how to solve problems associated with PV diagrams, interna...
look at PV diagrams. A PV diagram is a graph of Pressure as a function of Volume. There are four different situations that you can expect to see shown in PV diagrams: 1. Isobaric: the gas is held at a constant pressure 2. Isochoric: the gas is held at a constant volume 3. Isothermal: the gas is held at a constant temperature 4. by ASD Adila · 2018 — For example, they tended to think of a curved P-V ... There were two types of problems presented in the P-V diagram (figure 1 & 2). First, we assigned. Midterm 1 Practice Problems 1. Calculate the present value of each cashflow using a discount rate of 7%. Which do you most prefer most? Show and explain all supporting calculations! Cashflow A: receive $60 today and then receive $60 in four years. Cashflow B: receive $12 every year, forever, starting today. The PV diagrams for a thermodynamical system is given in the figure below. Calculate the total work done in each of the cyclic processes shown. Solution. In the case (a) the closed curve is anticlockwise. So the net work done is negative, implying that the work done on the system is greater than the work done by the system.
Practice: Thermodynamics questions. This is the currently selected item. ... First law of thermodynamics problem solving. PV diagrams - part 1: Work and isobaric processes. PV diagrams - part 2: Isothermal, isometric, adiabatic processes. Second law of thermodynamics. High School Physics Skills Practice. The following PV diagram represents a gas taken from state A to state B. Determine the work done on the gas during this event. answer choices. Answers: -0.16 ... This page contains P-V Diagram Problems and Solutions on heat and thermodynamics for JEE and Competitive examinations. Problem #6: A 12.0 g sample of gas occupies 19.2 L at STP. What is the molecular weight of this gas? Solution: This problem, as well as the two just above can be solved with PV = nRT. You would solve for n, the number of moles. Then you would divide the grams given by the mole calculated. 1) Use PV = nRT: (1.00 atm) (19.2 L) = (n) (0.08206) (273 K)
PV of ordinary annuity = $5,550.18 c) two years from today. PV of a deferred annuity = $5,550.18 / 1.04 = $5,336.71 d) three years from today. PV of a deferred annuity = $5,550.18 / 1.042 = $5,131.45 e) four years from today. PV of a deferred annuity = $5,550.18 / 1.043 = $4,934.09 Solutions to Time Value of Money Practice Problems 4
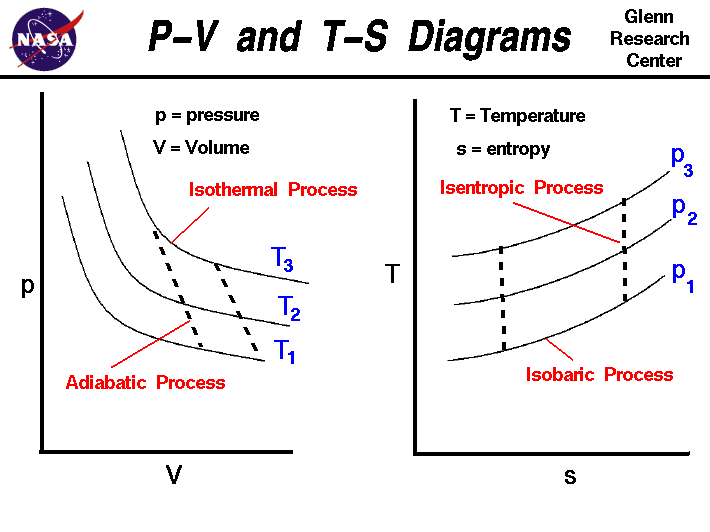
diagram, the clockwise and counterclockwise directions indicate power and heat pump cycles, respectively. Relationship to work Example of P-V diagram of a thermodynamic cycle. Because the net variation in state properties during a thermodynamic cycle is zero, it forms a closed loop on a PV diagram. A PV diagram's Y axis shows pressure (P) and X ...
Examples and Problems Reading: Elements Ch. 1-3. Physics 213: Lecture 3, Pg 2 ... Lecture 3, p 3 For an ideal gas at constant T, p is inversely proportional to the volume. Ideal Gas p-V, p-T Diagrams NkT p V = increasing T Volume Pressure p vs V at various constant T's 0 Pressure Temperature 0 Pressure →zero as ... pV γ= constant ...
Chapter 8 - Gases - Practice Problems Section 8.1 - Properties of Gases Goal: Describe the kinetic molecular theory of gases and the units of measurement used for gases. Summary: • In a gas, particles are so far apart and moving so fast that their attractions are negligible. • A gas is described by the physical properties: pressure (P), volume (V), temperature (T) in Kelvins (K)
A system can be described by three thermodynamic variables — pressure, volume, and temperature. Well, maybe it's only two variables. With everything tied together by the ideal gas law, one variable can always be described as dependent on the other two.
PV Diagram. PV Diagram to mainly show you about a pressure volume diagram work in a system with some examples. Welcome to 101diagrams.com, the site that provide great resources of images for your education and knowledge about various kind of diagrams. Including the engineering diagrams, mathematics diagrams symbol, biology diagrams, anatomy ...

Solved Bio Work Done By The Lungs The Graph In Fig E19 4 Shows A Pv Diagram Of The Air In A Human Lung When A Person Is Inhaling And Then Exhaling A Deep
The VT diagram shows: In the segment AB the volume of the gas is directly proportional to the temperature. This means that in this phase the pressure is constant, it is an isobaric process. In the pV diagram it is represented by a horizontal line. We can see that the volume in the first phase (from A to B) increases.
Problems practice. One mole of an ideal, monatomic gas runs through a four step cycle. All processes are either isobaric or isochoric. The pressure and volume of the gas at the extreme points in the cycle are given in the table below. Sketch the PV graph of this cycle. Determine the temperature at state A, B, C, and D.
A convenient way to visualize these changes in the pressure and volume is by using a Pressure Volume diagram or PV diagram for short. Each point on a PV diagram corresponds to a different state of the gas. The pressure is given on the vertical axis and the volume is given on the horizontal axis, as seen below.
Pressure-Volume Diagrams: A pressure-volume (PV) diagram is a graph with pressure on the y-axis and volume on the x-axis. This graph can be used to plot the thermal processes through which a gas ...
3. pV diagram of a cycle (like PQ15.1, and W15:26 (worksheet 15, problem 26)) This is just like the skill set, except for E) which is from 13.1 A) Temperatures of vertices - (PQ15.1#1, W15:26cde) (Use pV=nRT, read p and V from graph OR use combined gas law)
pV γ=constant =1 1 =constant pV γ pVγ 1 constant 2 2 1 1 1 = = T Vγ− T V γ− pV =nRT During an adiabatic expansion process, the reduction of the internal energy is used by the system to do work on the environment. During an adiabatic compression process, the environment does work on the system and increases the internal energy.
Isothermal thermodynamic processes - problems and solutions. 1. PV diagram below shows an ideal gas undergoes an isothermal process. Calculate the work is done by the gas in the process AB. Solution. Work done by a gas is equal to the area under the PV curve. AB = triangle area + rectangle area. W = [½ (8 x 10 5 -4 x 10 5)(3-1)] + [4 x 10 ...
What scientific concept do you need to know in order to solve this problem? Our tutors have indicated that to solve this problem you will need to apply the Work & PV Diagrams concept. You can view video lessons to learn Work & PV Diagrams. Or if you need more Work & PV Diagrams practice, you can also practice Work & PV Diagrams practice problems.
Practice Problems, Chapters 1 - 4 1. Use the P-V diagram below to answer the following questions 1a) The Net Work for the cyclic process is: a) Zero b) Positive c) Negative d) Cannot tell from the diagram 1b) The processes from states 1 to 2 and 3 to 4 are: a) Isothermal b) Isobaric c) Isochoric d) Isometric
This physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into PV diagrams. It explains how to calculate the work done by a gas for an isobaric process, iso...
Practice solving Work & PV Diagrams problems. Master even the most complex scientific problems with our step-by-step explanation videos.

Consider The Thermodynamics Cycle Shown On P V Diagram The Process A B Is Isobaric B C Is Isochoric And C A Is Straight Line Process The











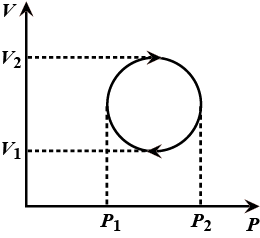



0 Response to "37 pv diagram practice problems"
Post a Comment