36 convex lens ray diagram
Ray 1 is parallel to the axis and refracts as if from F. Ray 2 heads towards F' before refracting parallel to the axis. Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens. image is always virtual, upright and reduced O F I F' Ray diagram for diverging lens A convex lens has a focal length of 10 cm. At what distance from the lens should the object be placed so that forms a real and inverted image 20 cm away from the lens? What would be the size of the image formed if th mobiect is 2 cm high2 Show the formation of image by drawing a ray diagram. Ans: 20 cm, 24
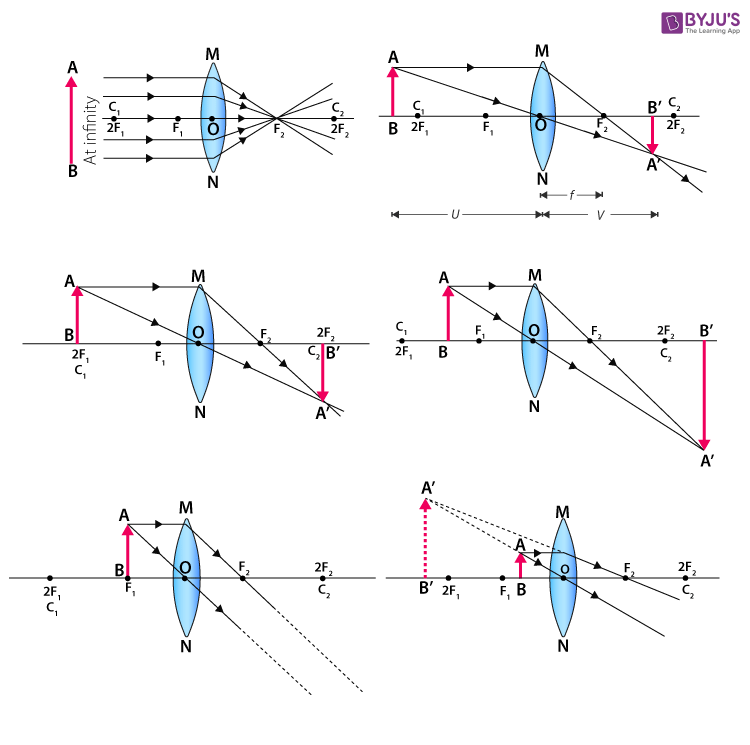
Convex Lens Ray Diagrams For lenses, the following three rays are typically used in ray diagrams. Keep in mind that an inflnite number of rays actually form the image. Ray # 1 For a lens, the flrst ray starts from the top of the object and extends parallel to the optical axis to the center of the lens. This ray, for a converging (convex) lens,
Convex lens ray diagram
A convex lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a convex lens. To draw a ray diagram and find the location of the image that would be created on a screen you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as "The two rules of refraction for converging lenses". Steps to a Convex Lens Ray Diagram. Look below and not at the animation to see the numbered steps for two scenarios and the analysis of the image produced. Start the First Ray: Start with your pencil on the top of the object (black thick arrow tip) and draw a line parallel to the principle axis to the center of the lens. Keep your pencil on the ... oPhysics: Interactive Physics Simulations. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex lenses. Move the tip of the "Object" arrow to move the object. Move the point named " Focus' " to change the focal length. Move the point named " Focus' " to the right side of the lens to change to a concave lens.
Convex lens ray diagram. 13+ Convex Lens Ray Diagram. This set of 3 rays is a standard way of simplifying the. Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a converging lens will refract through the lens and travel. To draw these ray diagrams, we will have to recall the three rules of refraction for a double convex lens: Wikipedia] the example ray ... Apr 26, 2020 · For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray pa A lens with one convex and one concave side is convex-concave or meniscus. It is this type of lens that is most commonly used in corrective lenses. If the lens is biconvex or plano-convex, a collimated beam of light passing through the lens converges to a spot (a focus) behind the lens. Uses of convex lens. These are used for a variety of purposes in our day-to-day lives. For example, The lens in the human eyes is the prime example. So the most common use of the lens is that it helps us to see. Another common example of the use of this type of lens is a magnifying glass. When an object is placed in front of it at a distance ...
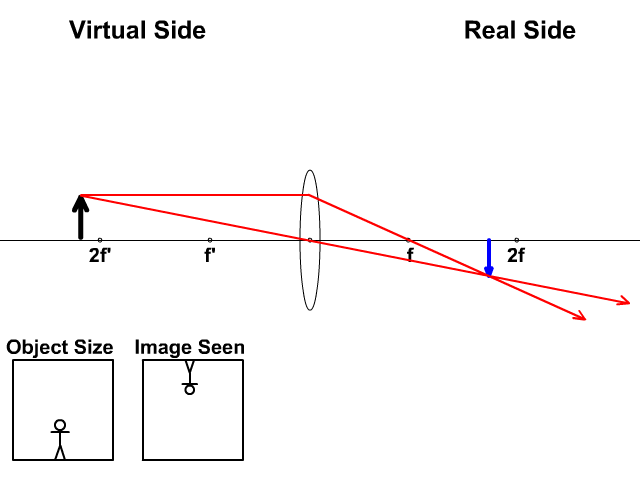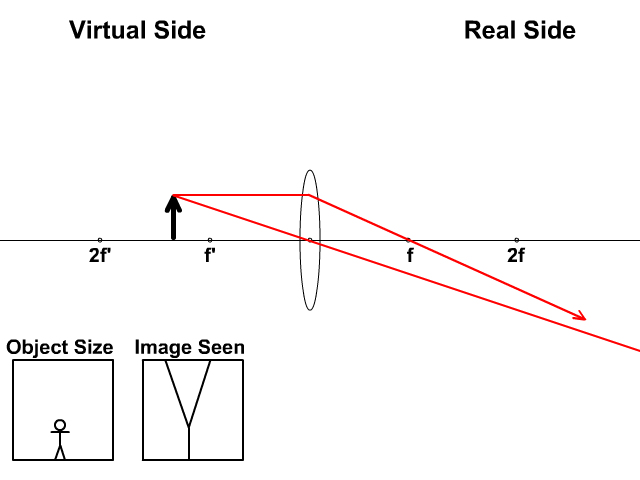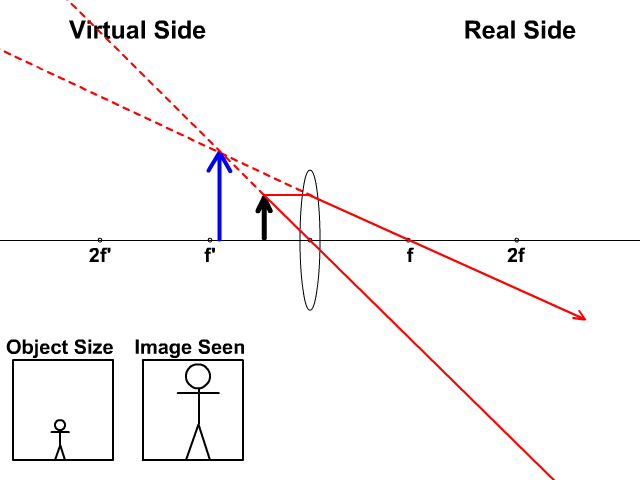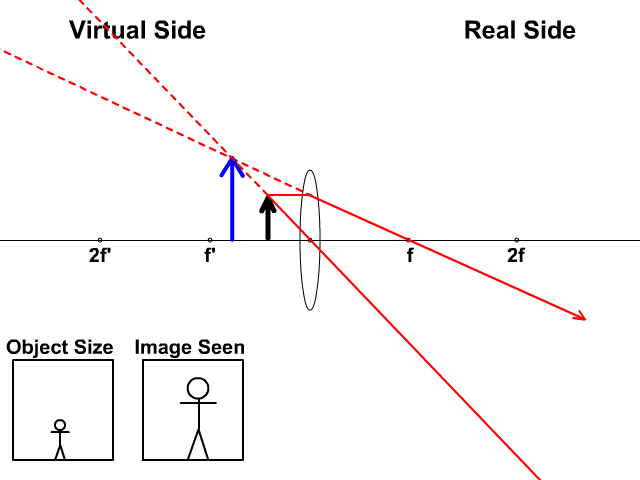
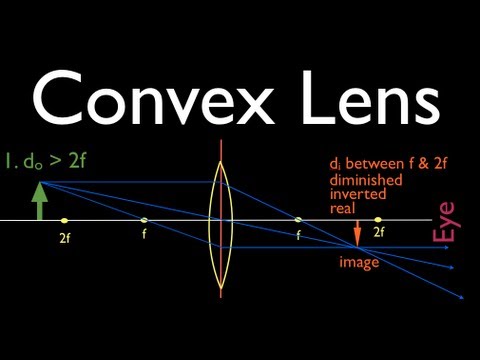
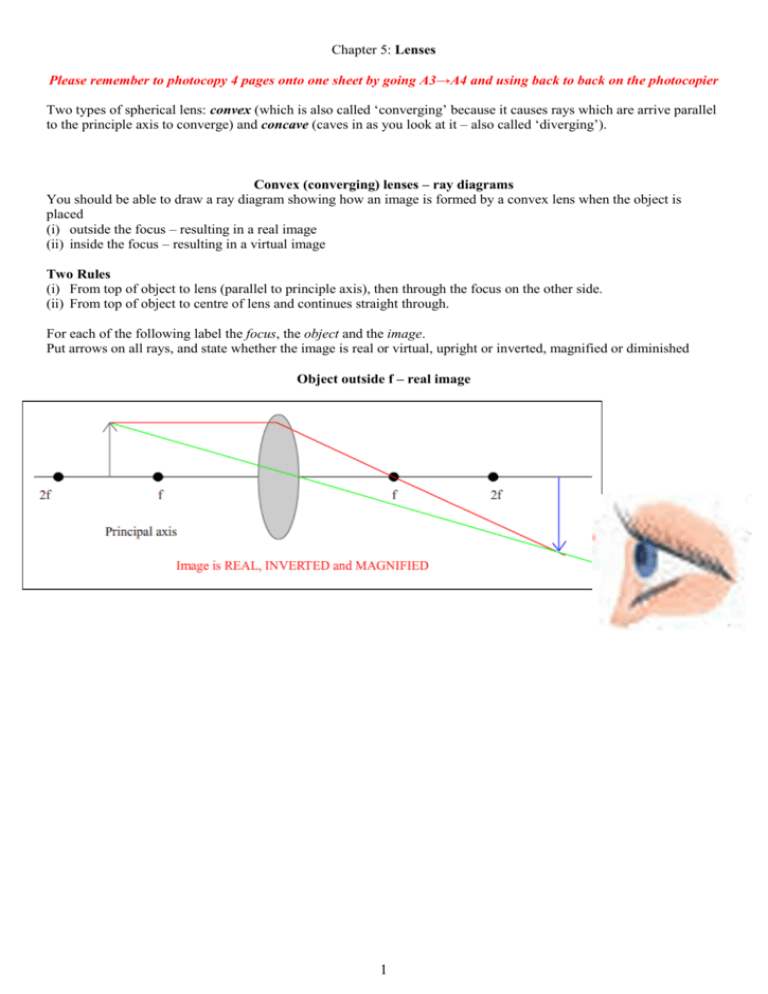
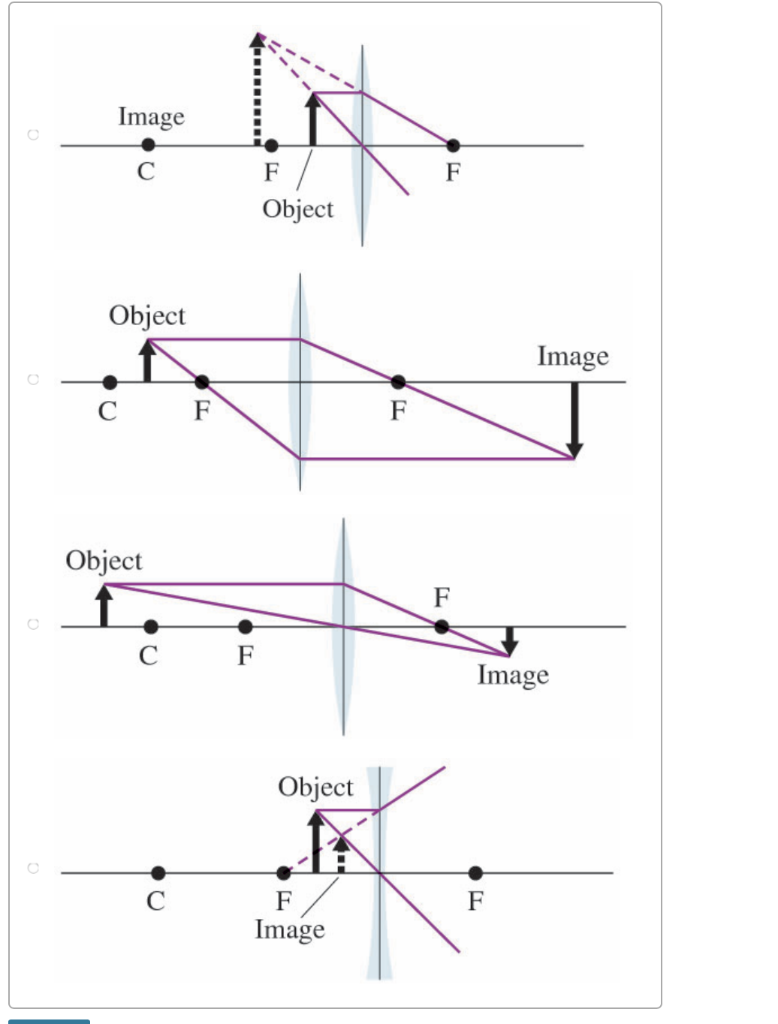
Image formation by convex lens ray diagrams. Image formation in a convex lens can be explained with the help of three principal rays shown in the figure. The ray parallel to the principal axis passes through the focal point after refraction by the lens. The ray passing through optical centre passes straight through the lens and remains undeviated. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. Ray diagram for an object placed between 2F and F from a convex lens In a film or data projector, this image is formed on a screen. Film must be loaded into the projector upside down so the ... Section 1: Introduction (Refraction and Lenses) 4 Convex (converging) and concave (diverging) lenses are drawn as, V W To understand image formation we use ray diagrams. Here is an example for aconvex lens: F The image of the top of the object is formed where the light rays cross. In a perfect lens all the rays from a point on the object will
The example "Ray tracing diagram for convex lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Ray tracing diagram. Used Solutions. Draw ray diagrams showing the image formation by a convex lens when an object is placed (a) between optical centre and focus of the lens (b) between focus an... Hi, in this quick video with animation of a Convex Lens , one can get a good feel for the lens itself, what it looks like, and how to draw Ray Diagrams from ... The example "Ray tracing diagram for convex lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Ray tracing diagram. Used Solutions.
Ray Diagram. We can draw a ray diagram for a plano convex lens as follows. A ray from the top of the object passing through the optical center without a change in direction. A parallel ray from the top of the object till the optical axis. It then refracts to pass through the focal point on the other side of the lens.
A worksheet to construct ray diagrams to show where images are formed by a converging convex lens and a diverging concave lens. Draw a ray diagram and use the information from the ray diagram to fill in the box. Aimed at aqa gcse physics. 10 draw a ray diagram for a 3 0 cm tall object placed 10 0 cm from a converging lens having a focal length ...
Rule 3 - Ray passing through Optical Center will emerge without deviation. For a both convex and concave lens, we see that ray passing through Optical center emerges without deviation. Next: Convex Lens - Ray diagram→. Facebook Whatsapp.
A Convex Lens Of Focal Length 15 Cm Forms An Image 10 Cm From The Lens How Far Is The Object Placed From The Lens Draw The Ray Diagram
Shows how to draw ray diagrams to locate the image formed by a convex lens. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscienc...
When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object.
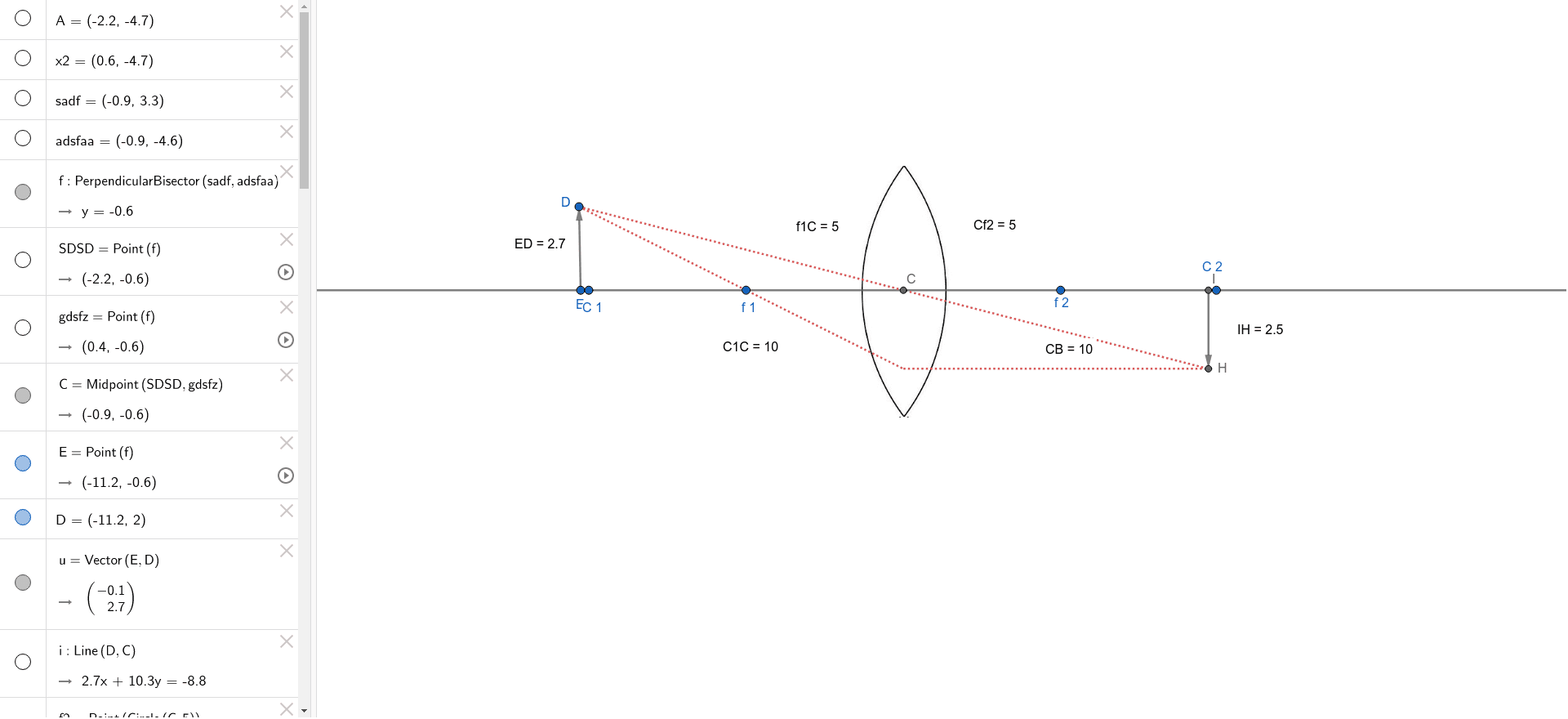
Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. You can also illustrate the magnification of a lens and the difference between real and virtual images. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. A light ray that enters the lens is an incident ray.
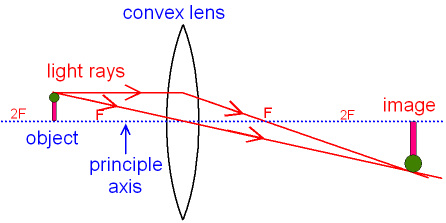
Gcse Physics Ray Diagram For An Image Made By A Convex Lens What Is A Real Image What Is An Inverted Image Gcse Science
The convex lens ray diagrams give people an idea about the position of the image and the object. The students can also have ideas about the nature of the lens. They can also know how the light rays experience a change in path due to a convex lens's presence there.

Draw Neat And Well Labelled Ray Diagrams For Image Formation By A Convex Lens When An Object Is At 2f 1
The method of drawing ray diagrams for double convex lens is described below. The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the 2F point of a double convex lens. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens.
A convex lens has a focal length of 1 0 c m. At what distance from the lens should the object be placed so that it gives a real and inverted image 2 0 c m away from the lens? What would be the size of the image formed if the object is 2 c m high? With the help of a ray, the diagram show the formation of the image by the lens in this case.
For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes through t
Image formation by convex lens ray diagrams. Use the thin lens equation to find the distance of the image. 5b explain why no image can be formed when the object is placed at the focal point. The point marked p is the focal point of the lens. For case 4 merely construct the ray diagram.
Ray Diagrams J.M. Gabrielse Outline • Reflection • Mirrors • Plane mirrors • Spherical mirrors • Concave mirrors • Convex mirrors • Refraction • Lenses • Concave lenses • Convex lenses J.M. Gabrielse A ray of light is an extremely narrow beam of light.
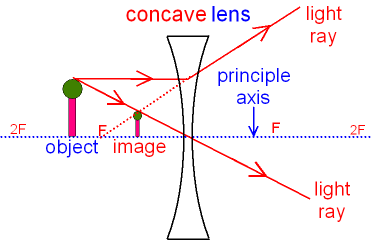
Gcse Physics What Is The Ray Diagram For A Concave Lens What Is A Virtual Image What Is An Upright Image Gcse Science
Ray diagrams for convex lenses. Typically this requires determining where the image of the upper and lower extreme of the object is located and then tracing the entire image. Image formation by convex lens ray diagrams. Im doing my best to draw this convex lens just like that. Ray diagrams the lens equation and the mirror equation.
Description Simulation of image formation in concave and convex mirrors. Move the tip of the Object arrow or the point labeled focus. Move the arrow to the right side of the mirror to get a convex mirror.

Figure 8 12 Action Of Lenses Illustrated With Ray Diagrams Optical Tweezers Principles And Applications
Ray diagrams for the thin lens. We have already discussed the use of a thin convex lens ( a converging lens) as a magnifying glass. If a small object is placed on the optical axis at a greater distance from the optical centre C than the focal length then the rays from each point on the object will be focused to a point on the opposite side of ...
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are:
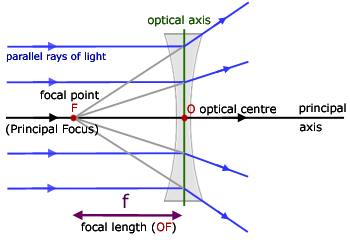
A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge. They come together at a point called the principal focus. In a ray diagram, a ...
oPhysics: Interactive Physics Simulations. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex lenses. Move the tip of the "Object" arrow to move the object. Move the point named " Focus' " to change the focal length. Move the point named " Focus' " to the right side of the lens to change to a concave lens.
Steps to a Convex Lens Ray Diagram. Look below and not at the animation to see the numbered steps for two scenarios and the analysis of the image produced. Start the First Ray: Start with your pencil on the top of the object (black thick arrow tip) and draw a line parallel to the principle axis to the center of the lens. Keep your pencil on the ...
A convex lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a convex lens. To draw a ray diagram and find the location of the image that would be created on a screen you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as "The two rules of refraction for converging lenses".

Convex Lens Concave Lens How To Determine Focal Length Ray Diagrams Image Properties Real Virtual Inverted Size Correction Of Eye Defects Causes Of Long Sight Short Sight Igcse Gcse 9 1 Physics Revision Notes

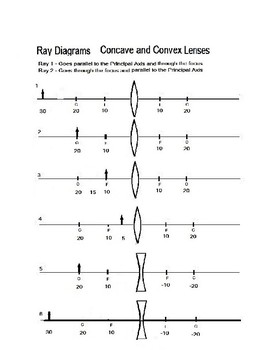
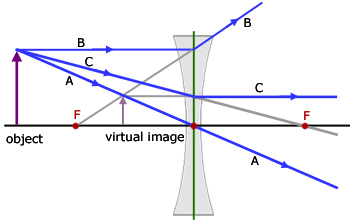


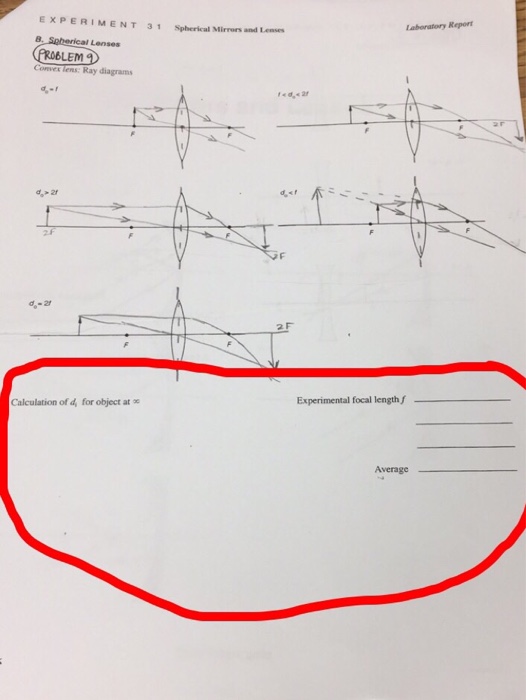












0 Response to "36 convex lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment